android-01 Introduction to Mobile Operating System
On This Page
What is Mobile OS?
- A mobile operating system is an operating system used for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, smart glasses
- Controls how device works
- Without OS, phone cannot function
What Mobile OS Does
- Starts device properly
- Runs applications
- Connects to internet
- Works smoothly
Examples of Mobile OS
- Android
- iOS
Why Mobile OS is Needed?
- Use apps like WhatsApp, YouTube
- Make calls and messages
- Use internet & Wi-Fi
- Control battery & memory
Features of Mobile OS
- Touch Screen Interface
- Multitasking
- Connectivity
- App Management
- Resource Management
Touch Screen Interface
- Touch screen users can use touch gestures
- Tap icons
- Swipe pages
- Easy to use
Multitasking
- Many apps run together
- Easy switching
- Example: Music + WhatsApp
Connectivity
- Mobile network
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
App Management
- Download apps
- Install apps
- Update apps
- Play Store / App Store
Resource Management
- RAM management
- Battery saving
- Processor control
Constraints of Smart Mobile OS
Limited Battery Power
- Mobile phones run on battery
- Battery drains fast
- Heavy apps and games consume more power
Limited RAM (Memory)
- Mobile devices have less RAM than computers
- Too many apps make phone slow
- Background apps are closed automatically
Limited Storage Space
- Mobile storage is limited
- Apps, photos, videos fill memory quickly
- User needs to delete data often
Small Screen Size
- Mobile screens are small
- Limited space to display information
- Not suitable for long work like desktop
Limited Processing Power
- Mobile processors are less powerful
- Heavy tasks reduce performance
- Apps must be optimized
Types of Mobile OS
- Mobile Operating Systems are used to run mobile devices such as smartphones
- Different companies have developed different Mobile Operating Systems
Android
- Developed by Google
- Most widely used Mobile Operating System
- Open-source operating system
- Used in smartphones and tablets
iOS
- Developed by Apple Inc.
- Used in iPhone and iPad
- Provides smooth and secure user interface
- Closed operating system
BlackBerry OS
- Developed by BlackBerry
- Known for high security
- Mostly used by business users
- Now discontinued
Microsoft (Windows Phone)
- Developed by Microsoft
- Used in Nokia Lumia phones
- Simple and user-friendly interface
- Discontinued by Microsoft
Symbian OS
- Developed by Nokia
- Used in early Nokia smartphones
- One of the first mobile operating systems
- Now discontinued
Generalized Architecture of Mobile Operating System
- A Mobile Operating System manages mobile hardware and provides a platform for applications.
Main Layers:
- Kernel Layer
- Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)
- Middleware
- Application Framework
- User Interface Layer
Kernel Layer
- Core part of Mobile OS
- Manages memory
- CPU scheduling
- Power management
- Device drivers
- Based on Linux kernel
Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)
- Interface between hardware and OS
- Hides hardware complexity
- Makes OS portable across devices
Middleware Layer
- Provides common services
- Multimedia support
- Database services
- Security services
Application Framework & UI Layer
Application Framework:
- APIs for app development
- Manages activities and resources
User Interface Layer
- Handles display and user interaction
Comparison of Mobile Operating Systems
| Feature | Android | iOS | BlackBerry | Windows Mobile | Symbian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developer | Apple | BlackBerry | Microsoft | Nokia | |
| Source Type | Open | Closed | Closed | Closed | Open |
