CN-04 Routing, IP Networking & Security
On This Page
IP addressing and subnetting
- An Internet Protocol (IP) address is the unique identifying number assigned to every device connected to the internet. An IP address definition is a numeric label assigned to devices that use the internet to communicate. Computers that communicate over the internet or via local networks share information to a specific location using IP addresses.
- IP addresses have two distinct versions or standards. The Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) address is the older of the two, which has space for up to 4 billion IP addresses and is assigned to all computers. The more recent Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) has space for trillions of IP addresses, which accounts for the new breed of devices in addition to computers. There are also several types of IP addresses, including public, private, static, and dynamic IP addresses. Every device with an internet connection has an IP address, whether it's a computer, laptop, IoT device, or even toys. The IP addresses allow for the efficient transfer of data between two connected devices, allowing machines on different networks to talk to each other.
How does an IP address work?
- An IP address works in helping your device, whatever you are accessing the internet on, to find whatever data or content is located to allow for retrieval.
- Common tasks for an IP address include both the identification of a host or a network, or identifying the location of a device. An IP address is not random. The creation of an IP address has the basis of math. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) allocates the IP address and its creation. The full range of IP addresses can go from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
- With the mathematical assignment of an IP address, the unique identification to make a connection to a destination can be made.
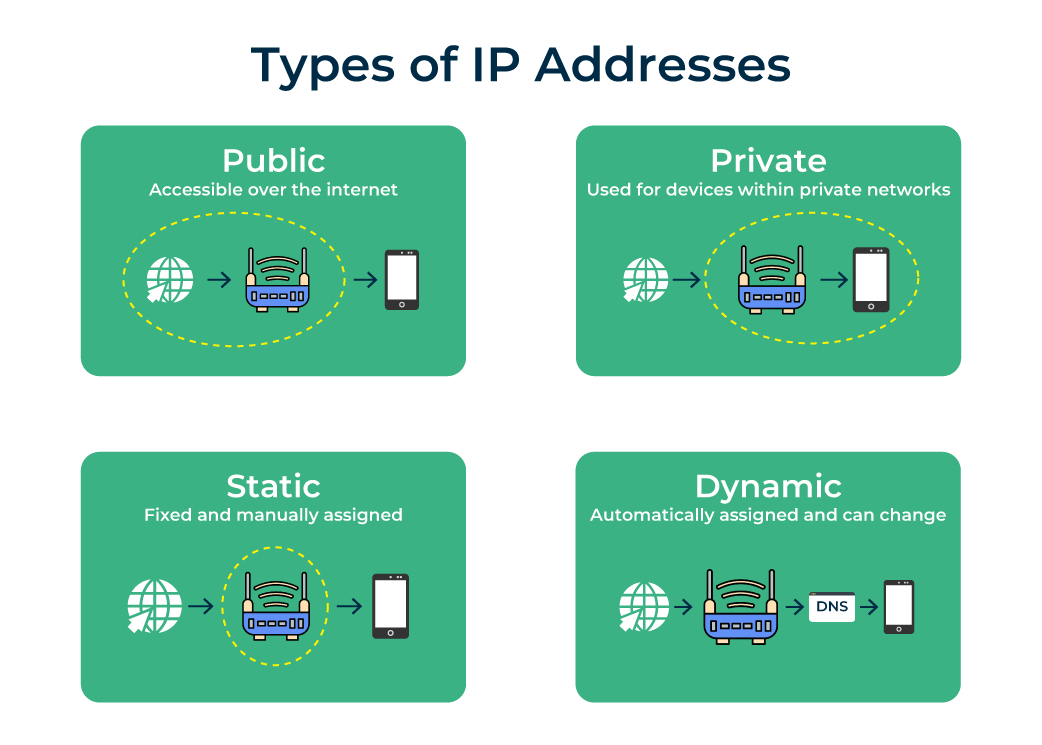
Public IP address
- A public IP address, or external-facing IP address, applies to the main device people use to connect their business or home internet network to their internet service provider (ISP). In most cases, this will be the router. All devices that connect to a router communicate with other IP addresses using the router’s IP address.
- Knowing an external-facing IP address is crucial for people to open ports used for online gaming, email and web servers, media streaming, and creating remote connections.
Private IP address
- A private IP address, or internal-facing IP address, is assigned by an office or home intranet (or local area network) to devices, or by the internet service provider (ISP). The home/office router manages the private IP addresses to the devices that connect to it from within that local network. Network devices are thus mapped from their private IP addresses to public IP addresses by the router.
- Private IP addresses are reused across multiple networks, thus preserving valuable IPv4 address space and extending addressability beyond the simple limit of IPv4 addressing (4,294,967,296 or 2^32).
- In the IPv6 addressing scheme, every possible device has its own unique identifier assigned by the ISP or primary network organization, which has a unique prefix. Private addressing is possible in IPv6, and when it's used it's called Unique Local Addressing (ULA).
Static IP address
- All public and private addresses are defined as static or dynamic. An IP address that a person manually configures and fixes to their device’s network is referred to as a static IP address. A static IP address cannot be changed automatically. An internet service provider may assign a static IP address to a user account. The same IP address will be assigned to that user for every session.
Dynamic IP address
- A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned to a network when a router is set up. The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) assigns the distribution of this dynamic set of IP addresses. The DHCP can be the router that provides IP addresses to networks across a home or an organization.
- Each time a user logs into the network, a fresh IP address is assigned from the pool of available (currently unassigned) IP addresses. A user may randomly cycle through several IP addresses across multiple sessions.
What Is IPv4?
- IPv4 is the fourth version of the IP. It is one of the core protocols of the standards-based methods used to interconnect the internet and other networks. The protocol was first deployed on the Atlantic Packet Satellite Network (SATNET), which was a satellite network that formed a segment of the initial stages of the internet, in 1982. It is still used to route most internet traffic despite the existence of IPv6.
- IPv4 is currently assigned to all computers. An IPv4 address uses 32-bit binary numbers to form a unique IP address. It takes the format of four sets of numbers, each of which ranges from 0 to 255 and represents an eight-digit binary number, separated by a period point.
IP Address Classes
-
Some IP addresses are reserved by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). These are typically reserved for networks that carry a specific purpose on the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which is used to interconnect devices. Four of these IP address classes include:
- 0.0.0.0: This IP address in IPv4 is also known as the default network. It is the non-routable meta-address that designates an invalid, non-applicable, or unknown network target.
- 127.0.0.1: This IP address is known as the loopback address, which a computer uses to identify itself regardless of whether it has been assigned an IP address.
- 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.254.254: A range of addresses that are automatically assigned if a computer is unsuccessful in an attempt to receive an address from the DHCP.
- 255.255.255.255: An address dedicated to messages that need to be sent to every computer on a network or broadcasted across a network.
-
Further reserved IP addresses are for what is known as subnet classes. Subnetworks are small computer networks that connect to a bigger network via a router. The subnet can be assigned its own IP address system, so that all devices connecting to it can communicate with each other without having to send data via the wider network.
-
The router on a TCP/IP network can be configured to ensure it recognizes subnets, then route the traffic onto the appropriate network. IP addresses are reserved for the following subnets:
- Class A: IP addresses between 10.0.0.0 and 10.255.255.255
- Class B: IP addresses between 172.16.0.0 and 172.31.255.255
- Class C: IP addresses between 192.186.0.0 and 192.168.255.255
- Class D or multicast: IP addresses between 224.0.0.0 and 239.255.255.255
- Class E, which are reserved for experimental usage: IP addresses between 240.0.0.0 and 254.255.255.254
-
IP addresses listed under Class A, Class B, and Class C are most commonly used in the creation of subnets. Addresses within the multicast or Class D have specific usage rules outlined in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) guidelines, while the release of Class E addresses for public use was the cause of plenty of debate before the IPv6 standard was introduced.
Internet Addresses and Subnets
- The IANA reserves specific IP address blocks for commercial organizations, government departments, and ISPs. When a user connects to the internet, their ISP assigns them an address from within one of the blocks assigned to it. If they only go online from one computer, then they can use the address assigned to it by their ISP.
- However, most homes now use routers that share a network connection with multiple devices. So if a router is used to share the connection, then the ISP assigns the IP address to the router, and then a subnet is created for all computers that connect to it.
- IP addresses that fall within a subnet have a network and a node. The subnet is identified by the network. The node, also known as the host, connects to the network and needs its own address. Computers separate the network and node via a subnet mask, which filters the appropriate IP address designation. When a large network is set up, the subnet mask that best fits the number of nodes or subnets required is determined.
- When it comes to IP addresses within a subnet, the first address is reserved for the subnet, and the final one indicates the broadcast address for the subnet’s systems.
IPv4 vs IPv6
- IPv4 has not been able to cope with the massive explosion in the quantity and range of devices beyond simply mobile phones, desktop computers, and laptops. The original IP address format was not able to handle the number of IP addresses being created.
- To address this problem, IPv6 was introduced. This new standard operates a hexadecimal format that means billions of unique IP addresses can now be created. As a result, the IPv4 system that could support up to around 4.3 billion unique numbers has been replaced by an alternative that, theoretically, offers unlimited IP addresses.
- That is because an IPv6 IP address consists of eight groups that contain four hexadecimal digits, which use 16 distinct symbols of 0 to 9 followed by A to F to represent values of 10 to 15.
5 ways to protect your IP address
- There are multiple ways to protect your IP address from cybercriminals. Some of these options include:
- Use a VPN
- Make use of a proxy server
- Have your ISP make use of dynamic IP addresses
- Employ a NAT firewall to hide your private IP address
- Resetting your modem may change your IP address
Subnetting
- Subnetting is a method of dividing a single physical network into logical subnetworks (subnets). Subnetting allows a business to expand its network without requiring a new network number from its Internet service provider. Subnetting helps to reduce the network traffic and also conceals network complexity. Subnetting is necessary when a single network number must be assigned to several portions of a local area network (LAN).
