PCMT-03 Network
On This Page
- A computer network is a system in which multiple computers are connected to each other to share information and resources.
- The physical connection between networked computing devices is established using either cable media or wireless media.
- The best-known computer network is the Internet.
Advantages
- File sharing:
- The major advantage of a computer network is that is allows file sharing and remote file access.
- A person sitting at one workstation that is connected to a network can easily see files present on another workstation, provided he is authorized to do so.
- Resource Sharing:
- All computers in the network can share resources such as printers, fax machines, modems, and scanners
- Better connectivity and communications:
- It allows users to connect and communicate with each other easily.
- Various communication applications included e-mail and groupware are used.
- Through email, members of a network can send message and ensure safe delivery of data to other members, even in their absence.
- Internet Access:
- Computer networks provide internet service over the entire network.
- Every single computer attached to the network can experience the high speed internet.
- Entertainment:
- Many games and other means of entertainment are easily available on the internet.
- Furthermore, Local Area Networks (LANs) offers and facilitates other ways of enjoyments, such as many players are connected through LAN and play a particular game with each other from remote location.
- Inexpensive system:
- Shared resources mean reduction in hardware costs.
- Shared files mean reduction in memory requirement, which indirectly means reduction in file storage expenses.
- A particular software can be installed only once on the server and made available across all connected computers at once.
- This saves the expense of buying and installing the same software as many times for as many users.
- Flexible Access:
- A user can log on to a computer anywhere on the network and access his files. This offers flexibility to the user as to where he should be during the course of his routine.
- Instant and Multiple Access:
- Many users can access the same information at the same time.
- Immediate commands such as printing commands can be made with the help of computer networks.
Disadvantages
- Lack of data security and privacy:
- Because there would be a huge number of people who would be using a computer network to get and share some of their files and resources, a certain user’s security would be always at risk.
- There might even be illegal activities that would occur, which you need to be careful about and aware of
- Presence of computer viruses and malware:
- If even one computer on a network gets affected by a virus, there is a possible threat for the other systems getting affected too.
- Viruses can spread on a network easily, because of the inter- connectivity of workstations.
- Moreover, multiple systems with common resources are the perfect breeding ground for viruses that multiply
- Lack of Independence:
- Since most networks have a centralized server and dependent clients, the client users lack any freedom whatsoever.
- Centralized decision making can sometimes hinder how a client user wants to use his own computer.
- Lack of Robustness:
- As previously stated, if a computer network’s main server breaks down, the entire system would become useless.
- Also, if it has a bridging device or a central linking server that fails, the entire network would also come to a standstill.
- Need an efficient handler:
- For a computer network to work efficiently and optimally, it requires high technical skills and know-how of its operations and administration.
- A person just having basic skills cannot do this job. Take note that the responsibility to handle such a system is high, as allotting permissions and passwords can be daunting.
- Similarly, network configuration and connection is very tedious and cannot be done by an average technician who does not have advanced knowledge.
Applications
- Financial Services:
- Nowadays, almost all the financial services depend on the computer network.
- You can access the financial services across the world.
- For example, a user can transfer money from one place to another by using the electronic fund transfer feature.
- You can use networking in various financial areas such as ATM, foreign exchange and credit history search.
- Business:
- Nowadays, most of the works of businesses are done over the computers.
- To exchange the data and ideas, you need an effective data and resources sharing features.
- To do this, you need to connect the computer with each other through a network.
- For example, a person of one department of an organization can share or access the electronic data of other department through network
- Email Services:
- A computer network provides you the facility to send or receive mails across the globe in few seconds.
- Mobile Applications:
- By using the mobile applications, such as cellular or wireless phones, you can communicate (exchange your views and ideas) with one other.
- Directory services:
- It provides you the facility to store files on a centralized location to increase the speed of search operation worldwide.
- Teleconferencing:
- It contains voice conferencing and video conferencing which are based in networking.
- In teleconferencing the participants need not to be presented at the same location.
