CN-01 Introduction
On This Page
Introduction
- A computer network is a group of computers linked to each other that enables the computer to communicate with another computer and share their resources, data, and applications.
- Computer networking refers to interconnected computing devices that can exchange data and share resources with each other.
Advantages
- Resource Sharing: Allows multiple users to access and utilize the same resources like printers, files, and software
- Centralized Management: Data and resources can be managed from a central location, simplifying administration and security.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Facilitates faster and more efficient communication and collaboration among users.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces the need for individual hardware and software licenses, leading to overall cost savings.
- Increased Flexibility and Scalability: Networks can be easily expanded or modified to accommodate changing needs.
- Centralized Data Management: Data can be stored and managed in a central location, improving data consistency and security.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced security measures can be implemented to protect sensitive data and resources.
Disadvantages
- High Initial Cost: Setting up a computer network can be expensive due to the cost of hardware, software, and installation.
- Security Risks: Networks are susceptible to various security threats like viruses, malware, and hacking attempts.
- Dependence on Infrastructure: Network failures or downtime can disrupt operations and lead to loss of productivity.
- Complexity: Managing and maintaining a complex network requires specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Potential for Data Loss: In case of system failures, data loss can occur if backups are not properly maintained.
- Vulnerability to Viruses and Malware: Viruses and malware can spread rapidly through a network, potentially affecting all connected devices.
Topology
- Topology defines the structure of the network of how all the components are interconnected to each other. There are two types of topology: Physical and Logical topology.
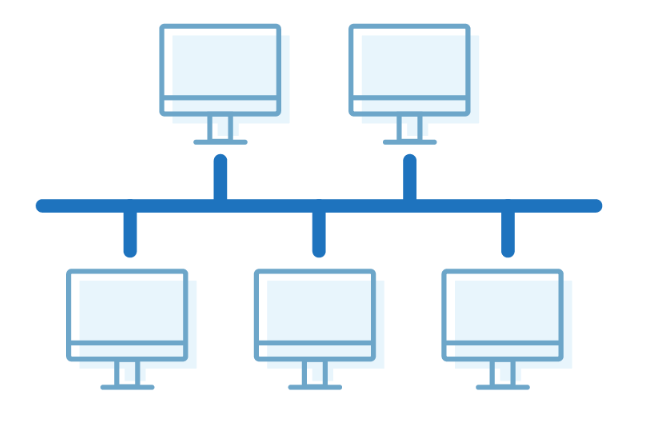
Bus Topology
-
The bus topology is designed in such a way that all the stations are connected through a Each node is either connected to the single cable known as a backbone cable.
-
Backbone cable by drop cable or directly connected to the backbone cable.
-
When a node wants to send a message over the network, it puts a message over the network.
-
All the stations available in the network will receive the message whether it has been addressed or not.
-
The bus topology is mainly used in 802.3 (Ethernet) and 802.4 standard networks.
-
The configuration of a bus topology is quite simpler as compared to other topologies.
-
The backbone cable is considered as a "single lane" through which the message is broadcast to all the stations.
-
Advantages:
- Low-cost cable: In bus topology, nodes are directly connected to the cable without passing through a hub. Therefore, the initial cost of installation is low.
- Moderate data speeds: Coaxial or twisted pair cables are mainly used in bus-based networks that support up to 10 Mbps.
- Familiar technology: Bus topology is a familiar technology as the installation and troubleshooting techniques are well known, and hardware components are easily available.
- Limited failure: A failure in one node will not have any effect on other nodes
-
Disadvantages:
- Extensive cabling: A bus topology is quite simpler, but still it requires a lot of cabling.
- Difficult troubleshooting: It requires specialized test equipment to determine the cable faults. If any fault occurs in the cable, then it would disrupt the communication for all the nodes.
- Signal interference: If two nodes send the messages simultaneously, then the signals of both the nodes collide with each other.
- Reconfiguration difficult: Adding new devices to the network would slow down the network.
- Attenuation: Attenuation is a loss of signal leads to communication issues. Repeaters are used to regenerate the signal.
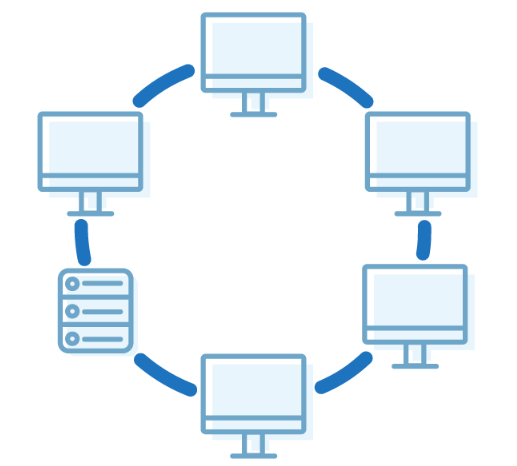
Ring Topology
-
In this topology, it forms a ring connecting devices with its exactly two neighbouring devices.
-
A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with a large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Hence to prevent data loss repeaters are used in the network
-
The transmission is unidirectional, but it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology
-
Advantages:
- Network Management: Faulty devices can be removed from the network without bringing the network down.
- Product availability: Many hardware and software tools for network operation and monitoring are available.
- Cost: Twisted pair cabling is inexpensive and easily available. Therefore, the installation cost is very low.
- Reliable: It is a more reliable network because the communication system is not dependent on the single host computer.