- A subnet, sometimes known as a subnetwork, is a part of a larger network. Subnets are the logical division of an IP network into many smaller network parts. To reduce traffic, a subnet’s purpose is to divide a huge network into a collection of smaller, interconnected networks. Subnets eliminate the need for traffic to pass through extraneous routs, resulting in faster network speeds. Subnets were created to alleviate the shortage of IP addresses on the internet. The purpose of subnetting is to establish a computer network that is quick, efficient, and robust. As networks grow in size and complexity, traffic must find more efficient pathways. Bottlenecks and congestion would arise if all network traffic traveled across the system at the same time, utilizing the same path, resulting in slow and wasteful backlogs. By creating a subnet, you can limit the number of routers that network traffic must pass through.
Use of Subnetting
- Large enterprises looking to expand technologically need to know how to organize a network efficiently. IP addresses can be kept geographically confined, allowing a subnet to be used to preserve efficiency and order. Let’s look at some of the major motivations for using subnetting.
- Reallocating IP Addresses:- A limited number of host allocations are available for each class; for example, networks with more than 254 devices require a Class B allocation. Suppose a network administrator works with a Class B or C network and needs to allocate 150 hosts across three physical networks in three different cities. In that case, they must either request more address blocks for each network or divide the network into subnets that allow administrators to use one block of addresses across multiple physical networks.
- Improves Network Speed:- Subnetting divides the large network into small subnets, and the purpose of these subnets is to divide a huge network into a collection of smaller, interconnected networks to reduce traffic. Subnets eliminate the need for traffic to pass through extraneous routs, resulting in faster network speeds.
- Improving Network Security:- Subnetting helps network administrators to reduce network-wide threats by quarantining compromised areas of the network and making it more complex for trespassers to travel throughout an organization’s network.
- Reliving Network Congestion:- If a large portion of an organization’s traffic is intended to be shared regularly across a group of computers, putting them all on the same subnet can help reduce network traffic. Without a subnet, data packets from every other computer on the network would be visible to all computers and servers.
- Efficiency:- Subnetting is used to simplify network traffic by eliminating the need for additional routers. This ensures that the data being sent can move as quickly as possible to its destination, avoiding any potential detours that can slow it down.
Work of Subnetting
- As we all know, subnetting divides the network into small subnets. Routers are used to communicate between subnets, whereas each subnet allows its linked devices to communicate with each other. The size of a subnet is determined by the network technology used and the connection needs. Within the restrictions of the address space available for its usage, each organization is responsible for determining the number and size of the subnets it generates. Let’s understand how subnetting splits a network into subnets.
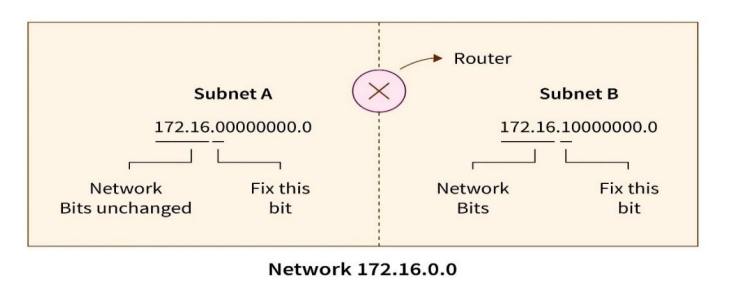
- A Network Prefix (also known as the Network ID) and a Host ID are the two fields that make up an IP address. Whether the Network Prefix and the Host ID are separated depends on whether the address is Class A, B, or C. The figure given below shows a 172.16.37.5 IPv4 Class B address. The Host ID is 37.5, and the Network Prefix is 172.16.0.0.
- Now, we generally fix MSB(Most Significant Bit) bits of the Host ID to generate the subnets. In the figure below, we fix one of the host’s MSB(Most Significant Bit) bits to generate two network subnets. We cannot change network bits because if we change network bits, the whole network is changed.
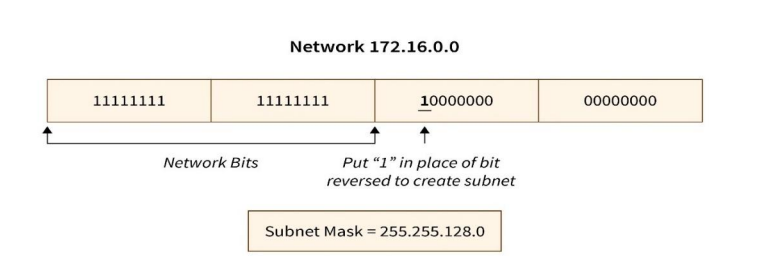
- To identify a subnet, we need a subnet mask which is calculated by putting ‘1’ in place of all Network ID bits and the number of bits we reserve in Host ID to generate the subnet. The subnet mask aims to route the data packet from the internet to its desired subnet network. A subnet mask also specifies which portion of an address should be utilized as the Subnet ID. A binary AND operation is used to apply the subnet mask to the whole network address. AND operations work by assuming that output is “true” if both inputs are “true.” Otherwise, “false” is returned. Only when both bits are 1.
This yields the Subnet ID. Routers use the Subnet ID to find the optimum path between subnetworks.
- If we want to generate variable-length subnets, then we apply permutations on the number of bits reserved to create subnets. This subnetting is called Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM).
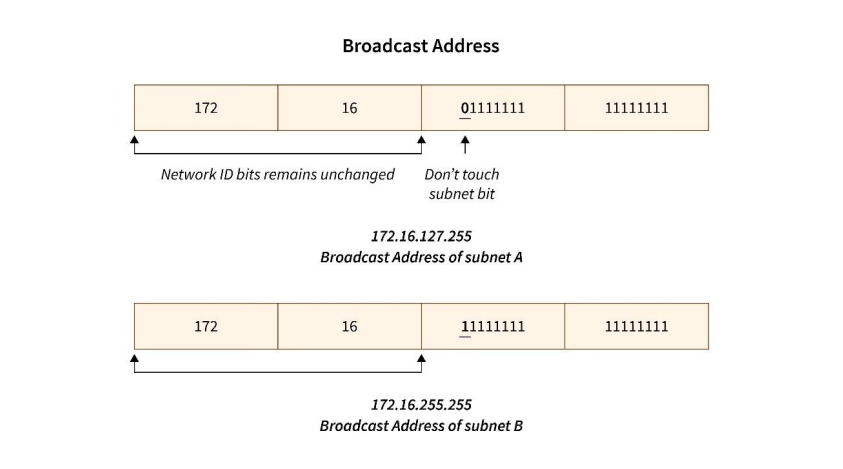
- The broadcast address of a subnet is calculated by making all the remaining bits as‘1’of Host Id after having some bits reserved to represent the subnet. The broadcast address is used to broadcast the message to all the network hosts.
Advantages of Subnetting
- Subnetting divides broadcast domains, allowing data to be routed more efficiently, and boosting network performance and speed.
- We can subnet a single large network into smaller networks via subnetting. It is simple to handle small networks.
- Subnetting enhances the network’s overall performance by removing redundant traffic.
- Subnetting reduces the requirement of an IP range.
- Subnets prevent devices from accessing the whole network, allowing businesses to control which gear and users have access to more sensitive data. It is possible to improve network security.
Disadvantages of Subnetting
- Subnetting increases the network’s complexity. An experienced network administrator must manage the subnetted network.
- More subnets mean more IP addresses are wasted because each subnet has its own network address and broadcast address.
- As we increase more subnets in the network, we require more routers which increases the overall cost and makes the maintenance process challenging.
- Subnetting necessitates the purchase of expensive internal routers, switches, hubs, and bridges, among other items, which increases the overall network cost.
We use subnetting because it now becomes challenging to send a data packet to the machine you want on that network. Subnetting is a method of dividing a single physical network into logical sub-networks (subnets).
Subnetting is aimed to achieve the following targets in the network. - Reallocating IP Addresses - Improving Network Security - Reliving Network Congestion - Improves Network Speed - Efficiency
- A subnet, sometimes known as a subnetwork, is a part of a larger network and its purpose is to divide a huge network into a collection of smaller, interconnected networks to reduce traffic. The subnet mask aims to route the data packet from the internet to its desired subnet network.
IPv4 And IPv6
- IP stands for Internet Protocol version v4 stands for Version Four (IPv4), is the most widely used system for identifying devices on a network. It uses a set of four numbers, separated by periods (like 192.168.0.1), to give each device a unique address. This address helps data find its way from one device to another over the internet.
- IPv4 was the primary version brought into action for production within the ARPANET in 1983. IP version four addresses are 32-bit integers which will be expressed in decimal notation. Example- 192.0.2.126 could be an IPv4 address.
