AWD-01 HTML5
On This Page
What is new in HTML5
- Making code easier to read for users and screen readers
- Reducing the overlap between HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- Promoting design responsiveness and consistency across browsers
- Supporting multimedia without the need for Flash or other plugins
- It has introduced new multimedia features which supports both audio and video controls by using and tags.
- There are new graphics elements including vector graphics and tags.
- Enrich semantic content by including
<header>,<footer>,<article>,<section>and<figure>are added. - The user can grab an object and drag it further dropping it to a new location.
- Geo-location services- It helps to locate the geographical location of a client.
- Web storage facility which provides web application methods to store data on the web browser
- Uses SQL database to store data offline
- Allows drawing various shapes like triangle, rectangle, circle, etc.
- Capable of handling incorrect syntax.
- Easy DOCTYPE declaration
- Easy character encoding
Semantic Elements
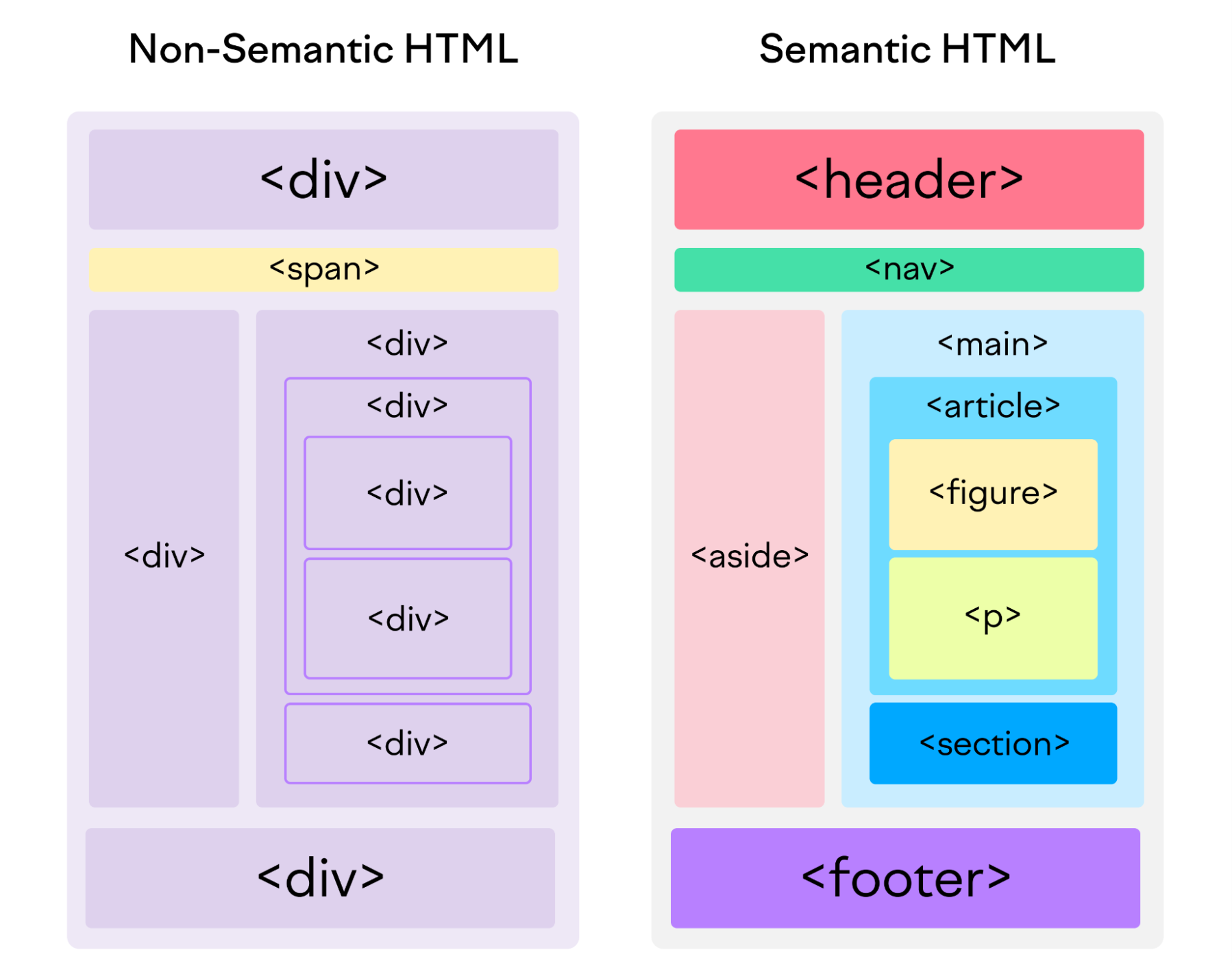
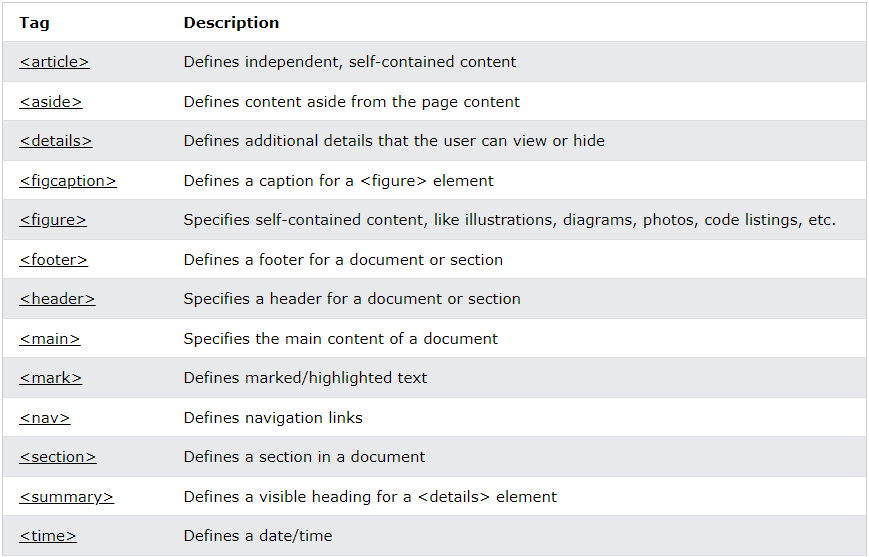
A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer In HTML there are some semantic elements that can be used to define different parts of a web page
<section> Element
- A section is a thematic grouping of content, typically with a heading.
- Examples of where a
<section>element can be used:- Chapters
- Introduction
- News items
- Contact information
- A web page could normally be split into sections for introduction, content, and contact information.
<section>
<h1>WWF</h1>
<p>
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is an international organisation
working on issues regarding the conservation, research and restoration of
the environment, formerly named the World Wildlife Fund. WWF was founded in
1961.
</p>
</section><article> Element
- The
<article>element specifies independent, self-contained content. - The
<article>tag is used to represent an article. - More specifically, the content within the tag
<article>is independent from the other content of the site (even though it can be related). - Examples of where the
<article>element can be used:- Forum posts
