AI-02 Problem Solving in AI
On This Page
AI Problem
-
A problem in AI is a task or situation where a computer or machine needs to think, decide, or learn in order to solve something intelligently
-
A problem in AI is defined by: Inputs, a goal, and a way to reach that goal using logic, rules, or learning.
-
Example:
- Problem: A self-driving car reaching a destination safely.
- Inputs: Current location, Map data, Traffic signals, Nearby vehicles, Weather conditions
- Goal: Reach the destination safely, quickly, and without breaking any traffic rules.
- Way to reach the goal: Use AI to analyze surroundings, make decisions (like when to stop or turn), and learn from past drives to improve navigation.
-
AI problem components:
- Initial State – Starting point
- Goal State – What we want to achieve
- Actions – What can be done
- Transition Model – What happens when actions are taken
- Path Cost (optional) – How much each step costs (used in optimization)
-
Real-life examples:
- Diagnosing diseases from symptoms
- Translating languages (e.g., Google Translate)
- Recommending movies (e.g., Netflix)
- Detecting banking fraud
| Problem Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Search problem | Find the best solution from many options . | GPS finding the shortest route |
| Planning problems | Decide steps to reach a goal. | Robot making tea |
| Classification | Group data into categories. | Spam or Not Spam emails |
| Prediction | Guess future results from past data. | Weather forecasting |
| Decision making | Pick the best option from choices. | Chess AI choosing next move |
| Perception | Understand inputs like images, sounds. | Face recognition, self-driving |
| Learning problems | Learn from past experience to improve. | Machine learning model training |
What does it mean to define AI Problem
-
In Artificial Intelligence, before solving a problem, we need to clearly define it — just like we need to understand the rules before playing a game
-
We define:
- Where we are (Initial State)
- Where we want to go (Goal State)
- What we can do (Possible Actions / Rules)
-
Example-1: Taxi Booking App (AI finding the best route)
- Initial State: Your current location
- Goal State: Your destination
- Actions: Choose among different routes, avoid traffic, follow navigation rules
-
Example-2: Cooking Assistant AI
- Initial State: Ingredients you have
- Goal State: Desired dish (e.g., pasta)
- Actions: Mix, boil, chop – in correct sequence
-
Example-3: Washing Clothes with AI Washing Machine
- Initial State: Dirty clothes in the basket
- Goal State: Clean, dry clothes
- Actions: Fill water, add detergent, wash, rinse, dry
Problem Space & State Space
- In AI, before solving any problem, we must clearly define what the problem is and how to approach it — that’s where problem space and state space come in.
- Problem space and state space help AI understand: "Where can I go, what can I do, and how do I get to my goal efficiently?"
State Space
- All possible situations (states) the system can be in while solving the problem
- It includes:
- The initial state
- The goal state
- All intermediate states you can reach by applying different actions
Problem Space
- Problem Space = The combination of: State Space + All possible actions (rules or moves that change one state to another)
- Problem Space = State Space + Actions
- It defines the entire environment in which the AI must operate to reach a goal.
- It defines all possible steps AI can use to reach the goal
Example
- Making a burger: AI as a cooking assistant
- Imagine you're teaching a robot (AI) how to make a burger.
- Problem space = Every action AI can take (adding patty, adding cheese etc)
- State space = Every stage in burger-making
- Goal = Perfect burger
Search Strategies
- Search strategies help an AI find the path from the starting point to the goal, especially when the AI has many choices to make.
- Imagine AI is playing a maze game, and it needs to find the quickest way out.
- Search strategies guide how it explores the maze.
