AI-01 Introduction to AI
On This Page
What is AI?
- AI is like teaching a computer to think a bit like a human—it learns from examples, makes decisions, and helps solve problems
- Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is like teaching computers to think and learn like humans.
- Artificial intelligence is the study of how to make computers do things which, at moment people do better. It’s like giving computers a brain to figure things out!
- AI helps machines do things that usually need human brains, such as solving puzzles, learning new things, or understanding Human interaction
- Smart machines simulate human intelligence, as they are programmed
- AI helps computers see, learn, think, and make choices, so they can help us with tasks like talking, solving puzzles, and finding answers—just like a smart helper!
- John McCarthy, the father of AI, defined it as: "The science and engineering of making intelligent machines."
Evolution of AI
| Year | Milestone | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1950s | Alan Turing & Turing Test | Questioned “Can machines think?” Introduced imitation game. |
| 1956 | Dartmouth Conference | Coined the term “Artificial Intelligence.” |
| 1960-70s | Symbolic AI / Logic | Rule-based systems and logic programming (e.g., SHRDLU). |
| 1980s | Expert Systems | E.g., MYCIN (diagnosis of blood infections). Used rules and facts. |
| 1997 | Deep Blue vs Kasparov | IBM’s Deep Blue beats world chess champion Garry Kasparov. |
| 2010s-Present | Deep Learning Era | AI surpasses human-level performance in tasks like vision, NLP (e.g., GPT, AlphaGo). |
Real Life Example
- Healthcare: AI reads X-rays to find diseases (like Google’s AI for eye problems in diabetes)
- Entertainment: Netflix suggests movies you’ll like using smart guessing
- Navigation: Google Maps shows traffic and best routes using past and live data
- Personal Assistants: Siri and Alexa understand voice using smart language tricks (NLP)
- Finance: AI helps catch fraud in bank transactions
- Robots: AI powers robots to clean homes, help in factories, or deliver packages
- Gaming: Games use AI to create smart enemies and exciting challenges
- Photos: Apps like Google Photos recognize faces and group your memories
- Education: AI apps give personal practice based on what students know
- Security: AI can help recognize faces or detect suspicious activity in CCTV
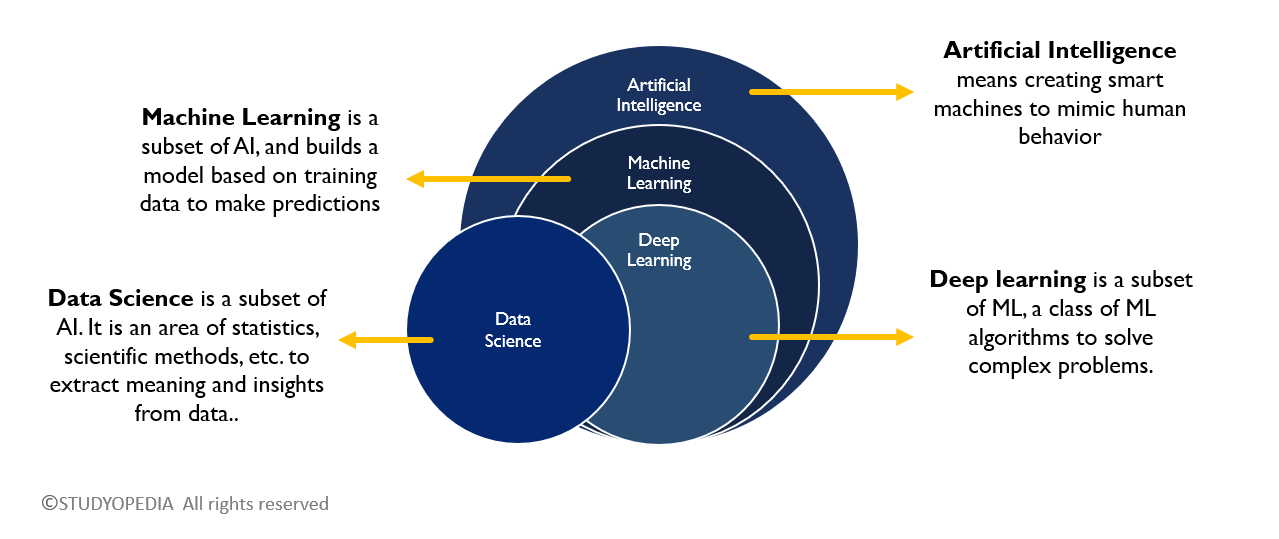
Difference between AI, ML, DL
-
Artificial Intelligence:
- Artificial Intelligence is the branch of computer science that focuses on creating machines that can think, learn, and act like humans.