-
Disadvantages:
- Difficult troubleshooting: It requires specialized test equipment to determine the cable faults. If any fault occurs in the cable, then it would disrupt the communication for all the nodes.
- Failure: The breakdown in one station leads to the failure of the overall network.
- Reconfiguration difficult: Adding new devices to the network would slow down the network.
- Delay: Communication delay is directly proportional to the number of nodes. Adding new devices increases the communication delay
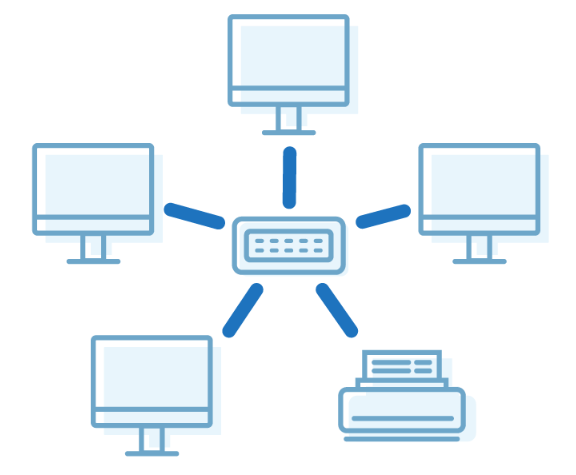
Star Topology
-
In star topology, all the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all other nodes are connected to the central node. The hub can be passive in nature i.e., not an intelligent hub such as broadcasting devices, at the same time the hub can be intelligent known as an active hub. Active hubs have repeaters in them.
-
A star topology having four systems connected to a single point of connection i.e. hub.
-
Advantages:
- Network control: Complex network control features can be easily implemented in the star topology. Any changes made in the star topology are automatically accommodated
- Limited failure: As each station is connected to the central hub with its own cable, therefore failure in one cable will not affect the entire network.
- Familiar technology: Star topology is a familiar technology as its tools are cost-effective.
- Easily expandable: It is easily expandable as new stations can be added to the open ports on the hub.
- Cost effective: Star topology networks are cost-effective as it uses inexpensive coaxial cable.
- High data speeds: It supports a bandwidth of approx. 100Mbps. Ethernet 100BaseT is one of the most popular Star topology networks.
-
Disadvantages:
- A Central point of failure: If the central hub or switch goes down, then all the connected nodes will not be able to communicate with each other.
- Cable: Sometimes cable routing becomes difficult when a significant amount of routing is required.
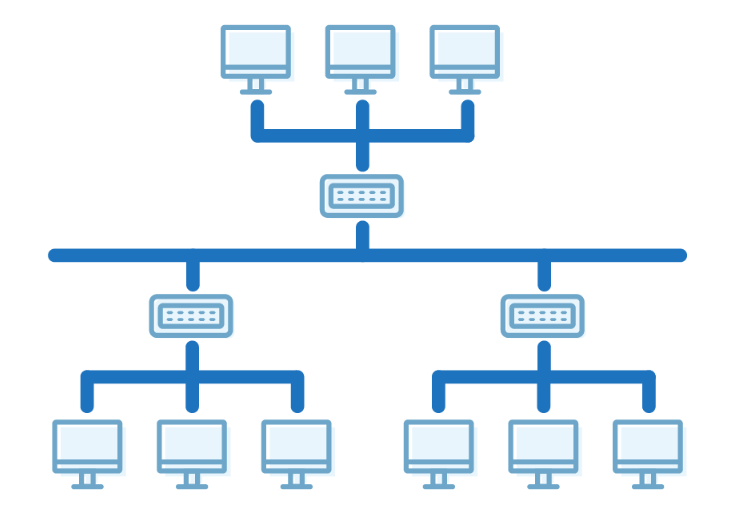
Tree Topology
-
A tree topology is a type of structure in which all the computers are connected with each other in hierarchical fashion.
-
Tree topology combines the characteristics of bus topology and star topology.
-
The top-most node in tree topology is known as a root node, and all other nodes are the descendants of the root node.
-
There is only one path exists between two nodes for the data transmission. Thus, it forms a parent-child hierarchy.
-
Advantages:
- Support for broadband transmission: Tree topology is mainly used to provide broadband transmission, i.e., signals are sent over long distances without being attenuated.
- Easily expandable: We can add the new device to the existing network. Therefore, we can say that tree topology is easily expandable.
- Easily manageable: In tree topology, the whole network is divided into segments known as star networks which can be easily managed and maintained.
- Error detection: Error detection and error correction are very easy in a tree topology.
- Limited failure: The breakdown in one station does not affect the entire network.
- Point-to-point wiring: It has point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
-
Disadvantages:
- Difficult troubleshooting: If any fault occurs in the node, then it becomes difficult to troubleshoot the problem.
- High cost: Devices required for broadband transmission are very costly.
- Failure: A tree topology mainly relies on main bus cable and failure in main bus cable will damage the overall network.
- Reconfiguration difficult: If new devices are added, then it becomes difficult to reconfigure.