- Blog posts
- User comments
- Product cards
- Newspaper articles
<article>
<h2>Google Chrome</h2>
<p>
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google, released in 2008. Chrome
is the world's most popular web browser today!
</p>
</article>Nesting <article> in <section> or Vice Versa?
- The
<article>element specifies independent, self-contained content. - The
<section>element defines section in a document. - Can we use the definitions to decide how to nest those elements? No, we cannot!
- So, you will find HTML pages with
<article>elements containing<section>elements, and<section>elements containing<article>elements.
<header> Element
- The
<header>element contains the section heading as well as other content, such as navigation links, table of contents, etc. - A
<header>element typically contains: - one or more heading elements
- logo or icon
- authorship information
- You can have several
<header>elements in one HTML document. However,<header>cannot be placed within a<footer>,<address>or another<header>element.
<header>
<h1>What Does WWF Do?</h1>
<p>WWF's mission:</p>
</header><footer> Element
- The
<footer>element defines a footer for a document or section. - A
<footer>element typically contains:- authorship information
- copyright information
- contact information
- sitemap
- back to top links
- related documents
- You can have several
<footer>elements in one document
<footer>
<p>Author: Hege Refsnes</p>
<p><a href="mailto:hege@example.com">hege@example.com</a></p>
</footer><nav> Element
- The
<nav>tag is used to declare the navigational section in HTML documents. - Websites typically have sections dedicated to navigational links, which enables users to navigate the site. These links can be placed inside a nav tag.
<nav>
<a href="/html/">HTML</a>
<a href="/css/">CSS</a>
<a href="/js/">JavaScript</a>
<a href="/jquery/">jQuery</a>
</nav><aside> Element
- The
<aside>element defines some content aside from the content it is placed in (like a sidebar). - The
<aside>tag is used to describe the main object of the web page in a shorter way like a highlighter. - It basically identifies the content that is related to the primary content of the web page but does not constitute the main intent of the primary page.