Types of Network
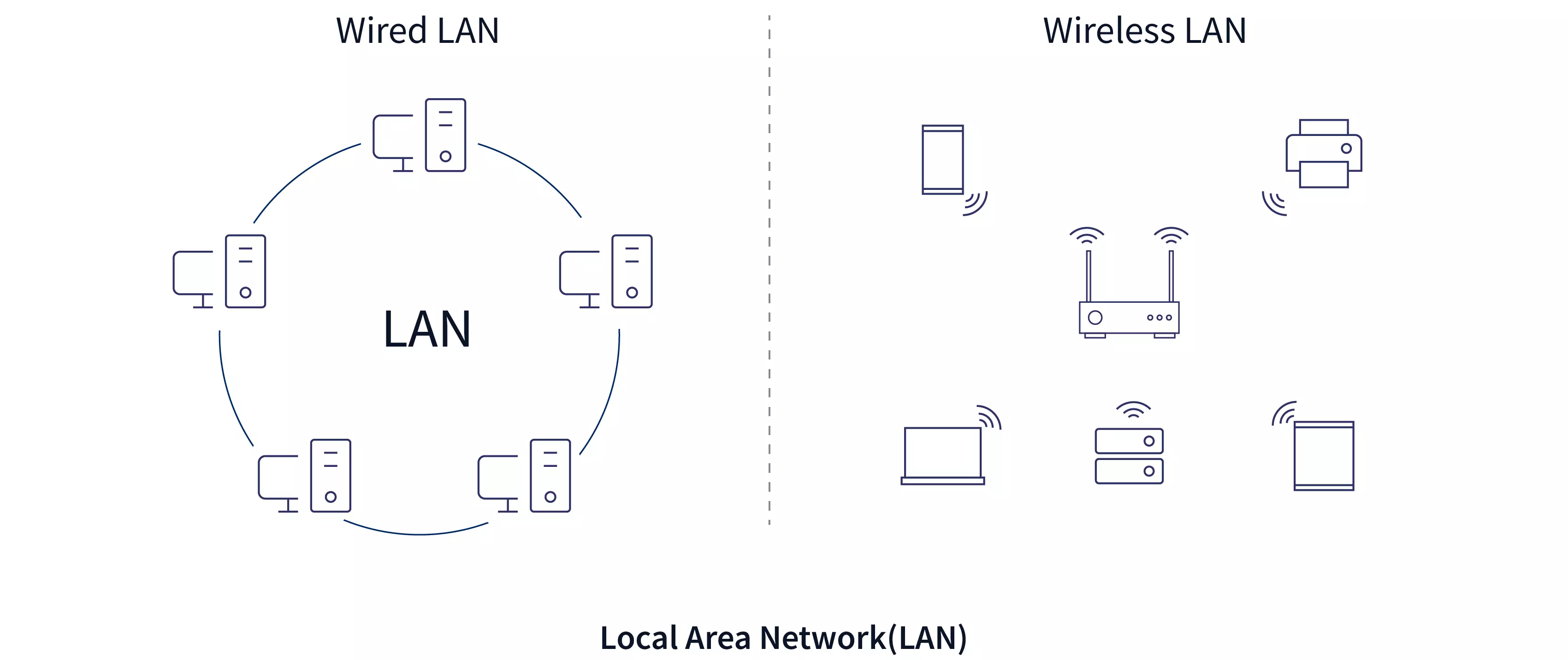
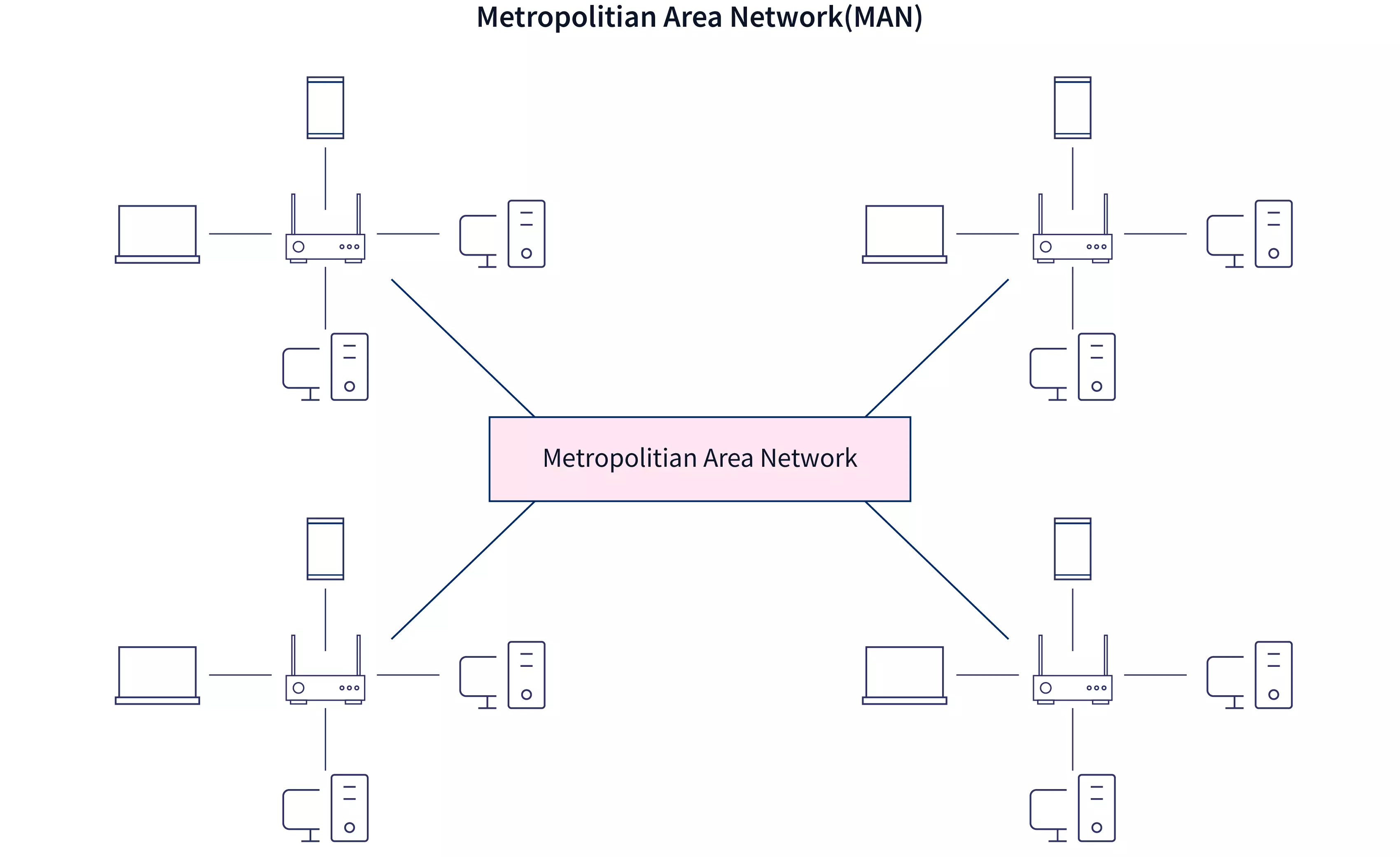
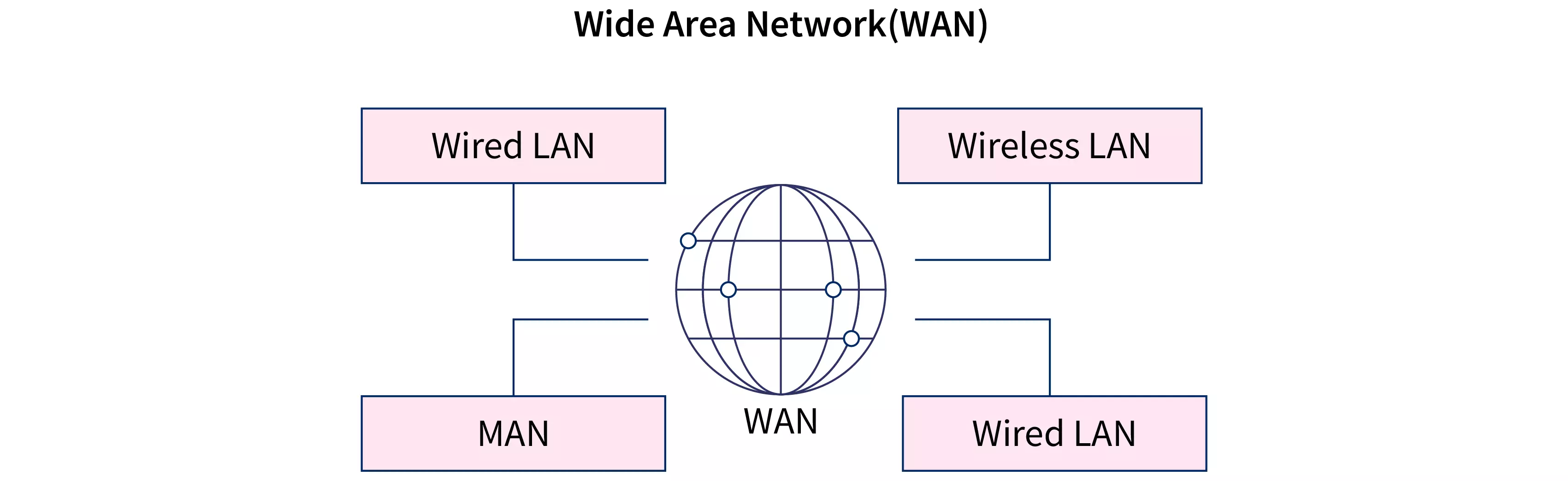
| Parameter | LAN | MAN | WAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full form | Local Area Network | Metropolitan Area Network | Wide Area Network |
| Area covered | Cover small area i.e., within building | Covers larger than LAN & smaller than WAN | Covers large area |
| Error rates | Lowest | Modest | Highest |
| Transmission Speed | High Speed | Moderate Speed | Low Speed |
| Equipment cost | Inexpensive | Moderate expensive | Most expensive |
| Design & maintenance | Easy | Moderate | Difficult |
Wireless Network
- A Wireless network is a type of the computer network that uses the wireless connections for connecting network nodes for data transfer.