Mesh Topology
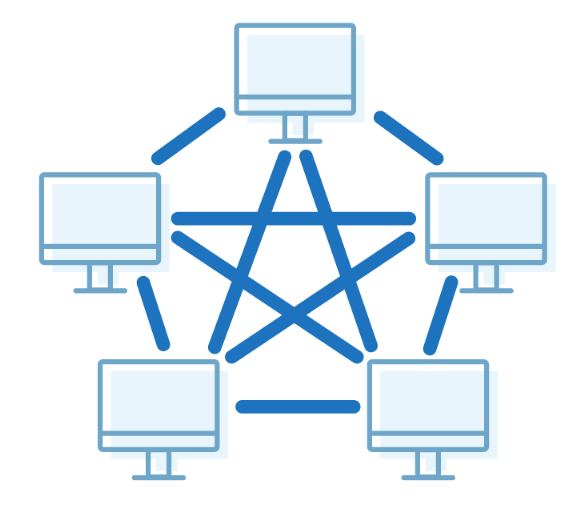
-
There are multiple paths from one computer to another computer.
-
It does not contain the switch, hub or any central computer which acts as a central point of communication.
-
The Internet is an example of the mesh topology.
-
Mesh topology is mainly used for WAN implementations where communication failures are a critical concern.
-
Mesh topology is mainly used for wireless networks.
-
Mesh topology can be formed by using the formula:
-
Number of cables =
(n*(n-1))/2 -
Advantages:
- Reliable: The mesh topology networks are very reliable as if any link breakdown will not affect the communication between connected computers.
- Fast Communication: Communication is very fast between the nodes.
- Easier Reconfiguration: Adding new devices would not disrupt the communication between other devices.
-
Disadvantages:
- Cost: A mesh topology contains a large number of connected devices such as a router and more transmission media than other topologies.
- Management: Mesh topology networks are very large and very difficult to maintain and manage. If the network is not monitored carefully, then the communication link failure goes undetected.
- Efficiency: In this topology, redundant connections are high that reduces the efficiency of the network.
Hybrid Topology
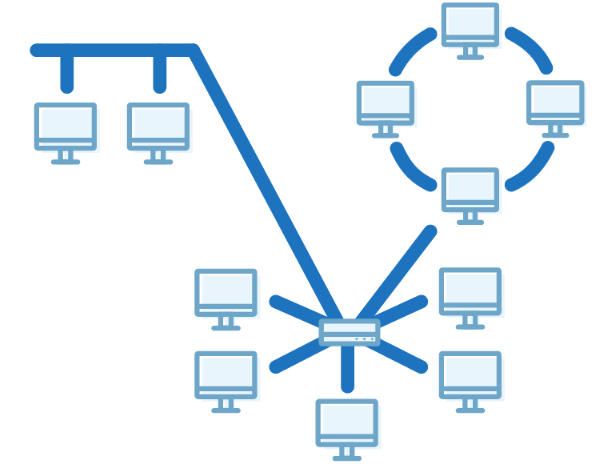
-
The combination of various different topologies is known as Hybrid topology.
-
A Hybrid topology is a connection between different links and nodes to transfer the data.
-
When two or more different topologies are combined together is termed as Hybrid topology and if similar topologies are connected with each other will not result in Hybrid topology.
-
For example, if there exist a ring topology in one branch of ICICI bank and bus topology in another branch of ICICI bank, connecting these two topologies will result in Hybrid topology.
-
Advantages:
- Reliable: If a fault occurs in any part of the network will not affect the functioning of the rest of the network.
- Scalable: Size of the network can be easily expanded by adding new devices without • affecting the functionality of the existing network.
- Flexible: This topology is very flexible as it can be designed according to the requirements of the organization.
- Effective: Hybrid topology is very effective as it can be designed in such a way that the strength of the network is maximized and weakness of the network is minimized.
-
Disadvantages:
- Complex design: The major drawback of the Hybrid topology is the design of the Hybrid network. It is very difficult to design the architecture of the Hybrid network.
- Costly Hub: The Hubs used in the Hybrid topology are very expensive as these hubs are different from usual Hubs used in other topologies.
- Costly infrastructure: The infrastructure cost is very high as a hybrid network requires a lot of cabling, network devices, etc.
OSI Model
- International standard organization (ISO) established a committee in 1977 to develop an architecture for computer communication.
- Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model is the result of this effort.
- In 1984, the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model was approved as an international standard for communications architecture.
- Term “open” denotes the ability to connect any two systems which conform to the reference model and associated standards.
- The OSI model is now considered the primary Architectural model for inter-computer communications.
- The OSI model describes how information or data makes its way from application programmes (such as spreadsheets) through a network medium (such as wire) to another application programme located on another network.