Understanding IPv4 Addressing
- An IPv4 address consists of series of four eight-bit binary numbers which are separated by decimal point. Although any numbering system can be used to represent a unique 32- bit number, most commonly you see IP address expressed in dot decimal notation. Some of the examples are :
| Site | Dot-decimal | Binary |
|---|---|---|
| Twitter.com | 104.244.42.129 | 01101000.11110100.00101010.10000001 |
| Reddit.com | 151.101.65.140 | 10010111.01100101.01000001.10001100 |
| Linkedin.com | 108.174.10.10 | 01101100.10101110.00001010.00001010 |
IPv4 Address Format
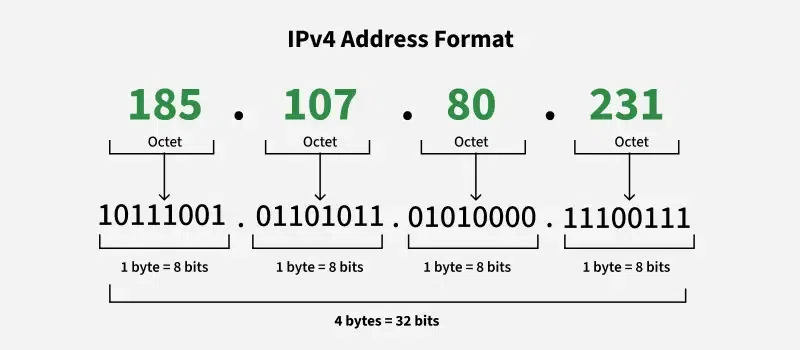
- An IPv4 address consists of 32 bit (binary digit), grouped into four section of known as octets or bytes. Each octet has 8 bits and this bits can be represented only in 0 or 1 form, and when they grouped together, they form a binary number. Since each octet has 8 bits, it can represent 256 numbers ranging from o to 255. These four octets are represented as decimal numbers, separated by periods known as dotted decimal notation. For example IPv4 address 185.107.80.231 consists of four octets.
Binary Representation
- IPv4 is basically converted into binary form by computer although these are usually seen in decimal form for human readability. Each octet is converted into 8 bit binary number . For instance 185.107.80.231 in binary looks like:
- 185: 10111001
- 107: 01101011
- 80: 01010000
- 231: 11100111
- So 185.107.80.231 in binary is: 10111001.01101011.01010000.11100111
Parts of IPv4
IPv4 addresses consist of three parts:
- Network Part: The network part indicates the distinctive variety that's appointed to the network. The network part conjointly identifies the category of the network that's assigned.
- Host Part: The host part uniquely identifies the machine on your network. This part of the IPv4 address is assigned to every host. For each host on the network, the network part is the same, however, the host half must vary.
- Subnet Number: This is the non obligatory part of IPv4. Local networks that have massive numbers of hosts are divided into subnets and subnet numbers are appointed to that.
Types of IPv4 Addressing
IPv4 basically supports three different types of addressing modes:
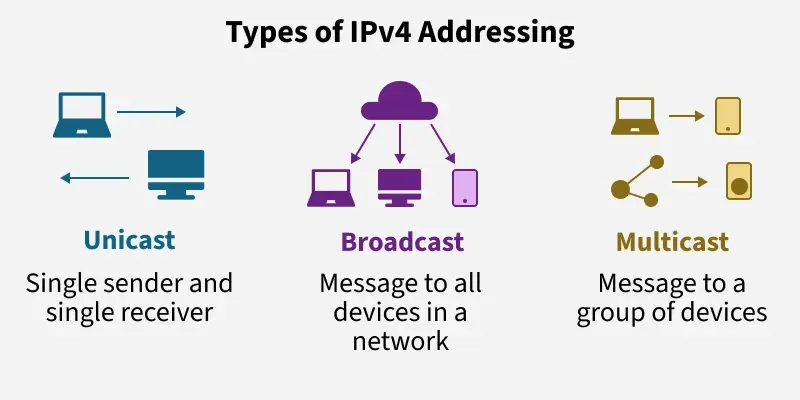
- Unicast Addressing Mode: This addressing mode is used to specify single sender and single receiver. Example: Accessing a website.
- Broadcast Addressing Mode: This addressing mode is used to send messages to all devices in a network. Example: sending a message in local network to all the devices.
- Multicast Addressing Mode: This addressing mode is typically used within a local network or across networks and sends messages to a group of devices. Example: Streaming audio to multiple devices at once.
IPv4 Datagram Header
These fields together ensure the proper delivery, routing, fragmentation, and reassembly of IP packets across the network.
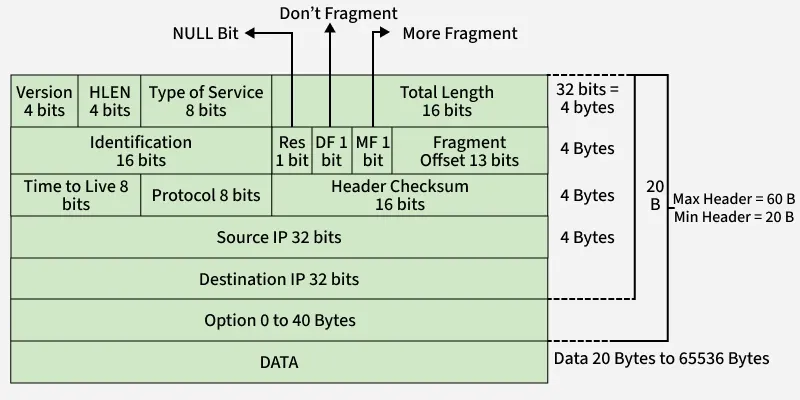
- VERSION: Version of the IP protocol (4 bits), which is 4 for IPv4
- HLEN: IP header length (4 bits), which is the number of 32 bit words in the header. The minimum value for this field is 5 and the maximum is 15.
- Type of service: Low Delay, High Throughput, Reliability (8 bits)
- Total Length: Length of header + Data (16 bits), which has a minimum value 20 bytes and the maximum is 65,535 bytes.
- Identification: Unique Packet Id for identifying the group of fragments of a single IP datagram (16 bits)
- Flags: 3 flags of 1 bit each : reserved bit (must be zero), do not fragment flag, more fragments flag (same order)
- Fragment Offset: Represents the number of Data Bytes ahead of the particular fragment in the particular Datagram. Specified in terms of number of 8 bytes, which has the maximum value of 65,528 bytes.
- Time to live: Datagram’s lifetime (8 bits), It prevents the datagram to loop through the network by restricting the number of Hops taken by a Packet before delivering to the Destination.
- Protocol: Name of the protocol to which the data is to be passed (8 bits)
- Header Checksum: 16 bits header checksum for checking errors in the datagram header
- Source IP address: 32 bits IP address of the sender
- Destination IP address: 32 bits IP address of the receiver
- Option: Optional information such as source route, record route. Used by the Network administrator to check whether a path is working or not.
Characteristics of IPv4
- IPv4 could be a 32-bit IP Address.
- IPv4 could be a numeric address, and its bits are separated by a dot.
- The number of header fields is twelve and the length of the header field is twenty.
- It has Unicast, broadcast, and multicast-style addresses.
- IPv4 supports VLSM (Virtual Length Subnet Mask).
- IPv4 uses the Post Address Resolution Protocol to map to the MAC address.
- RIP may be a routing protocol supported by the routed daemon.
- Networks ought to be designed either manually or with DHCP.
- Packet fragmentation permits from routers and causes host.
Advantages of IPv4
- IPv4 security permits encryption to keep up privacy and security.
- IPV4 network allocation is significant and presently has quite 85000 practical routers.
- It becomes easy to attach multiple devices across an outsized network while not NAT.
- This is a model of communication so provides quality service also as economical knowledge transfer.
- IPV4 addresses are redefined and permit flawless encoding.
- IPv4 has high System Management prices and it's labor-intensive, complex, slow & prone to errors.
- Routing is scalable and economical as a result of addressing its collective more effectively.
- Data communication across the network becomes a lot of specific in multicast organizations.
Limitations of IPv4
- IP relies on network layer addresses to identify end-points on the network, and each network has a unique IP address.
- The world's supply of unique IP addresses is dwindling, and they might eventually run out theoretically.
- If there are multiple hosts, we need the IP addresses of the next class.
- Complex host and routing configuration, non-hierarchical addressing, difficult to renumbering addresses, large routing tables, non-trivial implementations in providing security, QoS (Quality of Service), mobility, and multi-homing, multicasting, etc. are the big limitations of IPv4 so that's why IPv6 came into the picture.
IPv6
- The next generation Internet Protocol (IP) address standard, known as IPv6, is meant to work in cooperation with IPv4. To communicate with other devices, a computer, smartphone, home automation component, Internet of Things sensor, or any other Internet-connected device needs a numerical IP address.
- Because so many connected devices are being used, the original IP address scheme, known as IPv4, is running out of addresses. This new IP address version is being deployed to fulfil the need for more Internet addresses. With 128-bit address space, it allows 340 undecillion unique address space. IPv6 support a theoretical maximum of 340, 282, 366, 920, 938, 463, 463, 374, 607, 431, 768, 211, 456.
Representation of IPv6
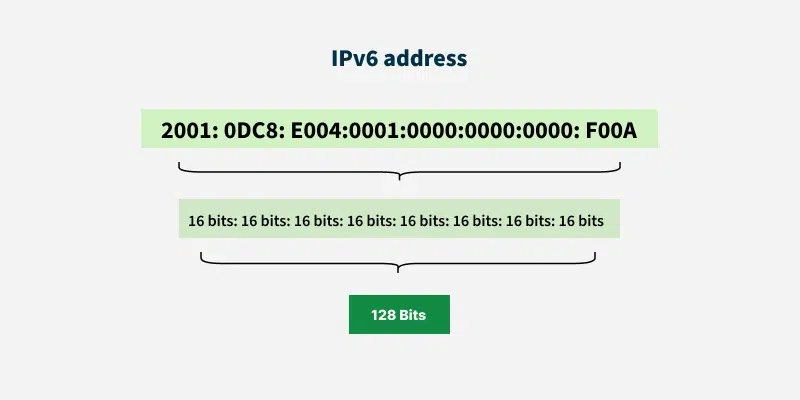
- An IPv6 address consists of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by ' . ' and each Hex digit representing four bits so the total length of IPv6 is 128 bits. Structure given below.