- The wireless networks are very useful, inexpensive, popular and widely used.
- They are easy setup and do not require the cables installation.
- The wireless networks are usually realized and administered using the radio communications.
- For example, Wi-Fi local networks, cell phone networks, communications satellites, terrestrial microwave networks, and many others
Network Model
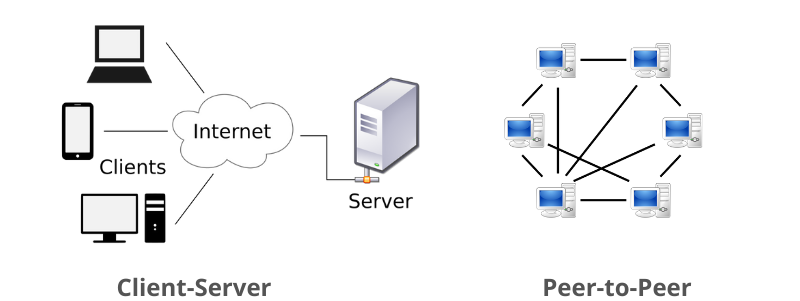
Peer-to-Peer Network (P2P)
- In this network group of computers is connected together so that users can share resources and information.
- There is no central location (server) for authenticating users, storing files, or accessing resources and each of them works as both client and server.
- This means that users must remember which computers in the workgroup have the shared resource or information that they want to access
- Advantages:
- It is easy to setup.
- There is no need of any committed server as each peer acts as both server and client.
- The network implementation is quite cheap.
- The resources of a peer can be shared with other peers very easily in the network
- Disadvantages:
- The speed of the network decreases due to heavy usage.
- It is not easy to keep track of information on each computer.
- There is no central backup of files and folders.
- Network and data security are weak
Client-Server Network (CS)
- A client/server network is a system where one or more computers called clients connect to a central computer named as server to share or use resources.