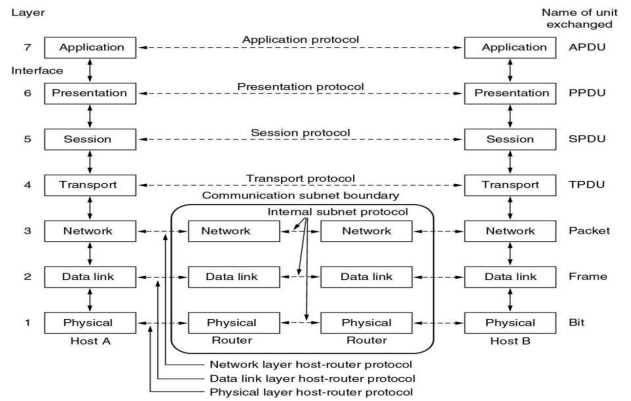
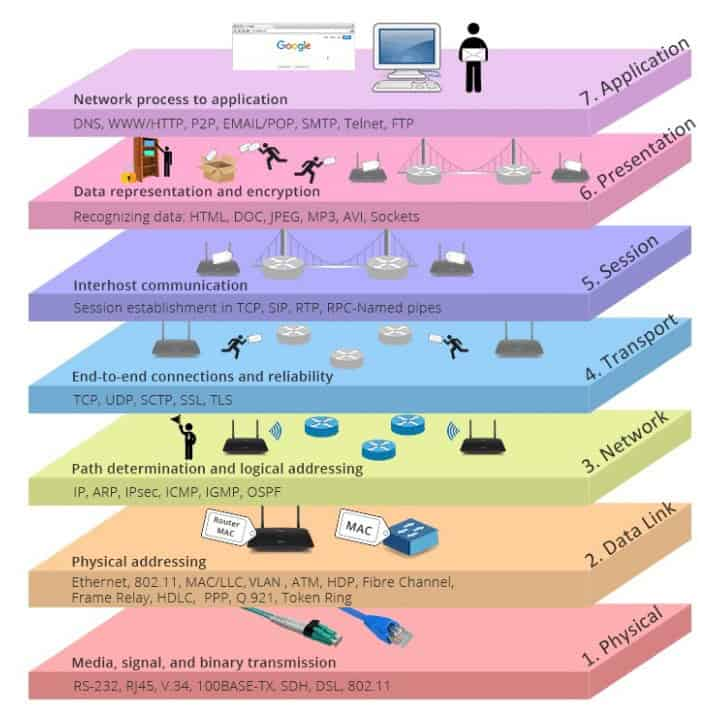
- The OSI reference model divides the problem of moving information between computers over a network medium into seven smaller and more manageable problems
- This separation into smaller more manageable functions is known as layering
- The process of breaking up the functions or tasks of networking into layers reduces complexity.
- Each layer provides a service to the layer above it in the protocol specification.
- Each layer communicates with the same layer’s software or hardware on other computers.
- The lower 4 layers (transport, network, data link and physical —Layers 4, 3, 2, and 1) are concerned with the flow of data from end to end through the network.
- The upper four layers of the OSI model (application, presentation and session— Layers 7, 6 and 5) are orientated more toward services to the applications.
- Data is Encapsulated with the necessary protocol information as it moves down the layers before network transit.
Physical Layer
- Provides physical interface for transmission of information.
- Defines rules by which bits are passed from one system to another on a physical communication medium.
- Covers all- mechanical, electrical, functional and procedural aspects for physical communication.
- Such characteristics as voltage levels, timing of voltage changes, physical data rates, maximum transmission distances, physical connectors, and other similar attributes are defined by physical layer specifications.
Data Link Layer
- Data link layer attempts to provide reliable communication over the physical layer interface.
- Breaks the outgoing data into frames and reassemble the received frames.
- Create and detect frame boundaries.
- Handle errors by implementing an acknowledgement and retransmission scheme.
- Implement flow control.
- Supports points-to-point as well as broadcast communication.
- Supports simplex, half-duplex or full-duplex communication.
- The data link layer provides:
- Link establishment and termination: establishes and terminates the logical link between two nodes.
- Frame traffic control: tells the transmitting node to "back-off" (stop) when no frame buffers are available.
- Frame sequencing: transmits/receives frames sequentially.
- Frame acknowledgment: provides/expects frame acknowledgments. Detects and recovers from errors that occur in the physical layer by retransmitting non-acknowledged frames and handling duplicate frame receipt.
- Frame delimiting: creates and recognizes frame boundaries.
- Frame error checking: checks received frames for integrity.
- Media access management: determines when the node "has the right" to use the physical medium.
Network Layer
- Implements routing of frames (packets) through the network.
- Defines the most optimum path the packet should take from the source to the destination
- Defines logical addressing so that any endpoint can be identified.
- Handles congestion in the network.
- Facilitates interconnection between heterogeneous networks (Internetworking).
- The network layer also defines how to fragment a packet into smaller packets to accommodate different media.
- The network layer provides:
- Routing: routes frames among networks.
- Subnet traffic control: routers (network layer intermediate systems) can instruct a sending station to "throttle back" its frame transmission when the router's buffer fills up.
- Frame fragmentation: if it determines that a downstream router's maximum transmission unit (MTU) size is less than the frame size, a router can fragment a frame for transmission and re- assembly at the destination station.
- Logical-physical address mapping translates logical addresses or names, into physical addresses.
- Subnet usage accounting: has accounting functions to keep track of frames forwarded by subnet intermediate systems, to produce billing information.
Transport Layer
- Purpose of this layer is to provide a reliable mechanism for the exchange of data between two processes in different computers.
- The transport layer ensures that messages are delivered error-free, in sequence, and with no losses or duplications. It relieves (release) the higher layer protocols from any concern with the transfer of data between them and their peers.
- The size and complexity of a transport protocol depend on the type of service it can get from the network layer. For a reliable network layer with virtual circuit capability, a minimal transport layer is required. If the network layer is unreliable and/or only supports datagrams, the transport protocol should include extensive error detection and recovery.
- The transport layer provides:
- Message segmentation: accepts a message from the (session) layer above it, splits the message into smaller units (if not already small enough), and passes the smaller units down to the network layer. The transport layer at the destination station reassembles the message.
- Message acknowledgment: provides reliable end-to-end message delivery with acknowledgments.
- Message traffic control: tells the transmitting station to "back-off" when no message buffers are available.