- It includes learning, reasoning, problem-solving, understanding language, and more.
- Example: Chatbots, self-driving cars, voice assistants like Alexa.
-
Machine Learning:
- Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed.
- It finds patterns in data and makes decisions based on experience.
- Example: Email spam detection, movie recommendations.
-
Deep Learning:
- Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers (just like a human brain) to learn from large amounts of complex data like images, videos, or speech.
- Example: Face recognition, voice assistants, self-driving car vision systems
Types of AI
Based on Capabilities
Narrow AI
- AI systems that are designed to perform one specific task.
- Narrow AI is everywhere today and helps us with specific tasks.
- They can’t perform tasks outside their defined function
- They simulate intelligence, but they don’t possess true understanding.
- These are AI systems designed to do one specific task really well. They can’t do things outside their programmed area.
- Siri or Alexa: They can answer questions, set alarms, or play music, but they can’t drive a car or cook food.
- Google Translate: It can translate languages but can’t write a story or solve math problems.
- ChatGPT: It can chat, write essays, or help with homework, but it can’t physically draw a picture or play sports.
- Facial Recognition: Used in phones to unlock them by recognizing your face, but it can’t recognize your voice.
- Recommendation Systems: Like Netflix suggesting movies or YouTube recommending videos based on what you’ve watched before.
General AI
- General AI is a type of AI that can think, learn, and do anything a human can do. It doesn’t exist yet, but scientists are working on it.
- A theoretical AI system that has general cognitive abilities like a human.
- Can learn, understand, and perform any intellectual task that a human can.
- An AI that can go to school, learn new subjects, and apply that knowledge in real life, just like a student.
- A machine that can paint a picture, write a poem, and solve a math problem, all while understanding emotions and feelings.
- Examples:
- A robot that can learn to cook, clean, play games, and even have a conversation like a human.
Super AI
- A hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence in all fields.
- Super AI is like a super-smart robot from the future that we see in movies but don’t have in real life yet!
- This would be an AI that is smarter than humans in every way.
- Creativity
- Emotions
- Problem-solving
- Decision-making
- It’s still just an idea and doesn’t exist in real life, but it’s often shown in movies and stories.
- Examples:
- Ultron (Avengers: Age of Ultron): A super-intelligent robot that wants to take over the world.
- Skynet (Terminator): An AI that becomes self-aware and tries to control humanity.
- J.A.R.V.I.S. (Iron Man): A highly advanced AI that helps Tony Stark with almost everything, but in a good way
Based on Functionality
Reactive Machines
- Oldest and most basic type of AI.
- Cannot use past experiences to make future decisions.
- They operate purely based on the present input, with no memory or ability to learn from past experiences.
- No memory, no learning, purely reactive.
- Like a calculator—it just does what you tell it, right away!
- These systems analyze the current situation and respond according to pre-programmed rules or algorithms
- Example: Picture a robot playing a game of tic-tac-toe.
- React Machines are
- Rule-based
- Highly predictable
- No adaptability
Limited Memory AI
- Temporary memory, learns from past data, improves over time.
- This is like a robot with a short memory.
- It can look at what’s happening now and remember a little bit of what happened before, so it can make smarter choices. But it doesn’t keep those memories forever—just for a little while.
- Self-driving cars. They use sensors to react to the environment
- These AIs use past data temporarily to make better decisions.
- Most modern AI systems fall into this category.