- The client requests a service from server, which may include running an application, querying database, printing a document, performing a backup or recovery procedure.
- The request made by the client is handled by server.
- A client/server network is that in which the files and resources are centralized. This means that the server can hold them and other computers (Client) can access them.
- Advantages:
- The server system holds the shared files.
- The server system can be scheduled to take the file backups automatically.
- Network access is provided only to authorize users through user security at the server.
- The server system is a kind of central repository for sharing printer with clients.
- Internet access, e-mail routing and such other networking tasks are quite easily managed by the server.
- The software applications shared by the server are accessible to the clients.
Network Services
File Services
- File services include sharing and transferring files over the network.
- File Sharing:
- One of the reason which gave birth to networking was file sharing.
- File sharing enables its users to share their data with other users.
- User can upload the file to a specific server, which is accessible by all intended users.
- As an alternative, user can make its file shared on its own computer and provides access to intended users.
- File Transfer:
- This is an activity to copy or move file from one computer to another computer or to multiple computers, with help of underlying network.
- Network enables its user to locate other users in the network and transfers files.
Communication Services
- Email:
- Electronic mail is a communication method and something a computer user cannot work without. This is the basis of today’s internet features.
- Email system has one or more email servers.
- All its users are provided with unique IDs.
- When a user sends email to other user, it is actually transferred between users with help of email server.
- Social Networking:
- Recent technologies have made technical life social.
- The computer savvy peoples, can find other known peoples or friends, can connect with them, and can share thoughts, pictures, and videos.
- Internet Chat:
- Internet chat provides instant text transfer services between two hosts.
- Two or more people can communicate with each other using text based Internet Relay Chat services.
- These days, voice chat and video chat are very common
- Discussion Boards:
- Discussion boards provide a mechanism to connect multiple peoples with same interests.
- It enables the users to put queries, questions, suggestions etc. which can be seen by all other users. Other may respond as well.
- Remote Access:
- Remote Access service enables user to access the data residing on the remote computer.
- This can be done via some remote device, e.g. mobile phone or home computer.
Application Services
These are nothing but providing network based services to the users such as web services, database managing, and resource sharing
- Resource Sharing:
- To use resources efficiently and economically, network provides a mean to share them.
- This may include Servers, Printers, and Storage Media etc.
- Databases:
- This application service is one of the most important services.
- It stores data and information, processes it, and enables the users to retrieve it efficiently by using queries.
- Databases help organizations to make decisions based on statistics.
- Web Services:
- World Wide Web has become the synonym for internet.
- It is used to connect to the internet, and access files and information services provided by the internet servers.
Print Services
- A print service enables users to send print jobs from their devices to network-connected printers.
- It allows multiple users to share a single printer, eliminating the need for individual printers at each workstation.
- Print services also provide options for managing print queues, controlling access to printers, and monitoring print jobs.
Database Services
- A database service provides a centralized platform for storing, managing, and retrieving structured data within a network.
- It allows multiple users to access and manipulate data simultaneously, ensuring data integrity and security.
- Database services are commonly used in applications that require efficient data storage, retrieval, and processing, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and online transaction processing (OLTP) systems.
- By offering these network services, organizations can enhance productivity, improve collaboration, and streamline data management.
- These services facilitate the efficient sharing of resources, such as files and printers, across the network, enabling users to access and utilize these resources from any location within the network.
- In conclusion, all of the given options - file service, print service, and database service - are examples of network services.
- These services play a crucial role in enabling communication, resource sharing, and data management within a networked environment.
Network Security Services
- Message Confidentiality:
- Message confidentiality or privacy means that the sender and the receiver expect confidentiality.
- The transmitted message must make sense to only the intended receiver. To all others, the message must be garbage.
- When a customer communicates with her bank, she expects that the communication is totally confidential.
- Message Integrity:
- Message integrity means that the data must arrive at the receiver exactly as they were sent.
- There must be no changes during the transmission, neither accidentally nor maliciously.
- As more and more monetary exchanges occur over the Internet, integrity is crucial.