- Typically, the transport layer can accept relatively large messages, but there are strict message size limits imposed by the network (or lower) layer. Consequently, the transport layer must break up the messages into smaller units, or frames, prepending a header to each frame.
- The transport layer header information must then include control information, such as message start and message end flags, to enable the transport layer on the other end to recognize message boundaries.
- In addition, if the lower layers do not maintain sequence, the transport header must contain sequence information to enable the transport layer on the receiving end to get the pieces back together in the right order before handing the received message up to the layer above.
Session Layer
- Session layer provides mechanism for controlling the dialogue between the two end systems. It defines how to start, control and end conversations (called sessions) between applications.
- This layer requests for a logical connection to be established on an end-user’s request.
- Any necessary log-on or password validation is also handled by this layer.
- Session layer is also responsible for terminating the connection.
- This layer provides services like dialogue discipline which can be full duplex or half duplex.
- Session layer can also provide check-pointing mechanism such that if a failure of some sort occurs between checkpoints, all data can be retransmitted from the last checkpoint.
Presentation Layer
- Presentation layer defines the format in which the data is to be exchanged between the two communicating entities.
- Also handles data compression and data encryption (cryptography).
- The presentation layer formats the data to be presented to the application layer. It can be viewed as the translator for the network. This layer may translate data from a format used by the application layer into a common format at the sending station, then translate the common format to a format known to the application layer at the receiving station.
- The presentation layer provides:
- Character code translation: for example, ASCII to EBCDIC.
- Data conversion: bit order, CR-CR/LF, integer-floating point, and so on.
- Data compression reduces the number of bits that need to be transmitted on the network.
- Data encryption: encrypt data for security purposes. For example, password encryption.
Application Layer
- Application layer interacts with application programs and is the highest level of OSI model.
- Application layer contains management functions to support distributed applications.
- Examples of application layer are applications such as file transfer, electronic mail, remote login etc.
- The application layer serves as the window for users and application processes to access network services.
- This layer contains a variety of commonly needed functions:
- Resource sharing and device redirection
- Remote file access
- Remote printer access
- Inter-process communication
- Network management
- Directory services
- Electronic messaging (such as mail)
- Network virtual terminals
TCP/IP Model
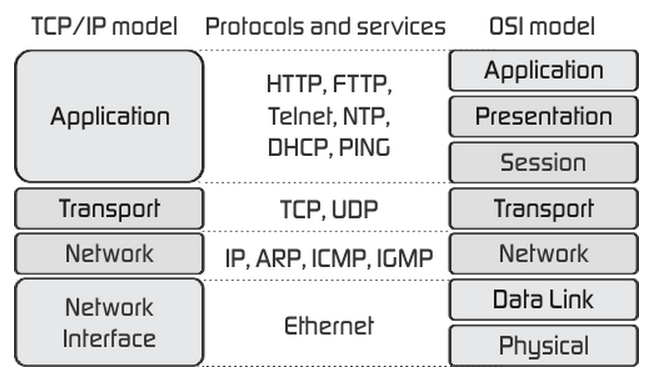
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol suite is the engine for the Internet and networks worldwide.
- TCP/IP either combines several OSI layers into a single layer or does not use certain layers at all.
- TCP/IP is a set of protocols developed to allow cooperating computers to share resources across the network.
- The TCP/IP model has five layers.
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Internet Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Physical Network
- The Network Access Layer in the TCP/IP model combines the functions of Data link Layer and Physical Layer.
Application Layer
- The application layer is the topmost layer of the four-layer TCP/IP model.
- The application layer is present on the top of the Transport layer.
- Application layer defines TCP/IP application protocols and how host programs interface with Transport layer services to use the network.
- Application layer includes all the higher-level protocols like DNS (Domain Naming System), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), Telnet, SSH, FTP (File Transfer Protocol), TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), X Windows, RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) etc.
Transport Layer
- The purpose of the Transport layer is to permit devices on the source and destination hosts to carry on a conversation.
- Transport layer defines the level of service and status of the connection used when transporting data.
- The transport layer provides the end-to-end data transfer by delivering data from an application to its remote peer.
- The most-used transport layer protocol is the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which provides:
- Reliable delivery data
- Duplicate data suppression
- Congestion control
- Flow control
- Another transport layer protocol is the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), which provides:
- Connectionless
- Unreliable
- UDP is used by applications that need a fast transport mechanism and can tolerate the loss of some data
Network Layer (Internet Layer)
- The internet layer also called the network layer.
- Internet layer pack data into data packets known as IP datagrams, which contain source and destination address (logical address or IP address) information that is used to forward the datagrams between hosts and across networks.
- The Internet layer is also responsible for the routing of IP datagrams.
- Internet Protocol (IP) is the most important protocol in this layer.
- It is a connectionless protocol that does not assume reliability from lower layers. IP does not provide reliability, flow control or error recovery.
- IP provides a routing function that attempts to deliver transmitted messages to their destination.
- These message units in an IP network are called an IP datagram.
- Example: IP, ICMP, IGMP, ARP, and RARP.
Network Interface Layer (Network Access Layer)
- Network Access Layer defines details of how data is physically sent through the network, including how bits are electrically or optically signalled by hardware devices that interface directly with a network medium, such as coaxial cable, optical fiber, or twisted pair copper wire.