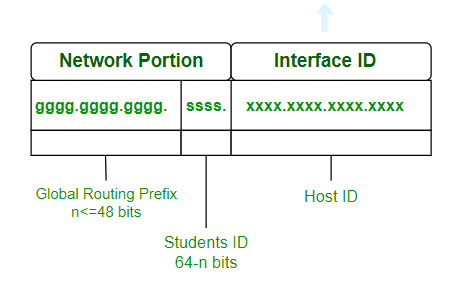
gggg.gggg.gggg.ssss.xxxx.xxxx.xxxx.xxxx
The first 48 bits represent Global Routing Prefix. The next 16 bits represent the student ID and the last 64 bits represent the host ID. The first 64 bits represent the network portion and the last 64 bits represent the interface id.
- Global Routing Prefix: The Global Routing Prefix is the portion of an IPv6 address that is used to identify a specific network or subnet within the larger IPv6 internet. It is assigned by an ISP or a regional internet registry (RIR).
- Student Id: The portion of the address used within an organization to identify subnets. This usually follows the Global Routing Prefix.
- Host Id: The last part of the address, is used to identify a specific host on a network.
Example: 3001:0da8:75a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
Types of IPv6 Address
Now that we know about what is IPv6 address let’s take a look at its different types.
- Unicast Addresses : Only one interface is specified by the unicast address. A packet moves from one host to the destination host when it is sent to a unicast address destination.
- Multicast Addresses: It represents a group of IP devices and can only be used as the destination of a datagram.
- Anycast Addresses: The multicast address and the anycast address are the same. The way the anycast address varies from other addresses is that it can deliver the same IP address to several servers or devices. Keep in mind that the hosts do not receive the IP address. Stated differently, multiple interfaces or a collection of interfaces are assigned an anycast address.
Difference between IPv6 and IPv4
- IPv6 was developed to overcome the limitations of IPv4, offering more address space, simplified headers, and improved efficiency.

| Feature | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| Address Length | 32-bit address | 128-bit address |
| Address Format | Decimal format (e.g., 192.168.0.1) | Hexadecimal format (e.g., 2001:0db8::1) |
| Configuration | Manual and DHCP configuration | Auto-configuration and renumbering supported |
| Connection Integrity | End-to-end integrity is unachievable | End-to-end integrity is achievable |
| Security | No built-in security; external tools like IPSec needed | IPSec is built-in for encryption and authentication |
| Fragmentation | Performed by sender and routers | Performed only by the sender |
| Flow Identification | Not available | Uses Flow Label field in header for packet flow identification |
| Checksum Field | Present | Not present |
| Transmission Scheme | Supports broadcast | Uses multicast and anycast; no broadcast |
| Header Size | Variable: 20–60 bytes | Fixed: 40 bytes |
| Conversion | Can be converted to IPv6 | Not all IPv6 addresses can be converted to IPv4 |
| Field Structure | 4 fields separated by dots (.) | 8 fields separated by colons (:) |
| Address Classes | Has address classes (A, B, C, D, E) | No concept of address classes |
| VLSM Support | Supports Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) | Does not support VLSM |
| Example | 66.94.29.13 | 2001:0000:3238:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:FEFB |
Advantages
- Faster Speeds: IPv6 supports multicast rather than broadcast in IPv4.This feature allows bandwidth-intensive packet flows (like multimedia streams) to be sent to multiple destinations all at once.
- Stronger Security: IPSecurity, which provides confidentiality, and data integrity, is embedded into IPv6.
- Routing efficiency
- Reliability
- Most importantly it's the final solution for growing nodes in Global-network.
- The device allocates addresses on its own.
- Internet protocol security is used to support security.
- Enable simple aggregation of prefixes allocated to IP networks; this saves bandwidth by enabling the simultaneous transmission of large data packages.
Disadvantages
- Conversion: Due to widespread present usage of IPv4 it will take a long period to completely shift to IPv6.
- Communication: IPv4 and IPv6 machines cannot communicate directly with each other.
- Not Going Backward Compatibility: IPv6 cannot be executed on IPv4-capable computers because it is not available on IPv4 systems.
- Conversion Time: One significant drawback of IPv6 is its inability to uniquely identify each device on the network, which makes the conversion to IPV4 extremely time consuming.
- Cross-protocol communication is forbidden since there is no way for IPv4 and IPv6 to communicate with each other.
Routing algorithms
Routing Protocol
- Routed Protocol: A Routed Protocol is a computer network protocol that can be used to send the user data from one network to another network. Routed Protocol carries user traffic such as e-mails, file transfers, web traffic etc.
- Routed protocols use an addressing system (example IP Address) which can address a particular network and a host (a computer, server, network printer etc.) inside that network. In other words, the address which is used by a Routed Protocol (Example IP (Internet Protocol)) has a network address part and a host (a computer inside a network) part.
- IP (Internet Protocol) is the most widely used Routed Protocol. Internet is using IP (IPv4 or IPv6) as its Routed Protocol. A Routed Protocol is an integral part of network protocol suit (such as TCP/IP protocol suit) and is supported by the networking devices (such as routers, switches, and host computers) participating in routing the user traffic.
- Routing Protocol : A Routing Protocol learns routes (path) for forwarding a Routed Protocol such as IP (Internet Protocol), IPX (Internetwork Packet Exchange) and AppleTalk. Routing Protocols are network protocols used to dynamically advertise and learn the networks connected, and to learn the routes (network paths) which are available. Routing protocols running in different routers exchange updates between each other and most efficient routes to a destination. Routing Protocols maintain routing tables that contain paths to a destination network node computed according to routing algorithms. Routing Protocols normally run only in Routers, Layer 3 Switches, End devices (firewalls) or Network Servers with Network Operating Systems. Routing Protocols are not available in a user computer.
- Examples of Routing Protocols are RIP (Routing Information Protocol) , EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First).
Routing protocol types
There are broadly three types of routing protocols:
- Distance Vector (Number of hops): Distance vector routing determines the direction (vector) and distance to any link in the inter-network. Typically, the smaller the metric, the better the path. Examples of distance vector protocols are RIP and IGRP. Distance vector routing is useful for smaller networks. The limitation is that any route which is greater than 15 hops is considered unreachable. One important thing that differentiates distance vector with Link state is that distance vector listens to second hand information to learn routing tables whereas, Link state builds its routing tables from first hand information. Distance vector algorithms call for each router to send its entire routing table to each of its adjacent neighbors.
-
Link State Routing: Link State algorithms are also known as Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithms. SPF recreates the exact topology of the entire network for route computation by listening at the first hand information. Link State takes bandwidth into account using a cost metric. Link State protocols only send updates when a change occurs, which makes them more attractive for larger networks. Bandwidth and delay are the most heavily weighed parts of the metric when using Link-State protocols. EX: OSPF and NLSP.
Benefits of Link State protocols:
- Allows for a larger scalable network
- Reduces convergence time
- Allows "supernetting"
- Balanced Hybrid: Balanced Hybrid combines some aspects of Link State and Distance Vector routing protocols. Balanced Hybrid uses distance vectors with more accurate metrics to determine the best paths to destination networks. EX: EIGRP.
Static and Default route
- Static Routes: Configured by the administrator manually. The administrator must also update the table manually every time a change to the network takes place. Static routes are commonly used when routing from a network to a stub (a network with a single route) network. A static route adds an entry to the routing table for a specific destination IP address or subnet.
- Default Routes: The default route (gateway of last resort) is used when a route is not known or is infeasible. Default route is used when there is no other known route to a given IP packet's destination. Default route is also known as gateway of last resort.
- Dynamic Routes: As soon as dynamic routing is enabled, the routing tables are automatically updated. Dynamic routing uses broadcasts and multicasts to communicate with other routers. Each route entry includes a subnet number, the interface out to that subnet, and the IP address of the next router that should receive the packet.
Distance vector and link-state routing protocols
- "Distance Vector" and "Link State" are terms used to describe routing protocols which are used by routers to forward packets between networks. The purpose of any routing protocol is to dynamically communicate information about all network paths used to reach a destination and to select from those paths, the best path to reach a destination network. The terms distance vector and link state are used to group routing protocols into two broad categories based on whether the routing protocol selects the best routing path based on a distance metric (the distance) and an interface (the vector), or selects the best routing path by calculating the state of each link in a path and finding the path that has the lowest total metric to reach the destination.
- Distance vector routing: In distance vector routing, a router need not know the entire path to every network segment, it only requires to know the direction or vector in which to send the packet. The technique determines the direction (vector) and distance (hop count) to any network in the internetwork. Distance vector routing algorithms periodically send all or parts of their routing table to their adjacent neighbors. The routers running a distance vector routing protocol will automatically send periodic updates even if there are no changes in the network. RIP and EIGRP is a commonly used distance vector protocol that uses hop counts or its routing metrics.
- Link-state routing: In link-state routing, each router attempt to construct its own internal map of the network topology. At the initial stage of start-up, when a router becomes active, it sends the messages into the network and collects the information from the routers to which it is directly connected. It also provides the information about whether the link to reach the router is active or not. This information is used by other routers to build a map of network topology. Then the router uses the map to choose the best path. OSPF protocol is the example for link state routing.
Difference between Distance-vector and Link-state
Distance vector:
- It uses Bellman Ford algorithm for calculating the shortest cost path.
- Each router periodically sends information to each of its neighbors.
- As the packet travels one node to another towards destination, a cost is incurred. In case of RIP, the cost relates to the hop count.
- It is decentralized routing algorithm.
- RIP is an example protocol, which follows the distance vector routing.
- It needs less CPU utilization and less memory space compare than Link state.
Link-state:
- It uses dijkstras algorithm for calculating the shortest path.
- Each router building up the complete topology of the entire internetwork, thus each router contains the same information.