| App Store | Play Store | App Store | BB World | Windows Store | Ovi Store |
| Security | Moderate | High | Very High | Moderate | Low |
| Customization | High | Low | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Market Share | High | High | Very Low | Negligible | Obsolete |
Android Operating System – Introduction
- Linux-based mobile operating system
- Developed by Google and Open Handset Alliance (OHA)
- Mostly programmed using Java
- Open-source and customizable
Open Handset Alliance (OHA)
- Consortium of 84 companies
- Led by Google
- Founded on 5 November 2007
- Develops open standards for Android
Features of Android
- Open-source platform
- Highly customizable
- Large number of applications
- User-friendly interface
Android Supported Services
- SMS and MMS
- Internet browser
- SQLite database
- Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GSM, CDMA
- Audio and video media
Categories of Android Applications
- Entertainment
- Communication
- Productivity
- Social
More Categories of Android Applications
- Music and Audio
- Media and Video
- Travel and Local
- Tools and Personalization
History of Android
- Founded by Andy Rubin in 2003
- Acquired by Google in 2005
- Initially developed for cameras
- Shifted from cameras to smartphones
- Android name came from Andy Rubin’s nickname
- First Android phone launched in 2008 (HTC)
Android Versions
- Android has evolved from Android 1.0 (2008) to latest versions
- Early Android versions (1.0 & 1.1) had no dessert names
- From Cupcake to Pie, Android followed alphabetical dessert naming
- From Android 10 onwards, public dessert names were removed
- Internal codenames still exist for each version
- Every new Android version focuses on:
- Better performance
- Improved security
- Enhanced user interface
- Support for new devices and hardware
Android Versions – Evolution Summary
- Android 1.0 – 2.3 (Cupcake to Gingerbread)
- Basic smartphone features, UI and performance improvements
- Android 3.0 (Honeycomb)
- Tablet-specific operating system
- Android 4.0 (Ice Cream Sandwich)
- Unified phone and tablet platform
- Android 4.1 – 4.4 (Jelly Bean to KitKat)
- Smooth UI, better notifications, low-RAM support
- Android 5.0 – 6.0 (Lollipop & Marshmallow)
- Material Design, runtime permissions, battery optimization
- Android 7.0 – 9.0 (Nougat to Pie)
- Multitasking, split screen, gesture navigation
- Android 10 – 12 (Android 10, 11, 12 / 12L)
- Privacy controls, UI redesign, tablet & foldable support
- Android 13 – 16 (Tiramisu to Baklava)
- Advanced security, performance improvements, large-screen optimization
Android Architecture (Software Stack)
- Linux Kernel
- Native Libraries
- Android Runtime
- Application Framework
- Applications
Linux Kernel (Android)
- Base of Android architecture
- Memory management
- Power management
- Device drivers
- Process management
Native Libraries
- WebKit – Browser support
- SQLite – Database
- OpenGL – Graphics
- Media – Audio and video
- FreeType – Font support
Android Runtime
- Core libraries
- Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM)
- Optimized for mobile devices
- Uses less memory than JVM
Application Framework
- Activity Manager
- Window Manager
- Resource Manager
- Content Providers
Applications Layer
- Built-in applications
- User-installed applications
- Uses Android framework
Building Blocks of Android Application
- Activity
- View
- Intent
- Service
- Content Provider
- Fragment
- AndroidManifest.xml
Android Activity Lifecycle
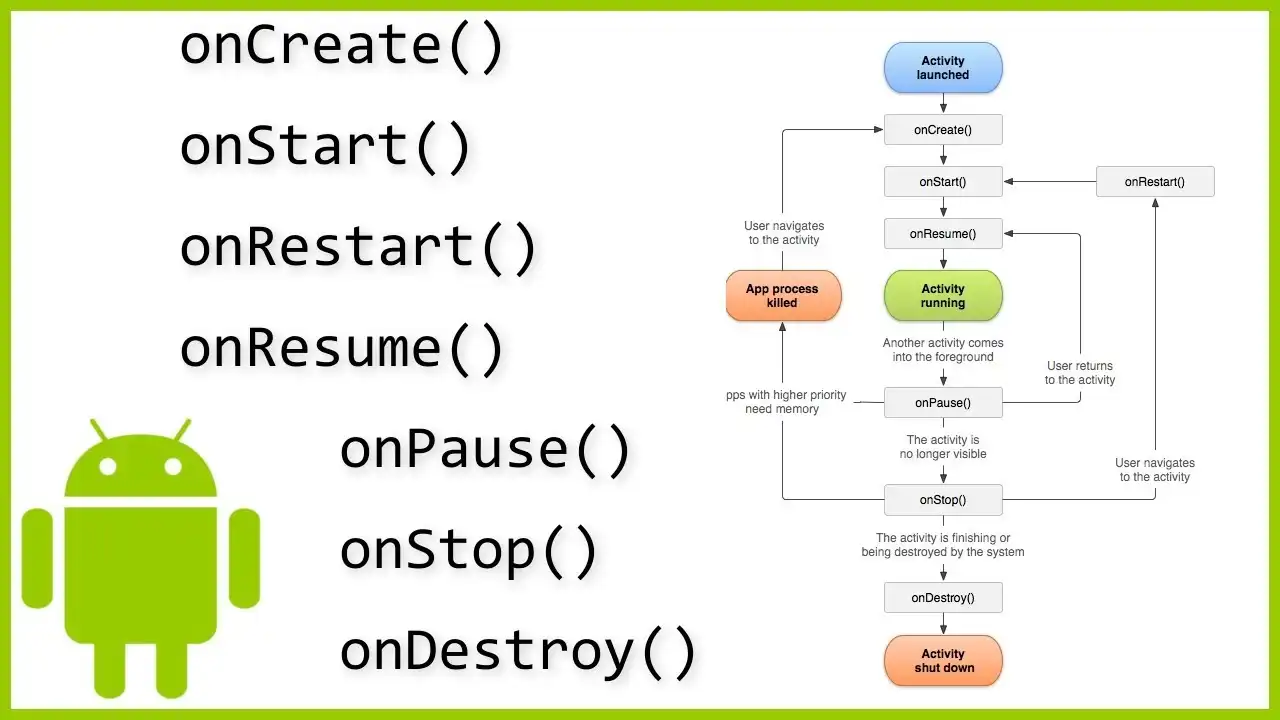
- onCreate() – Activity created
- onStart() – Activity visible
- onResume() – User interaction
- onPause() – Activity partially hidden
- onStop() – Activity not visible
- onRestart() – Activity restarted
- onDestroy() – Activity destroyed