- The protocols included in Network Access Layer are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay etc
Difference: OSI Model & TCP/IP Model
| OSI | TCP/IP |
|---|---|
| It has 7 layers | It has 4 layers |
| OSI provides layer functioning and also defines functions of all the layers. | TCP/IP model is more based on protocols and protocols are not flexible with other layers. |
| In the OSI model, the transport layer guarantees the delivery of packets | In the TCP/IP model, the transport layer does not guarantee delivery of packets. |
| Follows horizontal approach | Follows a vertical approach. |
| OSI model has a separate presentation layer | TCP/IP doesn’t have a separate presentation layer |
| OSI is a general model. | TCP/IP model cannot be used in any other application. |
| The network layer of the OSI model provides both connection-oriented and connectionless service. | The Network layer in the TCP/IP model provides connectionless service. |
| OSI model has a problem of fitting the protocols in the model | TCP/IP model does not fit any protocol |
| Protocols are hidden in the OSI model and are easily replaced as the technology changes. | In TCP/IP replacing protocol is not easy. |
| OSI model defines services, interfaces, and protocols very clearly and makes a clear distinction between them. | In TCP/IP, it is not clearly separated its services, interfaces, and protocols |
Network Devices
-
Network devices are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with each other.
-
Network devices like hubs, repeaters, bridges, switches, routers, gateways, and router help manage and direct data flow in a network.
-
They ensure efficient communication between connected devices by controlling data transfer, boosting signals, and linking different networks.
-
Each device serves a specific role, from simple data forwarding to complex routing between networks.
-
Network devices work as a mediator between two devices for transmission of data, and thus play a very important role in the functioning of a computer network.
-
Functions of Network Devices
- Network devices help to send and receive data between different devices.
- Network devices allow devices to connect to the network efficiently and securely.
- Network devices improves network speed and manage data flow better.
- It protects the network by controlling access and preventing threats.
- Expand the network range and solve signal problems.
-
Common Types of Networking Devices:
- Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Routers, Gateway, NIC, Modem
Repeater
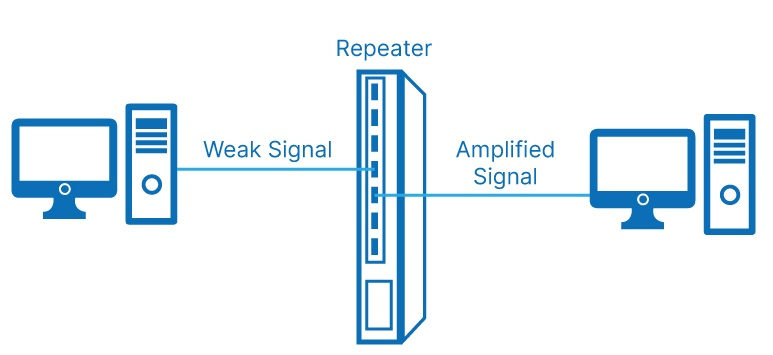
- Description: A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal and retransmits it at a higher power level or to the other side of an obstruction, so the signal can cover longer distances.
- Function: It cleans and strengthens weak or corrupted signals.
- Usage: Used in long-distance communication or in extending LANs.
- OSI Layer: Physical Layer (Layer 1)
- Limitation: Cannot filter or manage data traffic.
Hub
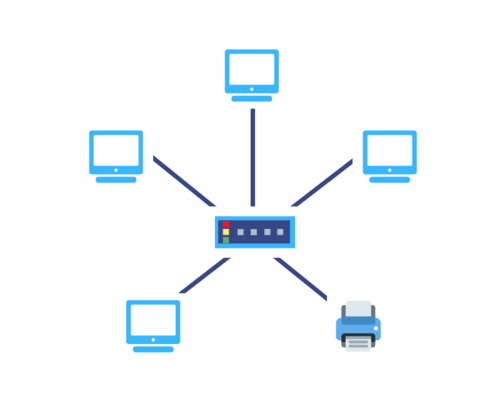
- Description: A hub is a basic networking device that connects multiple computers in a network. It does not manage traffic and simply sends the data it receives to all connected devices.
- Function: Acts as a common connection point in a LAN.
- OSI Layer: Physical Layer (Layer 1)
- Limitation: Causes unnecessary traffic and collisions; not secure or efficient.
Switch
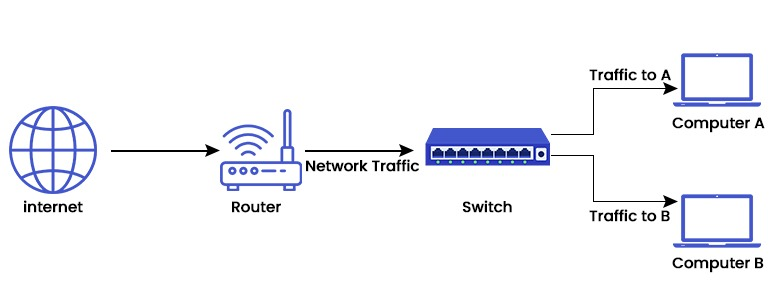
- Description: A switch is a smarter device than a hub. It identifies the MAC address of devices connected to it and sends data only to the correct destination.
- Function: Improves network efficiency by reducing collisions.
- OSI Layer: Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
- Advantage: Offers faster data transfer and better performance in LANs.
Router

- Description: A router is used to connect different networks together and routes data between them using IP addresses
- Function: Connects LAN to the internet and determines the best path for data.
- OSI Layer: Network Layer (Layer 3)
- Smart Features: Supports security, DHCP, NAT, and wireless routing.