- Message Authentication:
- Message authentication is a service beyond message integrity.
- In message authentication, the receiver needs to be sure of the sender's identity and that an imposter has not sent the message.
- Message Nonrepudiation:
- Message nonrepudiation means that a sender must not be able to deny sending a message that he or she, in fact, did send.
- The burden of proof falls on the receiver.
- For example, when a customer sends a message to transfer money from one account to another, the bank must have proof that the customer actually requested this transaction.
- Entity Authentication:
- In entity authentication (or user identification), the entity or user is verified prior to access to the system resources (files, for example).
- For example, a student who needs to access her university resources needs to be authenticated during the logging process.
- This is to protect the interests of the university and the student.
Network Topologies
- Network Topology is the schematic description of a network arrangement, connecting various nodes (sender and receiver) through lines of connection.
- A Network Topology is the arrangement with which computer systems or network devices are connected to each other.
Bus Topology
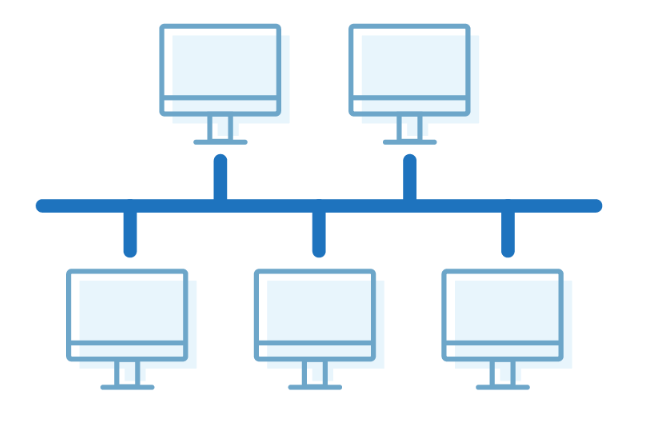
- Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to a single cable.
Ring Topology
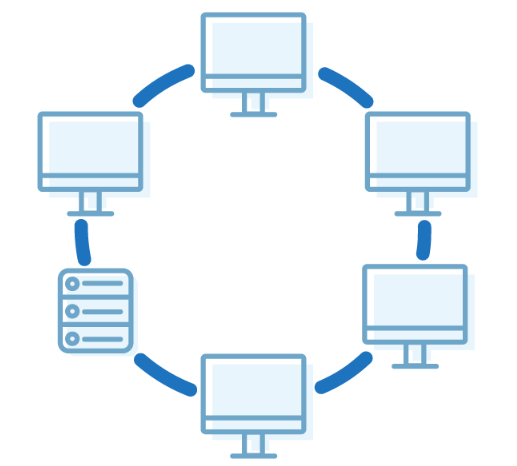
- It is called ring topology because it forms a ring as each computer is connected to another computer, with the last one connected to the first.
- Exactly two neighbours for each device.
- A number of repeaters are used and the transmission is unidirectional.
- Advantages:
- Transmitting network is not affected by high traffic or by adding more nodes, as only the nodes having tokens can transmit data.
- Cheap to install and expand.
- Disadvantages:
- Troubleshooting is difficult in a ring topology.
- Adding or deleting the computers disturbs the network activity.
- Failure of one computer disturbs the whole network.
Star Topology
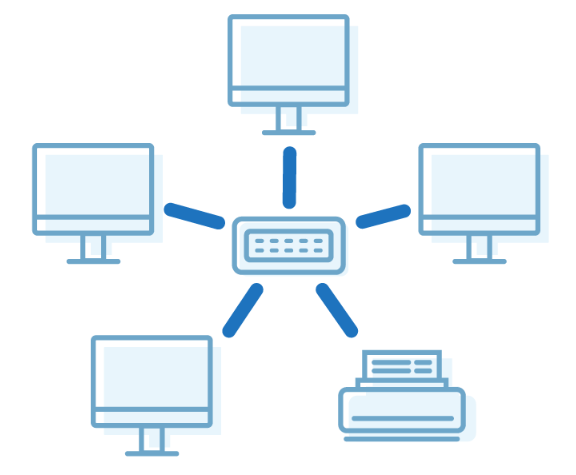
- In this type of topology, all the computers are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all others nodes are connected to the central node
- Every node has its own dedicated connection to the hub.