- Two main types:
- Informed Search
- Uninformed Search
| Informed | Uninformed |
|---|---|
| Search with extra information | Search without an information |
| Uses knowledge to guide steps | No prior knowledge |
| Finds solution quickly | Slower & time-consuming |
| Less complex (Time + Space) | More complex (Time + Space) |
| Uses: DFS and BFS | Uses A*, Heuristic DFS, |
- References:
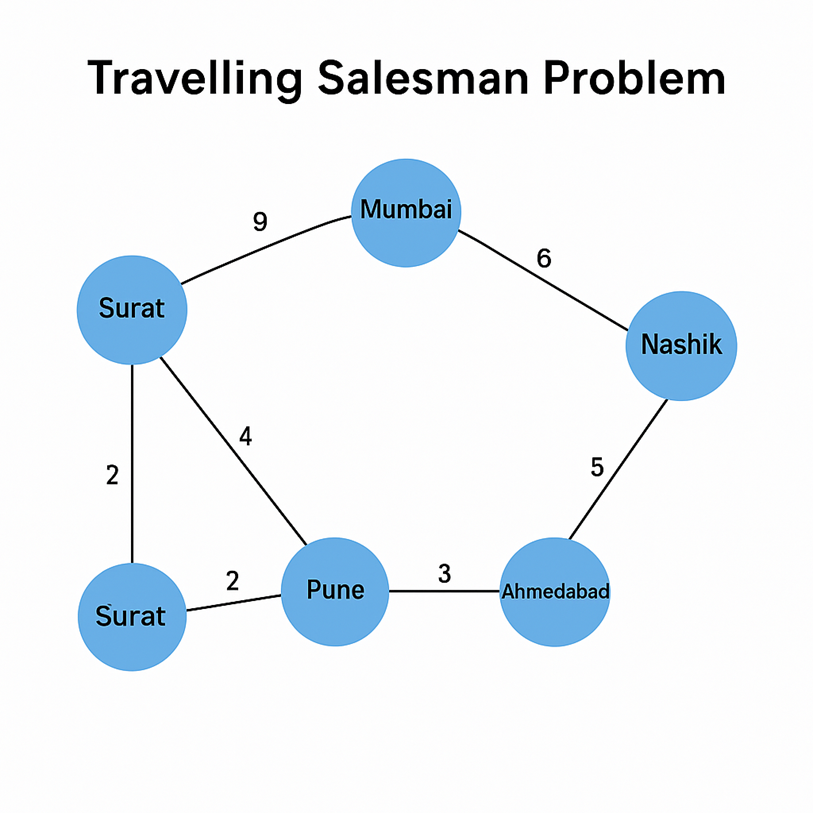
Travelling Salesman Problem
-
Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair, what is the shortest possible route that:
- Visits each city exactly once, and
- Returns to the starting city
-
Example: A salesman needs to visit 5 cities:
Surat → Mumbai → Pune → Nashik → Ahmedabad -
Goal:
- Visit each city once
- Travel the least distance (or time/cost)
- Return to the starting city
-
Uninformed Search (Brute Force):
- Tries every possible route
- For n cities, number of possible paths =
(n − 1)! - For 5 cities:
(5 − 1)! = 24possible paths - Guaranteed to find optimal solution
- But not scalable — what if 99 cities?
-
Informed Search (Heuristics):
- Uses smart logic or heuristics
- Doesn’t check every path
- Much faster and more efficient
Breadth First Search (BFS)
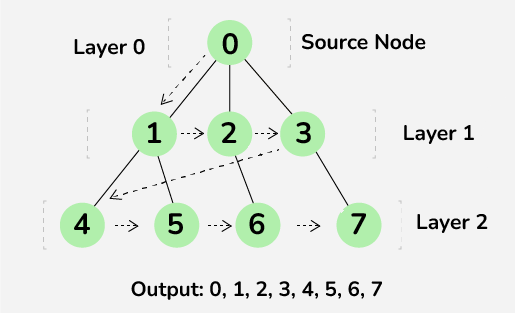
- BFS is a traversal approach in which we first walk through all nodes on the same level (horizontal movement) before moving on to the next level.
- BFS visits siblings before children
- BFS uses Queue data structure for finding the shortest path.
- It works on the concept of FIFO (First In First Out).
- BFS is more suitable for searching vertices closer to the given source.
- In BFS, each node is traversed only once.
- BFS will definitely find a solution if it exists
- BFS uses more memory than DFS
- How it works:
- Start from the root/start node
- Visit all its immediate neighbours
- Then go to next level of their neighbours
- Keep repeating until goal is found or all nodes are visited
- Real-life example:
- Social Media Friend Suggestions: Starting from you, BFS checks all your direct friends (level 1). Then their friends (level 2), and so on.
- Web Crawlers: Search engines like Google crawl the web page level by level. First links on page → then links inside those links
- Use cases:
- Shortest path in maps (like Google Maps)
- Puzzle solvers (like 8-puzzle, word ladder)
- Web Crawling
- Social networks – friend suggestion
Depth First Search (DFS)
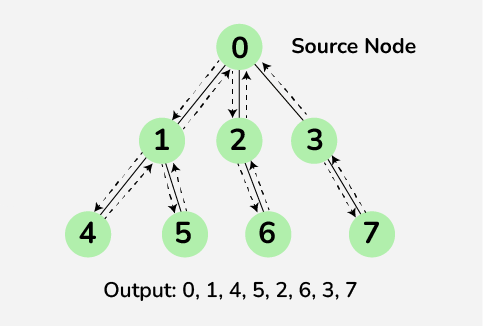
- DFS is a traversal approach in which the traverse begins at the root node and proceeds through the nodes as far as possible until we reach the node with no unvisited nearby nodes
- DFS visits children before siblings
- DFS uses Stack data structure.