Bridge
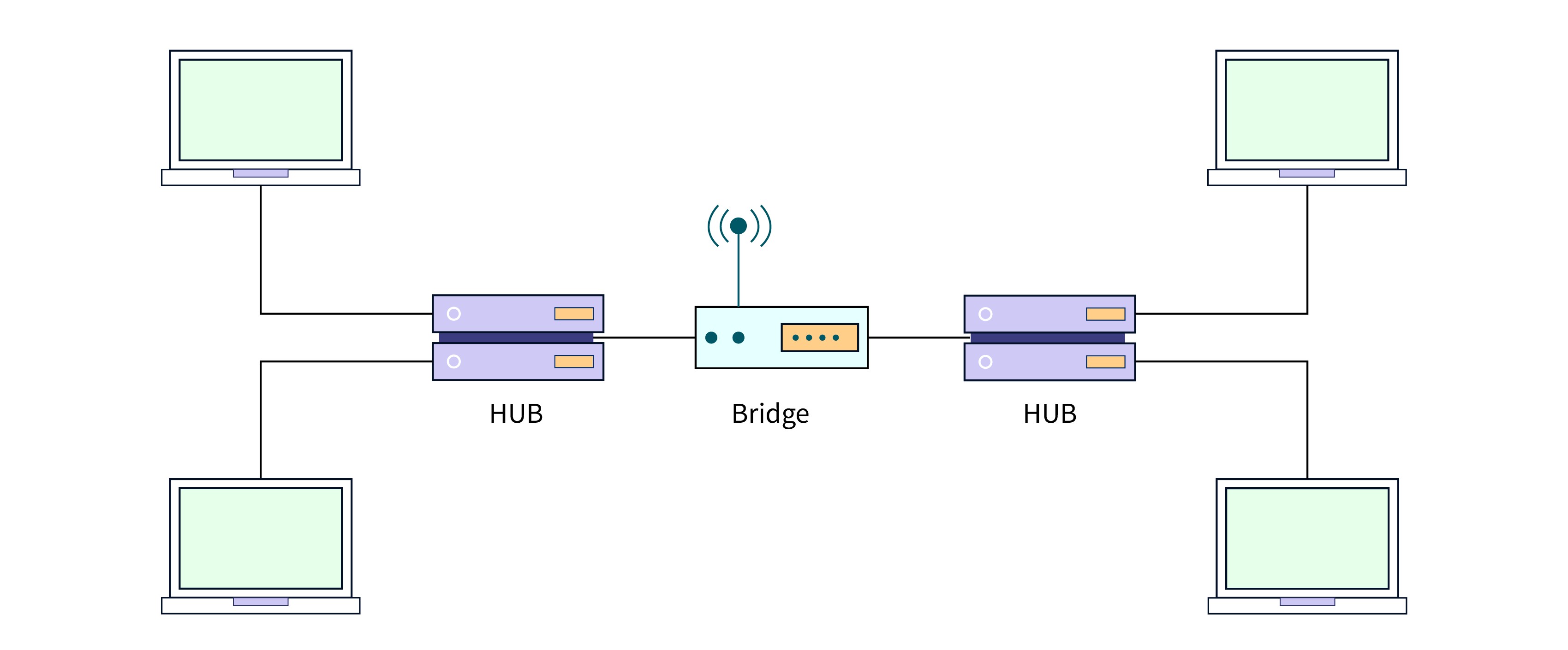
- Description: A bridge connects two or more separate LANs (of the same type) to form a single network.
- Function: Filters traffic using MAC addresses and reduces traffic by dividing collision domains.
- OSI Layer: Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
- Usage: Useful in managing traffic in large LANs.
Gateway
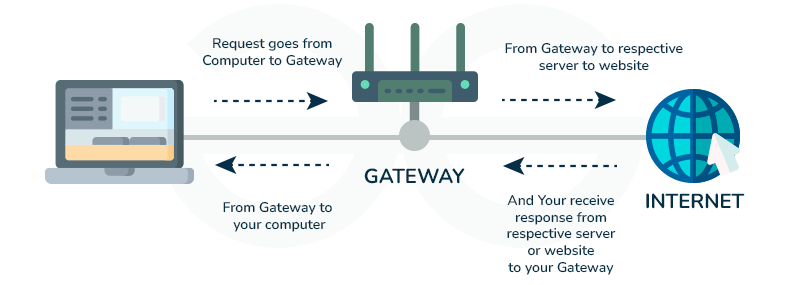
- Description: A gateway connects networks that use different protocols. It translates communication between different architectures or data formats.
- Function: Protocol converter; often used to connect enterprise networks to the internet.
- OSI Layer: Application Layer (Layer 7) and sometimes all layers.
- Example: Connecting a private company network with cloud services.
Modem (Modulator/Demodulator)
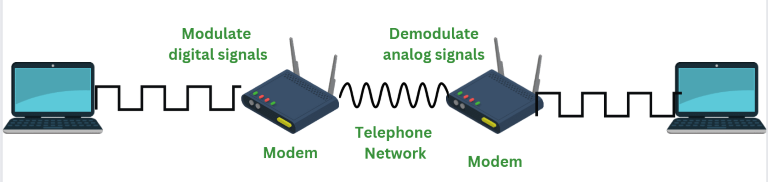
- Description: A modem converts digital data from a computer to analog signals for transmission over telephone lines and vice versa.