- Link-state is also known as the shortest path first.
- OSPF, BGP and EGP are the examples for link state.
- It needs more CPU utilization and more memory space compare than Distance vector.
ICMP
Introduction
- The Internet is a web of interconnected devices that communicate using protocols. One such protocol is the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), which helps network devices diagnose communication issues. ICMP protocol plays a significant role in determining whether the data is reaching its intended destination on time or not. Typically, routers and other network devices utilize the ICMP protocol. It does not carry your actual data, like an email or a webpage. Instead, its only job is to deliver messages about the connection status. In this blog, we will mainly focus on what ICMP in computer networks is, its history, purpose, and how it works, and last, we will look into how ICMP is used in DDoS attacks.
What is ICMP Protocol?
- ICMP or Internet Control Message Protocol is a kind of protocol that operates at the network layer on top of the Internet Protocol (IP). IP handles the transportation of data packets between sources and destinations, whereas ICMP is responsible for transmitting control and error messages among network devices. For instance, if a router encounters an issue while forwarding an IP packet, it can utilize ICMP to send an error message to the source host. Similarly, if a host wishes to assess connectivity or latency with another host, it can employ ICMP to transmit an echo request and await an echo reply.
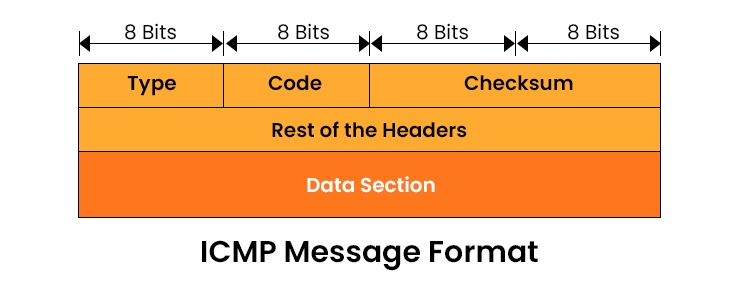
- ICMP messages are enclosed within IP datagrams. This means they consist of an IP header followed by an ICMP header and accompanying data. The ICMP header contains two fields: type and code. The type field specifies the purpose of the message (echo request, echo reply, destination time exceeded). On the other hand, the code field provides information about the message type (e.g., reason for error or query subtype).
Now that we have a basic understanding of ICMP protocol, let’s discuss its history.
History of ICMP
- ICMP came into action in 1981 as part of the TCP/IP suite of protocols as defined in RFC 792. Its purpose was to offer feedback regarding communication issues and assist tools, like ping and traceroute. Initially meant for IPv4, the fourth version of IP. A newer version of ICMP, also known as ICMPv6 (defined in RFC 4443), came into action with the introduction of IPv6, the sixth version of IP, in 1998. ICMPv6 differs from ICMPv4 by employing message types and codes. It supports IPv6 features like fragmentation and neighbor discovery and integrates security measures such as IPsec.
Used Of ICMP
-
ICMP serves various purposes in computer networks: error reporting, querying, and Performing Network Diagnostics.
-
Error reporting is used to notify hosts or routers about issues that arise during the transmission of IP packets. For instance, if a router cannot find a route to the intended destination host, it can send an ICMP message indicating that the destination is unreachable back to the source host. This helps the source host become aware of the problem and either halt transmissions or explore routes.
-
Querying, on the other hand, it is employed to request or provide information regarding the status or configuration of hosts or routers. Let’s say a host wants to determine the round-trip time or hop count to another host; it can send an ICMP message requesting an echo. Wait for an ICMP reply carrying that echo. This enables the host to measure latency or trace its route to reach its intended destination.
-
Performing Network Diagnostics By offering feedback and diagnostic functions, ICMP helps overcome the limitations of IP. For example, IP lacks a built-in mechanism for sending error or control messages as reliable delivery service and congestion control mechanisms. By utilizing ICMP, network devices are able to communicate errors, queries, and congestion information without relying on higher-layer protocols like TCP or UDP. Further, this can help in determining the sources for network delay.
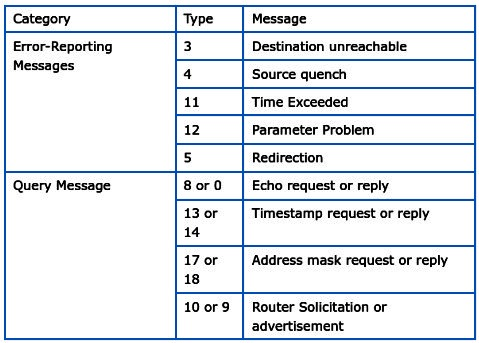
Types of ICMP Messages
Here are the various types of ICMP Protocol messages –
- Information Messages: In information messages, the sender shares a question with the host, or we can say router and expect a reply. In other words, the host wants to know whether the router is active or not.
- Error-reporting message: This means that when the router encounters a problem while processing an IP packet, it reports a message.
- Query messages: Query messages allow a router or network administrator to learn specific information from another host or router.
- Source Mitigation: It appeals to reduce the traffic rate of messages shared from the source to the router (destination).
- Time Exceeded: The fragments held by the router will be released when the fragments disappear in the network, and then ICMP will receive the source IP from the rejected packet. This provides information to the source that the datagram has been rejected as the live field time reaches zero, by sending time exceeded message.
- Fragmentation Required: The Don’t Fragment (DF) bit is adjusted when a route is unable to forward a datagram because it exceeds the MTU of the next hop. The router is required to respond to the ICMP Destination Unreachable message via a code at the source of the datagram, which requires fragmentation and a DF (Don’t Fragment) adjustment.
- Destination Unreachable: This message shows an error i.e. the destination, network or port number mentioned in the IP packet is unreachable. Because the destination host device is not working, a middle-router cannot figure out the path to forward the packet, and a firewall is built to disrupt the connection to the packet’s source.
- Redirect message: This is used when a router wants to inform a sender to take a different path to a particular destination. This happens when the router knows the shortest path to the destination.
ICMP Protocol work
-
ICMP operates by exchanging messages between network devices using IP datagrams. An ICMP message comprises an IP header followed by an ICMP header and data. The IP header contains details like source and destination addresses, protocol number (1 for ICMP) and a checksum. The ICMP header includes information such as message type, code, another checksum and optional identifier, and sequence numbers. The data section carries information depending on the type and code of the message.
-
When a network device sends an ICMP message, it packages it within an IP datagram. Forward it to the specified destination address mentioned in the IP header. Upon receiving an ICMP message, a network device unpacks it from the IP datagram. It then checks the type and code fields in the ICMP header. Based on these values, different actions or responses may be triggered.
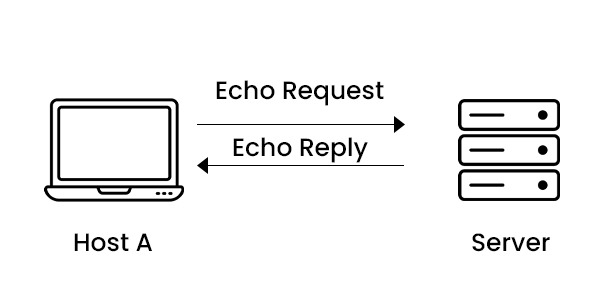
- The most common type of ICMP message is an echo request or echo reply, which is primarily used for the ping utility. An echo request is a message that sends a response from the destination device. In contrast, an echo reply is a confirmation that the destination device has indeed received the echo request.
- The ICMP header contains two fields for the echo request and reply messages. Identifier (16-bit): A number that helps to match the echo request and reply messages. Sequence number (16-bit): A number that increments with each echo request and reply message.
ICMP Packet Format
- The ICMP protocol header comes before the IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers.
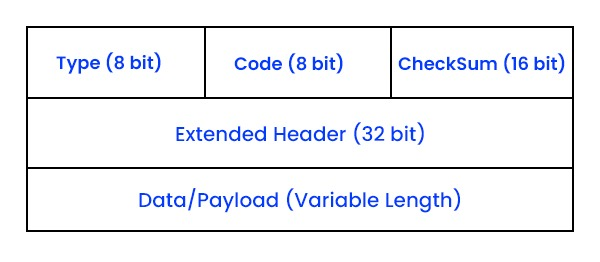
The first 32 bits of the packet hold three fields in the ICMP packet format:
-
Type (8-bit): For message type, the first 8 bits of the packet provide a short description of the message. This allows the receiver to identify what type of message it is receiving and how to respond to it. Here are some common message types:
- Type 0 – Echo reply
- Type 3 – Destination unreachable
- Type 5 – Redirect Message
- Type 8 – Echo Request
- Type 11 – Time Exceeded
- Type 12 – Parameter problem
-
Code (8-bit): The code is the next 8 bits of the ICMP packet format containing the error message and some additional information.
-
Checksum (16-bit): In the ICMP packet header, the last 16 bits are for the checksum field. The checksum helps check the number of bits in the complete message and enables the ICMP tool to ensure that the complete data is sent.
-
The Extended Header is the next 32 bits of the ICMP header that identifies the problem in the IP message. The byte locations are analysed through a pointer containing the problem message and the receiving device looks here to see the problem.
-
The last part of the ICMP packet is the Data or Payload of variable length. The bytes involved in IPv4 are 576 bytes and in IPv6 are 1280 bytes.
Below, we have explained how ICMP protocol can be used for DDoS attacks.
Advantages of ICMP
ICMP Protocol offers various advantages, some of which are:
- Report Errors: ICMP is like a messenger for your network. It tells you when something is wrong. If your computer sends information that can’t arrive, ICMP sends a message back. This message explains the problem, which helps you resolve it more quickly.