- It works on the concept of LIFO (Last In First Out).
- DFS is more suitable when there are solutions away from source.
- In DFS each node is traversed twice due to backtracking.
- DFS may lead to situations where the algorithm gets stuck in an infinite loop.
- DSF may not give shortest path
- The amount of memory required for DFS is less than that of BFS.
- How it works:
- Start from the root/start node
- Visit one child node deeply until no further move
- Then backtrack and explore other branches
- Continue until goal is found or all paths are explored
- Real-life examples:
- File System Traversal: Opening folders inside folders (deep nesting). DFS goes till the last subfolder, then comes back. Used in file explorers (Windows, Mac, Linux)
- Puzzle Solving (Sudoku, 8-Puzzle, etc.): DFS explores one possible solution path fully. If it doesn’t work, it backtracks. Useful in game trees or AI bots solving puzzles.
- Use Cases:
- Topological Sorting
- Cycle detection in graphs
- Solving puzzles and mazes
- Searching deep decision trees
BFS vs DFS
| Aspect | BFS (Breadth First Search) | DFS (Depth First Search) |
|---|---|---|
| Traversal Order | Explores level by level (siblings before children). | Explores depth first (children before siblings). |
| Data Structure Used | Queue (FIFO). | Stack (LIFO) or recursion. |
| Path Finding | Finds the shortest path if it exists. | Does not guarantee shortest path. |
| Suitability | Best when the solution is closer to the source. | Best when the solution is far from the source. |
| Memory Usage | Requires more memory (stores all nodes at current level). | Requires less memory compared to BFS. |
| Node Visits | Each node is traversed only once. | Each node may be traversed twice due to backtracking. |
| Guarantee of Solution | Always finds a solution if one exists. | May get stuck in infinite loop and fail to find a solution. |
| Concept | FIFO – First In First Out. | LIFO – Last In First Out. |
| Real-life Examples | - Social media friend suggestion- Web crawlers- Google Maps shortest path | - File system traversal- Puzzle solving (Sudoku, 8-puzzle)- Game trees |
| Use Cases | - Shortest path in graphs- Web crawling- Social networks | - Topological sorting- Cycle detection- Maze/puzzle solving |
Hill Climbing Algorithm
-
Hill Climbing is an informed search algorithm (a type of greedy algorithm) used in Artificial Intelligence for optimization problems.
-
The main goal is to reach the best possible solution by iteratively moving to better neighboring states until no further improvement is possible.
-
Type: Informed Search (Greedy)
-
Goal: Reach the peak (best solution) by always moving to a better state
-
Strategy: Move in the direction where the heuristic/value function improves
Concept
Imagine climbing a hill in thick fog where you cannot see the entire landscape. You can only look at the immediate neighbors and decide the next step:
- Start at some point (initial solution).
- Check the neighboring solutions.
- Move to the neighbor with the highest value (steepest ascent).
- Repeat until no better neighbor exists.
- Stop at the point where no further improvement is possible.
Important: Hill Climbing does not backtrack or remember past paths. It only moves forward toward better states.
How Hill Climbing Works
- Start from an initial state.
- Evaluate the neighboring states.
- Move to the neighbor with a higher value.
- Repeat until:
- No better neighbor is found, or
- A stopping criterion is met.
Key Features
- Advantages:
- Simple and fast
- Requires less memory
- Works well when heuristic function is good
- Limitations (Problems faced):
- Local Maxima: The algorithm may stop at a peak that is not the global maximum.
- Plateau: The algorithm may get stuck in a flat region where all neighbors are of the same value.
- Ridges: The algorithm may fail in narrow regions that require sideways movement before going upward.
Common Problems in Hill Climbing
- Local Maximum
- Definition: A point higher than its neighbors but lower than the global maximum.
- Example: Climbing a small hill and assuming it is the highest point while a taller mountain exists nearby.
- Plateau (Flat Maximum)
- Definition: A flat area with no change in value in any direction.