- Function: Enables internet access through telephone lines.
- OSI Layer: Physical and Data Link Layer
- Example: DSL or cable modem at home.
Network Interface Card
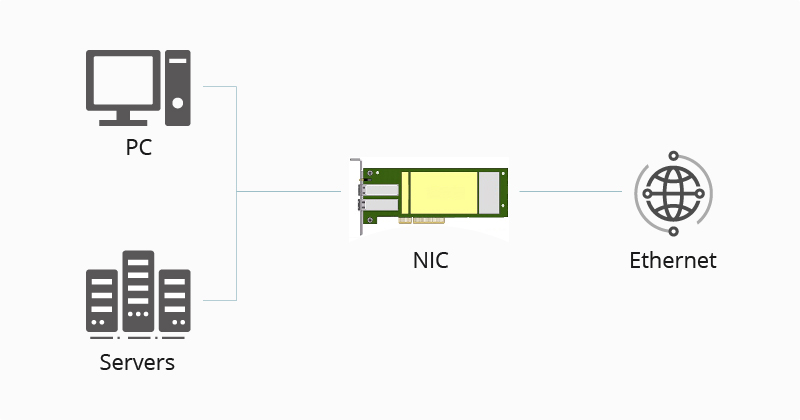
- Network interface card is a network adapter that is used to connect the computer to the network. It is installed in the computer to establish a LAN.
- It has a unique ID that is written on the chip, and it has a connector to connect the cable to it.
- The cable acts as an interface between the computer and the router or modem.
- NIC is a layer 2 device which means that it works on both the physical and data link layers of the network model.
Networks Protocol & Standard
- Protocols and standards are important in computer networks.
- They are like the rules and guidelines that allow different devices and systems to communicate and work together smoothly.
- Protocols define how data is sent, received, and processed, while standards ensure that various technologies are compatible with each other.
- This coordination is critical for the Internet and other networks to function constantly and efficiently.
- Protocol ensures that different technologies and components of the network are compatible with one another, reliable, and able to function together.
- In this article, we are going to discuss every point about protocols and standards in computer networks.
Protocols
-
A protocol is a set of rules that determines how data is transmitted and received over a network. It ensures smooth communication between sender and receiver
- Like a language for devices to talk to each other.
- Used for data formatting, transmission, error handling, and security.
-
Key elements of a protocol:
- Syntax – Format and structure of data (e.g., sender/receiver address, message).
- Semantics – Meaning of each part of the message.
- Timing – When and how fast data should be sent.
- Sequence Control – Ensures correct order of data packets.
- Flow Control – Controls data speed to avoid congestion.
- Error Control – Detects and corrects transmission errors.
- Security – Protects data using encryption and authentication.
-
Types of Protocols:
| Type | Example | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Network Layer | IP, ICMP | Routing and addressing |
| Transport Layer | TCP, UDP | End-to-end delivery |
| Application Layer | HTTPS, FTP, SMTP | App-to-app communication |
| Wireless | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LTE | Wireless data transfer |
| Routing | RIP, OSPF, BGP | Path selection for data |
| Security | SSL, TLS | Secure communication |
| Internet Protocols | IPv4, IPv6 | Unique device addressing |
-
Important Protocols:
- TCP: Reliable data delivery (with error checking).
- IP: Addressing and routing of packets.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Web data transfer (HTTPS is secure).
- FTP: File sharing between computers.
- SMTP: Sending emails.
- DNS: Converts website names into IP addresses.
- DHCP: Auto-assigns IP addresses to devices.
- SSH: Secure remote access.
- SNMP: Manages and monitors network devices.
-
Protocols in Cyber Attacks:
- Hackers misuse protocols (e.g., SYN flood attack on TCP) to overload systems.
- Security tools like Cloudflare help prevent such attacks by managing connections and filtering traffic.
Standards
-
A standard is a set of accepted rules for designing systems and ensuring compatibility between devices.
-
Types of Standards:
- De Facto:
- Means “by fact” or practice
- Not officially approved but widely used (e.g., Apple ecosystem)
- De Jure:
- Means “by law”
- Approved by official bodies like ISO, IEEE, ANSI
- E.g., TCP, IP, HTTP are official standards
- De Facto:
-
Importance of Protocols and Standards in Security:
- Interoperability: Ensures systems/devices can work together.
- Security Baseline: Implements security best practices (encryption, authentication).
- Vulnerability Management: Helps detect and fix network weaknesses.
-
Best Practices for Compliance:
- Use strong encryption tools.
- Perform regular security checks.
- Limit user access to sensitive data zones.
-
Protocols and standards are essential for reliable, secure, and efficient communication in computer networks. Following them ensures compatibility, performance, and protection from cyber threats.
Questions
- Explain with examples: What is a computer network? List any three advantages and two disadvantages of computer networks.
- A company wants to connect two offices located in different cities. Which network type will you suggest (LAN, MAN, WAN)? Justify your answer with reasons and a diagram.
- Compare OSI and TCP/IP models. Why is TCP/IP more commonly used in real-world networks?
- You are tasked with choosing between bus topology and star topology for a college computer lab. Which would you select? Discuss with at least three points considering cost, performance, and reliability.
- Suppose data sent over a network is arriving in the wrong order and some packets are missing. Which elements of a protocol will handle this problem? Explain how.
- Any four networking devices (e.g., hub, switch, router, modem) with their functions and the OSI layer they operate on.