- Example:
- Imagine a robot car driving down the road.
- It sees a kid on a bike and remembers that the bike was moving fast a second ago, so it slows down to be safe.
- It’s like how you might remember where you hid your toys yesterday, but not last month!
Theory of Mind AI
- Emotional intelligence, understanding of intentions, social awareness.
- This robot is like a friend who can guess how you’re feeling. It doesn’t just see what you do—it tries to understand why you’re doing it, like if you’re happy, sad, or mad.
- Theory of Mind AI is a hypothetical next step where AI can understand and model the emotions, intentions, and thoughts of humans or other agents.
- Requires a deep understanding of psychology and context; still largely theoretical.
Self Aware AI
- Consciousness, self
- An understanding of its own existence, goals, and limitations.
- This is the sci-fi dream of machines that think and feel like humans.
- Understand its own state
- Think independently
- Form goals and desires
Turing Test
-
A method to determine whether a machine can demonstrate human intelligence.
-
Proposed by: Alan Turing in his 1950 paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”.
-
Main Question: “Can machines think?”
-
Imagine a game with 3 players:
- A = A real person (human)
- B = A computer (machine)
- C = A judge (also a human)
-
How they play:
- The judge chats with both the person (A) and the computer (B).
- The judge can’t see or hear them — only text messages (like using WhatsApp or chat apps).
-
What’s the goal?
- The judge has to guess: "Which one is the human, and which one is the machine?"
-
How does Turing Test works?
- The judge talks to both — a human and a machine — using text only (like chatting on a phone). No voice, no pictures — just words
- The judge’s job is to guess who is human.
- If the machine fools the judge and the judge can’t guess correctly more than half the time.
- The machine passes the Turing Test — it acts smart enough to feel human!
-
Purpose of the Turing Test:
- The Turing Test was created to check if a machine can think and talk like a human
- It tests whether a computer can answer questions like a human would.
- If a human judge can't tell if they’re chatting with a person or a machine, the machine passes the test
- It helps us see how smart or human-like AI has become.
- The Turing Test is a benchmark for checking how smart an AI really is
- It’s not about how the machine works, but what it can do — can it talk and respond like a human?
-
It checks if the AI can:
- Understand natural language (like chatting in real sentences)
- Represent knowledge (remember facts or information)
- Reason (think and give smart answers)
- Learn (improve from past experiences)
-
Examples:
- Chatbots like ChatGPT, Google Bard, or Cleverbot are smart programs that can chat just like humans
- These AIs are trained to understand and respond using natural language — the way we talk every day.
- Many people can’t tell if they’re chatting with a real person or a machine at first
- That’s exactly what the Turing Test is all about
-
Limitation:
- Focuses only on behavior
- It checks what the machine says, not how it thinks or understands.
- A machine can fool a judge with smart replies, but that doesn’t mean it truly understands!
- Can be tricked with clever scripts
- Some chatbots are good at pretending — using funny or vague answers to confuse the judge.
- Short conversations
- In short chats, it’s easier for machines to act smart. Longer talks often show the machine’s real limits.
- Biased by the judge
- Judges are human too! They might guess wrong, or be fooled easily
- Doesn’t test full intelligence
- It only checks language skills — not things like emotions, creativity, or solving real-world problems.
- Focuses only on behavior
AI Challenges
-
Data Bias:
- AI systems learn from data. If the data reflects human biases, the AI will replicate or even amplify those biases.
- Example: A hiring algorithm trained on past employee data may prefer male applicants if the historical dataset is biased.
- Impact: Discrimination in hiring, lending, healthcare.
-
Lack of Explainability
- Modern AI models (like Deep Neural Networks) are complex black boxes.
- It is often not clear how a model arrived at a decision.
- Example: Why did a model reject a loan application? It’s hard to explain clearly to the user.
- Need: Explainable AI (XAI) for trust and transparency.
-
Ethical Concerns:
- Privacy: AI surveillance systems raise concerns about individual rights.
- Autonomous Weapons: Can AI make life-or-death decisions in war?