- It acts as a repeater for data flow.
- It can be used with twisted pair, Optical Fibre or coaxial cable.
- Advantages:
- Fast performance with few nodes and low network traffic.
- Hub can be upgraded easily.
- Easy to troubleshoot.
- Easy to set up and modify.
- Only that node is affected which has failed rest of the nodes can work smoothly.
- Disadvantages:
- Cost of installation is high.
- Expensive to use.
- If the hub is affected then the whole network is stopped because all the nodes depend on the hub.
- Performance is based on the
Mesh Topology
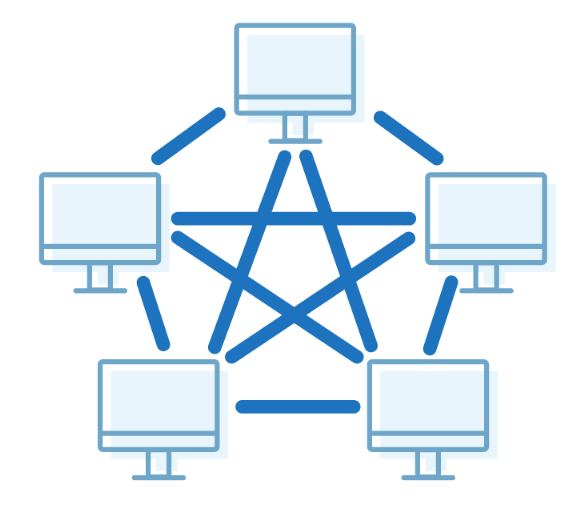
- It is a point-to-point connection to other nodes or devices.
- Traffic is carried only between two devices or nodes to which it is connected.
- Fully connected
- Robust
- Not flexible
- Advantages:
- Each connection can carry its own data load.
- It is robust.
- A fault is diagnosed easily.
- Provides security and privacy.
- Disadvantages:
- Installation and configuration are difficult.
- Cabling cost is more.
- Bulk wiring is required.
Tree Topology
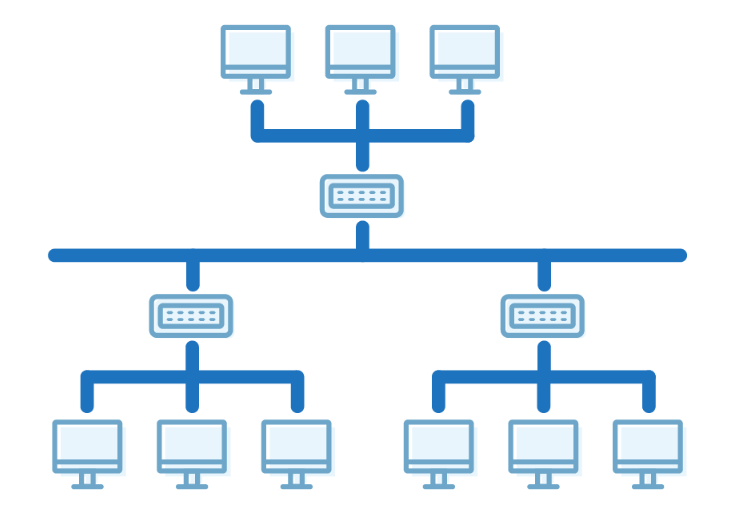
- It has a root node and all other nodes are connected to it forming a hierarchy.
- It is also called hierarchical topology.
- It should at least have three levels to the hierarchy
- Ideal if workstations are located in groups.
- Used in Wide Area Network.
- Advantages:
- Extension of bus and star topologies.
- Expansion of nodes is possible and easy.
- Easily managed and maintained.
- Error detection is easily done.
- Disadvantages:
- Heavily cabled.
- Costly.
- If more nodes are added maintenance is difficult.
- Central hub fails then network fails.