- Example: Reaching a flat surface on the hill where every step looks the same, leaving the algorithm “stuck.”
- Ridge
- Definition: A narrow path that requires sideways movement before going upward.
- Example: The algorithm insists on moving straight up, missing the correct zigzag path.
Variants of Hill Climbing
- Simple Hill Climbing: Chooses the first better neighbor found.
- Steepest-Ascent Hill Climbing: Evaluates all neighbors and selects the steepest upward move.
- Stochastic Hill Climbing: Chooses randomly among the better neighbors to avoid being stuck.
Applications of Hill Climbing
- Artificial Intelligence in Games: For decision-making in games like Tic Tac Toe.
- Function Optimization: Finding maximum/minimum values of mathematical functions.
- Robotics and Pathfinding: To optimize paths or movement.
- Machine Learning Parameter Tuning: Adjusting parameters to improve performance.
Key Insight
-
Hill Climbing is like climbing a mountain with a flashlight in fog:
- You can only see a few steps ahead.
- You always move upward if possible.
- You stop when no better step is visible.
-
Reference: https://www.scaler.com/topics/hill-climbing-in-ai/
Heuristic Search
- Heuristic Search is an informed search technique that uses additional knowledge (heuristics) to guide the search process towards the goal more efficiently.
- Type: Informed Search
- Heuristic: An educated guess or rule of thumb that helps estimate how close a state is to the goal.
- Goal: Reduce unnecessary exploration by selecting the most promising paths first.
Concept
- In heuristic search, instead of exploring all possible paths (as in uninformed search), the algorithm uses a heuristic function h(n) to estimate the cost or distance from a node n to the goal.
- Heuristic acts like a hint or shortcut.
- It does not always guarantee the optimal solution, but it often finds a good solution faster.
- The effectiveness of heuristic search depends heavily on the quality of the heuristic function.
How Heuristic Search Works
- Start from the initial node.
- Use the heuristic function h(n) to evaluate which node seems closer to the goal.
- Select the most promising node.
- Expand the chosen node and repeat the evaluation for its successors.
- Continue until the goal node is reached.
Real-Life Analogies
-
Treasure Hunt Analogy
- Instead of checking every possible place, you use hints (“warmer/colder”) to guess where the treasure might be.
-
Candy Search at Home
- You want to find candy but instead of checking every location (drawers, fridge, shoe rack…), you use your intuition:
- “Maybe in the fridge?” (likely)
- “Under the bed?” (unlikely)
- You want to find candy but instead of checking every location (drawers, fridge, shoe rack…), you use your intuition:
-
Navigation Apps (Google Maps)
- Example: Traveling from Srinagar to Pahalgam.
- Google suggests the route based not only on distance but also on estimated time.
- This estimation = heuristic in action.
Example: Search Tree with Heuristics
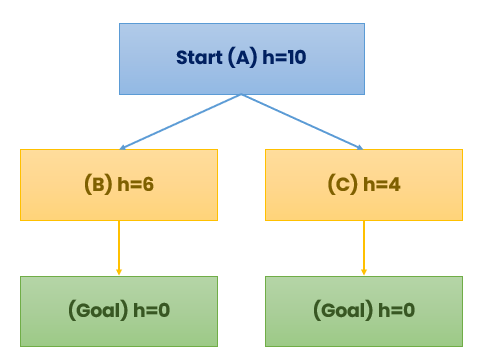
- Both B and C lead to the goal, but the heuristic indicates C looks closer (h=4 < h=6).
- The algorithm selects C first and reaches the goal faster.
Key Features
-
Advantages:
- Faster than uninformed searches like BFS and DFS.
- Can skip irrelevant or bad branches.
- Requires less memory and computation if heuristics are good.
-
Disadvantages:
- Heuristic must be accurate and admissible (should not overestimate cost).
- Poor heuristics may lead to misleading paths or incorrect solutions.
- Designing good heuristics is often challenging.
Applications of Heuristic Search
- Navigation systems: Google Maps, Uber routes
- Game AI: Chess, Tic Tac Toe
- Puzzle solving: 8-Puzzle, Sudoku
- Decision-making: Intelligent agents, smart bots
Key Insight
-
Heuristic Search is like searching with a guide: instead of blindly exploring every possibility, you follow hints (heuristics) that lead you towards the goal faster.
-
Reference: https://www.scaler.com/topics/artificial-intelligence-tutorial/informed-search/#heuristics-function