- Courtroom AI: Risk of using biased data for legal decision-making.
- Solution: Ethical frameworks and AI governance are critical.
-
Large Data & Compute Requirements:
- Deep learning models require massive labeled datasets.
- They also need powerful GPUs or TPUs for training.
- Challenge: Tech giants have resources; small entities struggle to keep up.
-
Security Threats:
- Deepfakes: AI-generated fake videos/images can spread misinformation.
- Adversarial Attacks: Tiny input changes (invisible to humans) can fool AI systems.
- Example: Altering pixels in a stop sign image can cause a self-driving car to ignore it.
Simple Real World AI Problems
-
Spam Detection
- ML models like Naïve Bayes or SVM are trained on labeled email data.
- They classify emails as spam or not spam based on features like keywords, sender, time, and links.
-
Product Recommendation
- Used by platforms like Amazon, Netflix, Flipkart, YouTube.
- Collaborative Filtering: Suggests items liked by similar users.
- Content-Based Filtering: Suggests items similar to what the user liked earlier.
-
Route Finding
- Used in GPS systems like Google Maps.
- Combines graph algorithms (like Dijkstra, A) with AI to find optimal routes.
- Factors include: real-time traffic, user history, roadblocks, and construction reports.
-
Game Playing AI – Tic Tac Toe
- Uses the Minimax Algorithm to play intelligently.
- AI explores all possible moves to maximize wins and minimize losses.
- Also applied in games like Chess and Checkers.
AI Techniques
Rule-Based Systems
-
A Rule-Based System (RBS) is an AI approach that applies predefined rules to process data and make decisions.
-
It follows simple IF-THEN logic, where each rule connects a condition to an action or output.
-
Key features:
- Based on IF-THEN logic:
- IF a certain condition is met, THEN a specific action is taken.
- Example: IF temperature > 100°F THEN alert = “High Fever”
- Easy to build and implement
- You don’t need machine learning or data training.
- Just define your rules and actions clearly.
- Used in Expert Systems
- Popular in early AI, especially for decision-making.
- Example: MYCIN, which helped doctors with medical diagnoses
- Mimics human experts
- Works like how an expert would think:
- "IF this symptom exists, THEN suggest this medicine."
- Transparent and explainable
- Every decision can be traced to a specific rule.
- Makes it easy to debug, audit, or explain to others.
- Deterministic
- Always gives the same output for the same input.
- No randomness or learning—it's rule-driven.
- Based on IF-THEN logic:
-
Advantages:
- Simple to understand and manage
- Works well for small, structured domains
- No need for large datasets
- Predictable and consistent behavior
-
Limitations:
- Rigid – Can’t adapt or learn on its own
- Not suitable for complex or dynamic environments
- Rule explosion – Too many rules can make the system hard to manage
- Cannot handle uncertainty or fuzzy situations
-
Real-World Examples
- MYCIN – Diagnosed bacterial infections
- Troubleshooting systems – For printers, cars, or electronics
- Home automation rules – IF it’s dark, THEN turn on the lights
- Shopping alerts – IF item in cart > ₹1000 THEN apply 10% discount
Simple Decision-Making Using Conditions
-
Decision-making using conditions is the foundation of programming and AI logic.
-
It means making choices based on whether a condition is true or false — just like how we make decisions in real life!
-
Key features:
- Based on "if-else" or conditional logic
-
Why It’s Important in AI & Coding?
- Helps systems take actions: Based on inputs or situations, the program decides what to do next.
- Guides the flow of a program: Determines which block of code runs and which doesn’t.
- Mimics real-life decisions: Just like how humans think before acting
-
Advantages:
- Simple to understand
- Easy to implement
- Works in every programming language
- Foundation for AI, automation & robotics
-
Limitations:
- Only handles simple situations
- Becomes complex when too many conditions are added
- Doesn’t learn or adapt (needs logic written by human)
-
Real-Life Examples:
- IF you finish homework → THEN you get ice cream
- IF bus is late → THEN wait or take auto
- IF battery < 10% → THEN stop playing game