Hybrid Topology
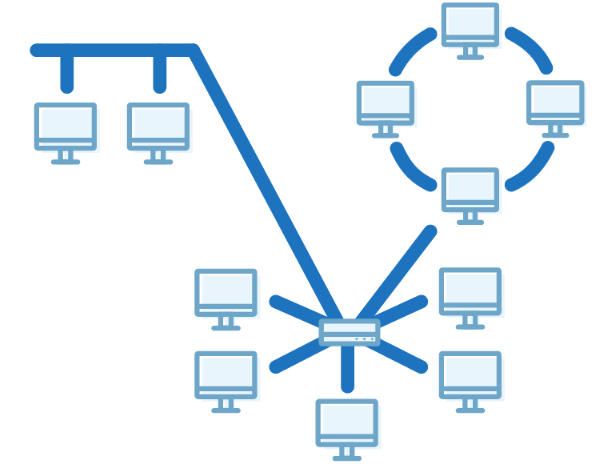
- A network structure whose design contains more than one topology is said to be hybrid topology.
- It is a combination of two or more topologies.
- Inherits the advantages and disadvantages of the topologies included.
- Advantages:
- Reliable as error detecting and troubleshooting is easy.
- Scalable as size can be increased easily.
- Flexible.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex in design.
- Costly
Communication Method
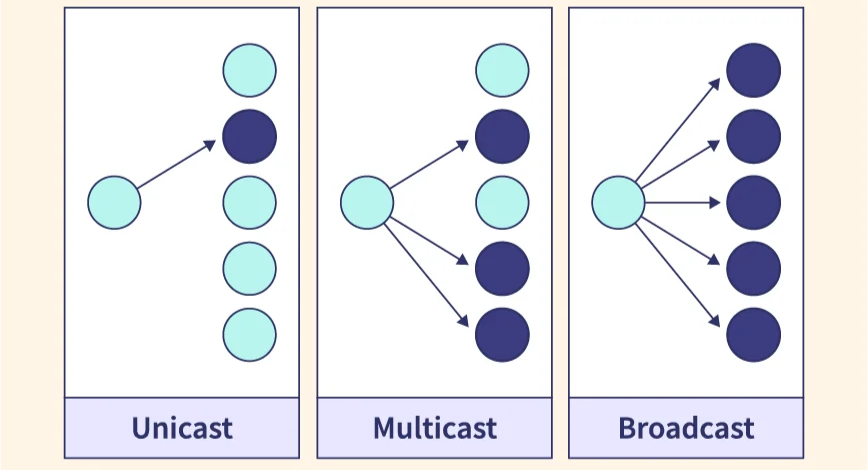
| Features | Unicast | Multicast | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A communication where a message is sent from one sender to one receiver. | A communication where a message is sent from one sender to a group of receivers | A communication where a message is sent from one sender to all receivers. |
| Transmission | Data is sent to a single recipient | Data is sent to a group of recipients | Data is sent to all recipients in a network |
| Addressing | Uses a unique destination address | Uses a special multicast address | Uses a special broadcast address |
| Delivery | Guaranteed delivery | Not all devices may be interested in the data | Not all devices may be interested in the data |
| Network Traffic | Generates the least amount of network traffic | Generates moderate network traffic | Generates the most amount of network traffic |
| Security | More secure because data is sent to a specific recipient | Moderately secure because data is sent to a specific group of devices | Less secure because data is sent to all devices in the network |
| Examples | Email, file transfer | Video streaming, online gaming | DHCP requests, ARP requests |
| Destination | Single receiver | Grop of receivers | All receivers |
| Bandwidth usage | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Latency | Low | Moderate | High |
Questions
- What is Computer Network? Give advantage Computer Network. (MID-05M)
- Explain Types of Networks in details. (MID-05M)
- What is peer-to-peer network? (MID-05M)
- What is client-server network? (MID-05M)
- What are the Network Services?
- Explain Network Topologies in details. (MID-08M)
- Explain Communication Methods: Unicasting, Multicasting, Broadcasting. (MID-04M)
- Difference between LAN, MAN, WAN