- Checks Connections: It helps you verify if other computers are functioning properly. A tool known as ping can be used; this one is based on ICMP. Ping directs a small message to a device. Getting the message back indicates that the device is online and connected.
- Maps Data Paths: This tool shows you the path your data travels. When you connect to a website, your data undergoes several steps. ICMP can help you map out this journey. This helps find out where a connection might be slow or broken.
- Keeps Things Fast: ICMP is simple and does not slow things down. It is a fundamental part of the internet that works in the background. It does its job without using much power or creating extra traffic. This keeps the network running smoothly and efficiently.
Disadvantages of ICMP
Apart from all the advantages that ICMP offers, there are also some disadvantages.
- Creates Security Problems: Hackers can use ICMP for attacks. They can flood a server with an excessive number of messages. This makes the server crash or stop working. It is a way to shut down a website or service. Attackers also use it to gather information about a network before launching an attack.
- Can Be Blocked by Firewalls: Many networks block ICMP to stay safe. This makes sense because of the security risks. But it can cause other issues. When ICMP is blocked, useful tools like ping stop working. You also won’t get important error messages, which makes it harder to fix connection problems.
- No Way to Verify the Sender: An ICMP message does not prove who sent it. It is not programmed to examine the sender’s identity. Any attacker can then easily send fake messages. Furthermore, they can steal sensitive information by pretending to be a safe computer.
- Can Be Used for Spying: Attackers can hide secret data inside ICMP packets. This is a tricky means of transferring information. It can also be used as a means of stealing files from a network unnoticed. Normal security tools may not detect this hidden traffic.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
- ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is an important protocol that plays an important role in the networking world. When working with your network systems, this protocol helps to identify specified network devices and find their addresses. Its main purpose is to duly transport data packets over the network, allowing them to move between devices connected to your heritage network.
- In this article, we will give you with information about the introductory principles of ARP protocol, how it works, and its significance. We'll also tell you why ARP is important and how it can be used in your networking systems.
What is the ARP Protocol?
- ARP stands for “Address Resolution Protocol”. It is a network protocol used to determine the MAC address (hardware address) from any IP address.
- In other words, ARP is used to mapping the IP Address into MAC Address. When one device wants to communicate with another device in a LAN (local area network) network, the ARP protocol is used.
- This protocol is used when a device wants to communicate with another device over a local area network or ethernet.
- ARP is a network layer protocol. This is a very important protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite. Although it was developed in the early 80s, it was defined in RFC 826 in 1982. ARP is implemented with important technologies like IPv4, X.25, frame relay, and ATM.
- ARP protocol finds the MAC address based on IP address. IP address is used to communicate with any device at the application layer. But to communicate with a device at the data link layer or to send data to it, a MAC address is required.
- When data is sent to a local host, the data travels between networks via IP address. But to reach that host in LAN, it needs the MAC address of that host. In this situation the address resolution protocol plays an important role.
Important ARP Terms
- ARP Cache : After receiving the MAC address, ARP passes it to the sender where it is stored in a table for future reference. And this is called ARP Cache which is later used to obtain the MAC address.
- ARP Cache Timeout : This is the time in which the MAC address can remain in the ARP Cache.
- ARP request : Broadcasting a packet over the network to verify whether we have arrived at the destination MAC address.
- ARP response/reply : It is a MAC address response that the sender receives from the receiver which helps in further communication of data.
Types of ARP
There are four types of ARP protocol they are as follows:- 1. Proxy ARP 2. Gratuitous ARP 3. Reverse ARP 4. Inverse ARP
- Proxy ARP: This is a technique through which proxy ARP in a network can answer ARP queries of IP addresses that are not in that network. That is, if we understand it in simple language, the Proxy server can also respond to queries of IP-address of other networks. Through this we can fool the other person because instead of the MAC address of the destination device, the MAC address of the proxy server is used and the other person does not even know.
- Gratuitous ARP: This is an arp request of a host, which we use to check duplicate ip-address. And we can also use it to update the arp table of other devices. That is, through this we can check whether the host is using its original IP-address, or is using a duplicate IP-address.This is a very important ARP. Which proves to be very helpful in protecting us from the wrong person, and by using it we can check the ip-address.
- Reverse ARP: This is also a networking protocol, which we can use through client computer. That is, it is used to obtain information about one's own network from the computer network. That is, if understood in simple language, it is a TCP/IP protocol which we use to obtain information about the IP address of the computer server. That is, to know the IP address of our computer server, we use Reverse ARP, which works under a networking protocol.
- Inverse ARP (InARP): Inverse ARP, it is the opposite of ARP, that is, we use it to know the IP address of our device through MAC Address, that is, it is such a networking technology, through this we convert MAC Address into IP address. Can translate. It is mainly used in ATM machines.
How ARP Protocol Works?
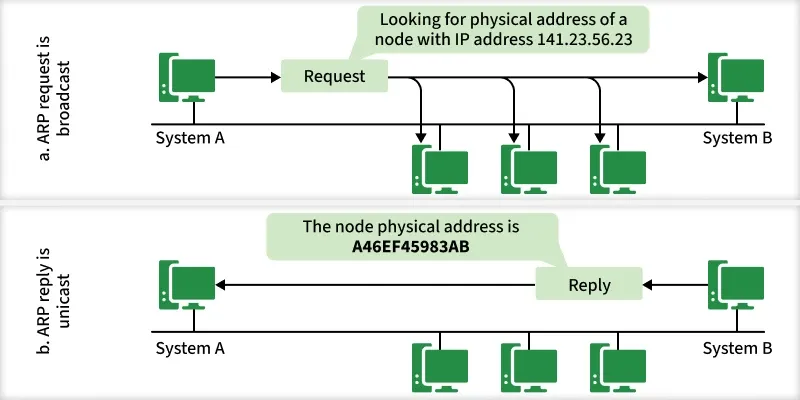
Below is a Working flow diagram of ARP Protocol
Below is the working of address resolution protocol is being explained in some steps:
- When a sender wants to communicate with a receiver, the sender first checks its ARP cache. Sender checks whether the receiver's MAC address is already present in the ARP cache or not?
- If the receiver's MAC address is already present in the ARP cache, the sender will communicate with the receiver using that MAC address.
- If the MAC address of the receiver device is not already present in the ARP cache, then in such a situation an ARP request message is prepared by the sender device. This message contains the MAC address of the sender, IP address of the sender and IP address of the receiver. The field containing the MAC address of the receiver is left blank because it is being searched.
- Sender device broadcasts this ARP request message in the LAN. Because this is a broadcast message, every device connected to the LAN receives this message.
- All devices match the receiver IP address of this request message with their own IP address. Devices whose IP address does not match drop this request message.
- The device whose IP address matches the receiver IP address of this request message receives this message and prepares an ARP reply message. This is a unicast message which is sent only to the sender.
- In ARP reply message, the sender's IP address and MAC address are used to send the reply message. Besides, in this message the receiver also sends its IP address and MAC address.
- As soon as the sender device receives this ARP reply message, it updates its ARP cache with the new information (Receiver's MAC address). Now the MAC address of the receiver is present in the ARP cache of the sender. The sender can send and receive data without any problem.
Message Format of ARP Protocol
- Messages are sent to find the MAC address through ARP(address resolution protocol). These messages are broadcast to all the devices in the LAN. The format of this message is being shown in the diagram below :
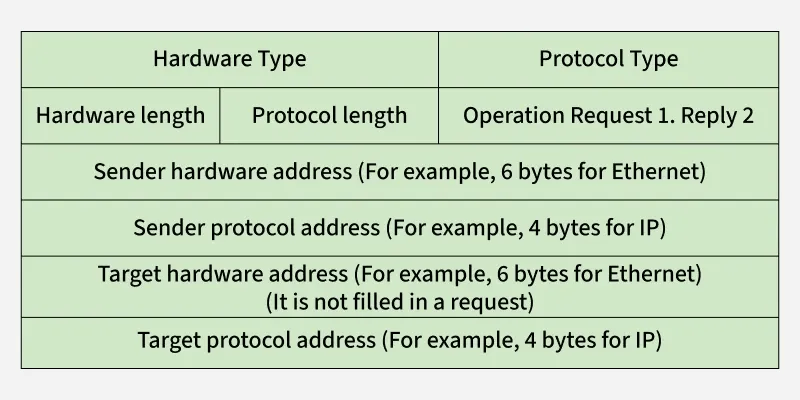
All the fields given in ARP message format are being explained in detail below:
- Hardware Type: The size of this field is 2 bytes. This field defines what type of Hardware is used to transmit the message. The most common Hardware type is Ethernet. The value of Ethernet is 1.
- Protocol Type: This field tells which protocol has been used to transmit the message. substantially the value of this field is 2048 which indicates IPv4.
- Hardware Address Length: It shows the length of the tackle address in bytes. The size of Ethernet MAC address is 6 bytes.
- Protocol Address Length: It shows the size of the IP address in bytes. The size of IP address is 4 bytes.
- OP law: This field tells the type of message. If the value of this field is 1 also it's a request message and if the value of this field is 2 also it's a reply message.
- Sender Hardware Address: This field contains the MAC address of the device transferring the message.
- Sender Protocol Address: This field contains the IP address of the device transferring the message.
- Target Hardware Address: This field is empty in the request message. This field contains the MAC address of the entering device.
- Target Protocol Address: This field contains the IP address of the entering device.
Advantages of ARP Protocol
There are many Advantages of ARP protocol but below we have told you about some important advantages.
- By using this protocol we can easily find out the MAC Address of the device.
- There is no need to configure the end nodes at all to extract the MAC address through this protocol.
- Through this protocol we can easily translate IP address into MAC Address.
- There are four main types of this protocol. Which we can use in different ways, and they prove to be very helpful.
RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol)
Introduction
- Reverse Address Resolution Protocol, also known as reverse ARP, is a networking protocol used to link a MAC address with an Internet Protocol (IP) address. It is the inverse of the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which links an IP address with a MAC address. RARP was originally developed in the stages of computer networking as a means to assign IP addresses to diskless workstations or other devices that were unable to store their IP addresses. In this blog, we will explain the RARP protocol, its purpose, and how it works, along with its advantages and disadvantages.
What is Reverse Address Resolution Protocol?
-
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol or RARP is the inverse of the more commonly used Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). ARP is a protocol that maps an IP address to a MAC address, which is needed for data link layer communication. RARP, on the other hand, maps a MAC address to an IP address, which is needed for network layer communication.
-
During its inception, Reverse Address Resolution Protocol was designed specifically for devices such as diskless workstations that lacked the capability to store their IP addresses. In this scenario, these devices would broadcast their MAC addresses and request an IP address. A RARP server on the network would then respond with an IP address corresponding to that MAC address.
-
The functionality and operation of RARP are documented in RFC 903. It functions within the data link layer of the OSI model. ARP and DHCP have largely replaced it in networks. It had a significant impact on the evolution of computer networking protocols and is still utilized in specific situations.
Now that we have a basic understanding of reverse ARP, let’s discuss its purpose.
Purpose of Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
- The primary goal of the Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is to allocate IP addresses to devices that lack storage or configuration files to store their IP addresses. These devices include workstations, embedded systems, network printers, routers, and switches.
- RARP enables these devices to dynamically acquire an IP address from an RARP server. The RARP server maintains a table associating MAC addresses with corresponding IP addresses. Once obtained, the device can utilize this IP address for communication with network devices or for accessing network resources.
- Additionally, the RARP protocol plays a role in preventing conflicts related to IP addresses. By ensuring that each MAC address is assigned an IP address, the RARP server prevents instances where two devices share the IP address within the network. Such conflicts can lead to communication errors and disruptions in network connectivity.
- We have explained what RARP is and its purpose. Let’s move on to the working of reverse ARP.
How does Reverse Address Resolution Protocol work?
The functioning of RARP can be summarized as follows:
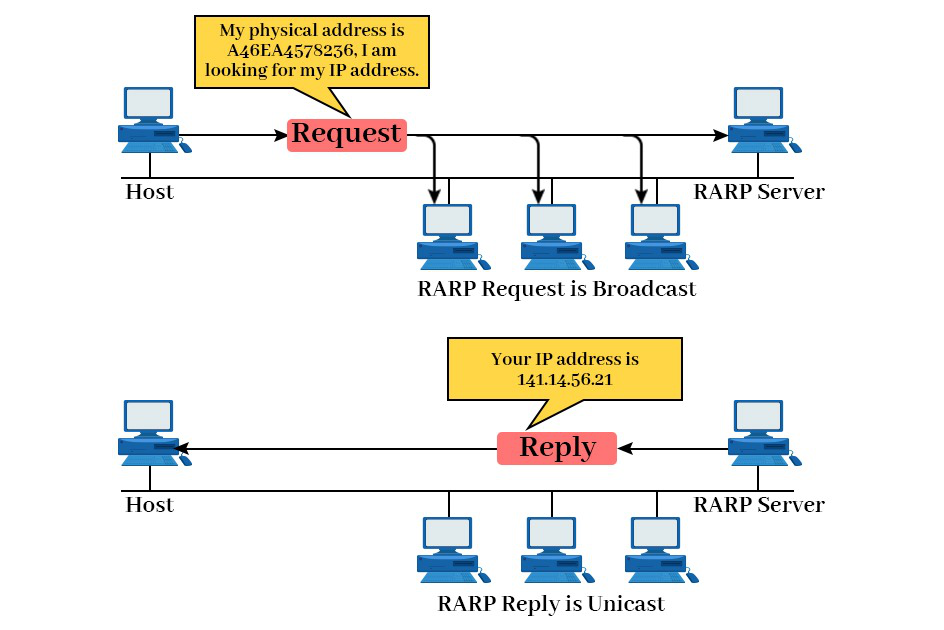
- When a device needs an IP address, it broadcasts a RARP request packet containing its MAC address in both the sender and receiver hardware address fields.
- A special host known as a RARP server configured on the network receives the RARP request packet. After that, it checks its table of MAC addresses and IP addresses.
- If the RARP server finds a matching entry for the MAC address, it sends back an RARP reply packet that includes both the MAC address and the corresponding IP address.
- The device that initiated the RARP request packet receives the RARP reply packet. After getting the reply, it then extracts the IP address from it. This IP address is then used for communication on the network.
RARP Structure
The RARP packet structure is similar to ARP’s but has minor differences. The packet contains:
- Hardware Type: Specifies the network technology (e.g., Ethernet).
- Protocol Type: Identifies the protocol being used (usually IP).
- Hardware Address Length: The length of the MAC address.
- Protocol Address Length: The length of the IP address.
- Operation Code: Specifies if it’s a request or a response.
- Sender/Receiver Hardware Address: The MAC addresses of the sender and receiver.
- Sender/Receiver Protocol Address: The IP addresses (if available).
Each field in the RARP packet helps the server determine which machine requests an IP and ensures the correct IP is returned.
Why Reverse Address Resolution Protocol Became Obsolete?
- With the advancement in protocols like DHCP and BOOTP, RARP became useless. These protocols offered more features, dynamic IP allocation, and better scalability, which made RARP unnecessary in most modern networks.
Alternatives to RARP
- Today, DHCP has almost entirely replaced RARP, offering a more efficient and secure way to assign IP addresses dynamically across networks.
Advantages of RARP Protocol
Some advantages of utilizing RARP include:
- Simplification of device configuration and management for those lacking storage or configuration files for storing their IP addresses.
- Reduction of overhead and complexity by eliminating manual assignment of individual IP addresses to each device.
- Prevention of potential conflicts by guaranteeing that every MAC address receives a distinct IP address assigned by the RARP server.
- Support for legacy devices that do not support newer protocols, like DHCP or BOOTP.
Disadvantages of RARP Protocol
Apart from all the advantages, RARP also has some disadvantages. Some disadvantages of using RARP are:
- It requires a RARP server on each network segment, which increases both cost and maintenance overhead for network infrastructure.
- Broadcasting is relied upon by RARP, causing consumption and potential network congestion.
- There is no provision for security or authentication mechanisms to verify the identity or validity of devices requesting or receiving IP addresses.
- It lacks support for any functionalities or choices like subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server, or lease time. These features are typically offered by protocols such as DHCP or BOOTP.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol
Introduction
- OSPF is a routing protocol that is widely used in large and complex networks. The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is classified as an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). It is utilized to determine the optimal routing path between a source and destination router by implementing the shortest path first (SPF) algorithm. OSPF Protocol is a link-state routing protocol where the routers exchange topology information with their closest neighbors and also use the Dijkstra algorithm to determine the optimal path in the network. If you want to learn about OSPF in-depth, then OSPF BGP Training might be the best choice for you.
What is OSPF protocol?
-
OSPF Protocol stands for Open Shortest Path First. It is defined in RFC 2328 for IPv4 and RFC 5340 for IPv6. It operates at the network layer of the OSI model and uses IP packets to exchange routing information.
-
In a network, routers need to know how to forward data packets to their intended destinations. OSPF protocol allows routers to exchange information about the network’s structure, including the links between routers and their associated costs. This information helps routers calculate the shortest and most efficient paths for transmitting data.
OSPF Protocol Features
- OSPF Protocol offers several features that make it a better option for large and complicated networks. Some of these are:
- It allows the network to be divided into smaller areas, which reduces the amount of routing information that each router has to process and store. Each area has an area border router (ABR) that connects it to other areas. The backbone area (area 0) is the core of the OSPF network and connects all other areas.
- It helps in securing communication between routers and prevents unauthorized or malicious updates.
- It uses multicast addresses to send routing updates to all routers in the same area or network. This reduces bandwidth consumption.
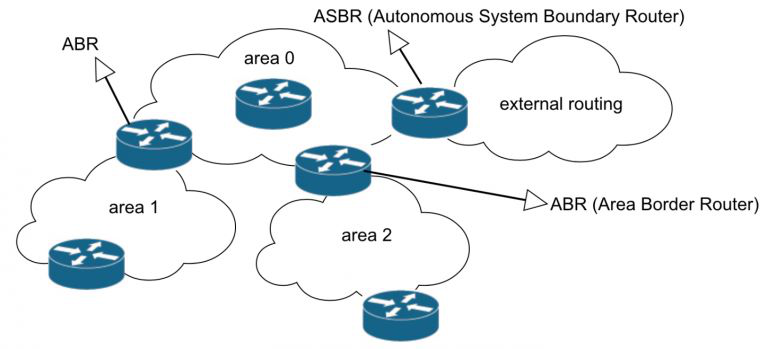
OSPF Terms
- Router ID – Router ID is an active IP address shown on the router and is considered the active IP address on the router’s interface when no loopback is configured. Otherwise, the highest loopback address is considered before the active IP address.
- Router Priority – An 8-bit value allocated to the router operating OSPF allows it to select DR and BDR in the broadcast network.
- Designated Router (DR) – DR is selected to reduce the number of adjacent locations and gives LSAs to all routers. All routers broadcast their DBD as it is selected in the broadcast network. In a broadcast network, the DR receives an appeal from the router for an update, so the DR responds to that appeal with an update.
- Backup Designated Router (BDR) – In a broadcast network, it is a backup to the DR and takes over the DR’s functions when the DR is down.
- DR and BDR elections – DR and BDR elections are done in broadcast or multi-access networks. Selection criteria are given below:
- The higher the router priority of a router, the higher the DR it will be declared.