- The
<aside>tag contains mainly author information, links, related content and so on - The
<aside>content should be indirectly related to the surrounding content.
<aside>
<h4>Epcot Center</h4>
<p>
Epcot is a theme park at Walt Disney World Resort featuring exciting
attractions, international pavilions, award-winning fireworks and seasonal
special events.
</p>
</aside><figure> and <figcaption> Elements
- The
<figure>tag specifies self-contained content, like illustrations, diagrams, photos, code listings, etc. - The
<figcaption>tag defines a caption for a<figure>element. - The
<figcaption>element can be placed as the first or as the last child of a<figure>element. - The
<img>element defines the actual image/illustration.
<figure>
<img src="pic_trulli.jpg" alt="Trulli" style="width:100%" />
<figcaption>Fig.1 - Trulli, Puglia, Italy.</figcaption>
</figure>
Multimedia
- Multimedia can be anything you can hear or see, like images, music, sound, videos, records, films, animations, and more.
- Web pages often contain multimedia elements of different types and formats.
- The first web browsers had support for text only, limited to a single font in a single colour.
- Later came browsers with support for colours, fonts, images, and multimedia!
HTML Video
- The
<video>tag is used to embed video content in a document, such as a movie clip or other video streams.
<video width="320" height="240" controls autoplay loop muted poster=”url/location” >
<source src="interstellar.mp4" type="video/mp4">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>- The
<video>tag contains one or more<source>tags with different video sources. The browser will choose the first source it supports. - The text between the
<video>and</video>tags will only be displayed in browsers that do not support the element. - Attributes
controls: Specifies that video controls should be displayed (such as a play, pause and volume buttons).autoplay: Specifies that the video will start playing as soon as it is readyloop: Specifies that the video will start over again, every time it is finished.muted: Specifies that the audio output of the video should be muted.poster: Specifies an image to be shown while the video is downloading, or until the user hits the play button (thumbnail).
- It is a good idea to always include width and height attributes. If height and width are not set, the page might flicker while the video loads.
HTML Audio
- To play an audio file in HTML, use the
<audio>element
<audio controls autoplay loop muted>
<source src="horse.mp3" type="audio/mp3" />
Your browser does not support the audio element.
</audio>- The
<audio>tag is used to embed sound content in a document, such as music or other audio streams. - The
<audio>tag contains one or more<source>tags with different audio sources. The browser will choose the first source it supports. - The text between the
<audio>and</audio>tags will only be displayed in browsers that do not support the<audio>element. - Attributes:
autoplay: Specifies that the audio will start playing as soon as it is readycontrols: Specifies that audio controls should be displayed (such as a play/pause button etc)loop: Specifies that the audio will start over again, every time it is finishedmuted: Specifies that the audio output should be muted
SVG
- SVG stands for Scalable Vector Graphics.
- SVG is used to define vector-based graphics for the Web
- SVG defines the graphics in XML format
- Every element and every attribute in SVG files can be animated.
Advantages:
- SVG images can be created and edited with any text editor
- SVG images can be searched, indexed, scripted, and compressed
- SVG images are scalable
- SVG images can be printed with high quality at any resolution
- SVG images are zoomable
- SVG graphics do NOT lose any quality if they are zoomed or resized
- SVG is an open standard
- SG files are pure XML
SVG Rectangle:
<svg width="400" height="110">
<rect
width="300"
height="100"
style="fill:rgb(0,0,255); stroke-width:3;
stroke:rgb(0,0,0)"
/>
</svg>- The
widthandheightattributes of the<rect>element define the height and the width of the rectangle
SVG Circle:
<svg height="100" width="100">
<circle cx="50" cy="50" r="40" stroke="black" stroke-width="3" fill="red" />
</svg>- The
cxandcyattributes define the x and y coordinates of the center of the circle. - If
cxandcyare omitted, the circle's center is set to (0,0) - The
rattribute defines the radius of the circle
SVG Ellipse:
<svg height="140" width="500">
<ellipse
cx="200"
cy="80"
rx="100"
ry="50"
style="fill:yellow;stroke:purple;stroke-width:2"
/>
</svg>- The
cxattribute defines the x coordinate of the center of the ellipse - The
cyattribute defines the y coordinate of the center of the ellipse - The
rxattribute defines the horizontal radius - The
ryattribute defines the vertical radius
SVG Line:
<svg height="210" width="500">
<line
x1="0"
y1="0"
x2="200"
y2="200"
style="stroke:rgb(255,0,0);
stroke-width:2"
/>
</svg>- The
x1attribute defines the start of the line on the x-axis - The
y1attribute defines the start of the line on the y-axis - The
x2attribute defines the end of the line on the x-axis - The
y2attribute defines the end of the line on the y-axis
SVG Polygon:
<svg height="210" width="500">
<polygon
points="200,10 250,190 160,210"
style="fill:lime;stroke:purple;stroke-width:1"
/>
</svg>- The
pointsattribute defines the x and y coordinates for each corner of the polygon
SVG Polyline:
<svg height="200" width="500">
<polyline
points="20,20 40,25 60,40 80,120 120,140 200,180"
style="fill:none;stroke:black;stroke-width:3"
/>
</svg>- The
pointsattribute defines the list of points (pairs of x and y coordinates) required to draw the polyline
HTML Form
Input Types:
<input type="button" />
<input type="checkbox" />
<input type="color" />
<input type="date" />
<input type="email" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="hidden" />
<input type="image" />
<input type="month" />
<input type="number" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />
<input type="range" />
<input type="reset" />
<input type="submit" />
<input type="tel" />
<input type="text" />
<input type="time" />
<input type="url" />
<input type="week" />Input Restrictions:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| checked | Specifies that an input field should be pre-selected when the page loads (for type="checkbox" or type="radio") |
| disabled | Specifies that an input field should be disabled |
| max | Specifies the maximum value for an input field |
| maxlength | Specifies the maximum number of character for an input field |
| min | Specifies the minimum value for an input field |
| pattern | Specifies a regular expression to check the input value against |
| readonly | Specifies that an input field is read only (cannot be changed) |
| required | Specifies that an input field is required (must be filled out) |
| size | Specifies the width (in characters) of an input field |
| step | Specifies the legal number intervals for an input field |
| value | Specifies the default value for an input field |
placeholder Attribute:
- Placeholder adds default text in input field that disappears when you click inside a text box
<form>
<label for="phone">Enter a phone number:</label>
<input type="text" id="phone" name="phone" placeholder="123-45-678" />
</form>required Attribute:
- If you want a text box to be filled in, you can use the
requiredattribute - The
requiredattribute specifies that an input field must be filled out before submitting the form.
<form>
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" required />
</form>HTML Form Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>HTML Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form
action="/submit"
method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data"
autocomplete="on"
novalidate
>
<fieldset>
<legend>Personal Information</legend>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input
type="text"
id="name"
name="name"
placeholder="Enter your name"
required
autofocus
maxlength="50"
pattern="[A-Za-z\s]+"
title="Only letters and spaces are allowed"
/>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input
type="email"
id="email"
name="email"
placeholder="Enter your email"
required
maxlength="50"
/>
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input
type="password"
id="password"
name="password"
placeholder="Enter your password"
required
minlength="8"
maxlength="20"
/>
<label for="dob">Date of Birth:</label>
<input
type="date"
id="dob"
name="dob"
required
min="1900-01-01"
max="2024-04-12"
/>
<label>Gender:</label>
<input type="radio" id="male" name="gender" value="male" required />
<label for="male">Male</label>
<input type="radio" id="female" name="gender" value="female" />
<label for="female">Female</label>
<input type="radio" id="other" name="gender" value="other" />
<label for="other">Other</label>
<label for="bio">Bio:</label>
<textarea
id="bio"
name="bio"
rows="4"
cols="50"
maxlength="250"
placeholder="Write something about yourself"
></textarea>
<label for="avatar">Avatar:</label>
<input type="file" id="avatar" name="avatar" accept="image/*" />
<label for="terms">Agree to terms:</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="terms" name="terms" required />
<label for="subscription">Subscribe to newsletter:</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="subscription" name="subscription" checked />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
<input type="reset" value="Reset" />
</fieldset>
</form>
</body>
</html>Questions
- What are semantic elements in HTML5, and why are they important for web development?
- How do multimedia elements enhance user experience on web pages? Provide examples.
- Explain the significance of form elements in web development and discuss their various types.
- What are some commonly used input types in HTML forms? Provide scenarios where each type is appropriate.
- How does the 'placeholder' attribute enhance user interaction in form fields? Give examples.
- Discuss the importance of the 'required' attribute in HTML forms and its impact on user input validation
- What is SVG? Explain different shapes in SVG?