- In router priority, the larger route should be considered if there is a tie. (The overactive IP address on the router’s interface is considered when no loopback is configured. Otherwise, the highest loopback address is considered before the overactive IP address).
How does OSPF Works?
- OSPF is a link-state routing protocol, which means that each router in the network maintains a database of the state of each link (interface) in the network. This database is called the link-state database (LSDB) and contains information such as:
- The router ID of each router in the network
- The IP address and subnet mask of each interface
- The cost (metric) of each interface
- The type and state of each interface
- The neighbors (adjacent routers) on each interface
- Each router periodically sends out link-state advertisements (LSAs) to its neighbors, which contain the information from its LSDB. The neighbors then flood these LSAs to their neighbors, and so on, until all routers in the network have received and stored the same LSAs in their LSDBs. This process is called link-state synchronization and ensures that all routers have a consistent network topology view.
- Using the information from the LSDB, each router then runs a shortest-path algorithm (such as Dijkstra’s algorithm) to calculate the best path to each destination in the network. This path is based on the cost of each link, which can be configured manually or derived from factors such as bandwidth, delay, reliability, and load. The result of this OSPF cost calculation is stored in a table called the routing table, which contains the next-hop router and interface for each destination.
OSPF Areas
- OSPF divides the Autonomous system into areas to mitigate the impact of congestion that arises from excessive flooding. As ISPs partition the internet into smaller, more manageable chunks called “autonomous systems,” OSPF Protocol does the same thing to further segment the autonomous into “areas” for easier administration.
There are different types of OSPF areas, such as:
- Backbone Area: The backbone area, also referred to as area0 or area 0.0.0.0, constitutes the fundamental component of an OSPF network, serving as the central point of connection for all other network areas. It distributes routing information among non-backbone area types.
- Standard area: This is a regular area that can have any area ID other than 0. It can only connect to the backbone area or another standard area through an ABR (Area Border Router).
- Stub Area: Stud Area relies fully on a default route for its routing needs. This is a special area that does not receive external routes from other AS.
- Not So Stubby Areas: NSSA can import external AS routes and send them to another area. However, it’s not possible to receive external routes of AS from any other areas.
- Totally stubby area: This is another variation of the stub area that does not receive any external routes or inter-area routes from other areas. It only has a default route to the backbone area through an ABR.
OSPF Protocol States
OSPF Protocol has different states that describe the status of a router or a neighbor relationship. The main states of OSPF are:
- Down: The initial state when a router has no information about a neighbor or a network.
- Init: The state when a router has received a hello packet from a neighbor but has not established bidirectional communication yet.
- Two-way: The state when a router has established bidirectional communication with a neighbor but has yet to decide whether to exchange routing information or not.
- Exstart: The state when a router has decided to exchange routing information with a neighbor and has negotiated the master-slave relationship and the initial sequence number.
- Exchange: The state when a router exchanges DBD packets with a neighbor to synchronize their LSDBs.
- Loading: The state when a router requests and receives more details about LSAs from a neighbor using LSR, LSU, and LSAck packets.
- Full: The final state when a router has synchronized its LSDB with a neighbor and is ready to forward packets.
OSPF Message Types
There are five types of messages used in OSPF Protocol –
- Hello: The Hello is used to create neighborhood relationships and analyze the proximity of neighbors. It means that “Hello” is necessary to establish a connection between routers.
- Database description: After making a connection, when the neighboring router wants to communicate with the system for the first time. It transmits the information to the database for network topology to the system; through this, the system can update or make changes accordingly.
- Link State Request: The router sends a link-state request to obtain information about the specified route. For example, Router 1 wants information about Router 2, so Router 1 shares a link-state request with Router 2. If Router 2 receives a link-state request, it sends link-state information to Router 1.
- Link State Update: The router uses link-state updates to announce the status of the link. When a route needs to broadcast the state of its link, it uses link-state updates.
- Link-State Acknowledgment: With link-state acknowledgment, routing is more reliable by forcing each node to share an acknowledgment on each link-state update. For example, Router A shares a link-state update with Routers B and C. In response, Router B and C share a link-state acknowledgment to Router A, thereby notifying Router A that both routers have received the link-state update.
Advantages of OSPF Protocol
OSPF has several benefits that make it a popular routing protocol, such as:
- It can scale to large and complex networks by using hierarchical design, areas, and route summarization.
- It supports variable-length subnet masking (VLSM) and classless inter-domain routing (CIDR), which allow more efficient use of IP addresses and reduce the size of routing tables.
- Quicker detection and restoration from a link or node failures are made possible by OSPF’s support for fast reroute (FRR) and bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD).
- It can support different types of networks, such as broadcast, non-broadcast, point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and virtual links.
- It supports different types of traffic, such as unicast, multicast, and anycast.
- It is an open standard that is widely implemented by different vendors and devices.
Disadvantages of OSPF Protocol
Here are the major disadvantages of the OSPF protocol
- It requires additional storage because the SPF algorithm requires additional CPU processing.
- Saving adjacent topologies requires more RAM.
- It is very complex, so it isn’t easy to troubleshoot.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- The protocol can connect any internetwork of the autonomous system using an arbitrary topology. The only requirement is that each AS have at least one router that can run BGP and that is the router connected to at least one other AS's BGP router. BGP's main function is to exchange network reachability information with other BGP systems. Border Gateway Protocol constructs an autonomous systems graph based on the information exchanged between BGP routers.
Characteristics of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- Inter-Autonomous System Configuration:** The main role of BGP is to provide communication between two autonomous systems.
- BGP supports the Next-Hop Paradigm.
- Coordination among multiple BGP speakers within the AS (Autonomous System).
- Path Information: BGP advertisements also include path information, along with the reachable destination and next destination pair.
- Policy Support: BGP can implement policies that can be configured by the administrator.
- Runs Over TCP.
- BGP conserves network Bandwidth.
- BGP supports CIDR.
- BGP also supports Security.
Functionality of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
BGP peers perform 3 functions, which are given below.
- The first function consists of initial peer acquisition and authentication. both the peers established a TCP connection and performed message exchange that guarantees both sides have agreed to communicate.
- The second function mainly focuses on sending negative or positive reach-ability information.
- The third function verifies that the peers and the network connection between them are functioning correctly.
Importance of Border Gateway Protocol(BGP)
- Security: BGP is highly secure because it authenticates messages between routers using preconfigured passwords through which unauthorized traffic is filtered out.
- Scalability: BGP is more scalable because it manages a vast number of routes and networks present on the internet.
- Supports Multihoming: BGP allows multihoming means an organization can connect to multiple networks simultaneously.
- Calculate the Best Path: As we know data packets is traveled across the internet from source to destination every system in between the source and destination has to decide where the data packet should go next
- TCP/IP Model: BGP is based on the TCP/IP model and it is used to control the network layer by using transport layer protocol.
Types of Border Gateway Protocol
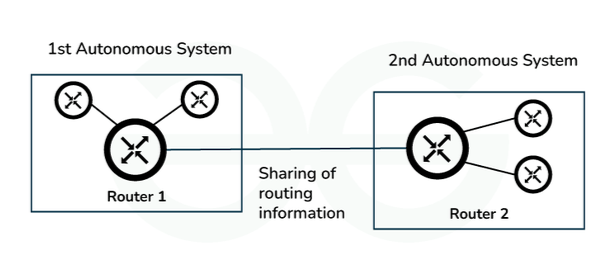
- External BGP: It is used to interchange routing information between the routers in different autonomous systems, it is also known as eBGP(External Border Gateway Protocol). The below image shows how eBGP interchange routing information.
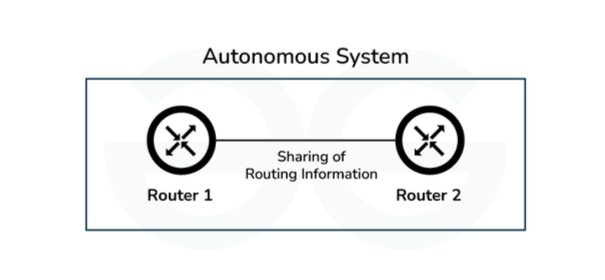
- Internal BGP: It is used to interchange routing information between the routers in the same autonomous system, it is also known as iBGP(Internal Border Gateway Protocol). Internal routers also ensure consistency among routers for sharing routing information. The below image shows how iBGP interchange routing information.
Elements of BGP
Some elements of BGP are assigned to each path and these elements help routers to select a path from multiple paths. Here below are some elements of BGP:
- Weight:* Weight is defined as a Cisco-specific attribute that tells a router which path is preferred. The weight having a higher value is preferred.
- Originate: This tells how a router choose routes and adds to BGP itself.
- Local Preference: Local Preference is an element used to select the outbound routing path. Greater local preference is preferred.
- Autonomous System Path: This element tells the router to select a path having a shorter length.
- Next Hop: To reach the destination the next hop elements specify the IP address that should be used as the next hop.
BGP Route Information Management Functions
- Route Storage: Each BGP stores information about how to reach other networks.
- Route Update: In this task, Special techniques are used to determine when and how to use the information received from peers to properly update the routes.
- Route Selection: Each BGP uses the information in its route databases to select good routes to each network on the internet network.
- Route advertisement: Each BGP speaker regularly tells their peer what is known about various networks and methods to reach them.
Difference Between BGP and OSPF
| BGP | OSPF |
|---|---|
| It follows the Path Vector Routing Algorithm | It follows the Link State Routing Algorithm |
| The speed of convergence is very slow in BGP | The speed of convergence is fast in the case of OSPF |
| BGP is also called inter-domain routing protocol | OSPF is also called intra-domain routing protocol |
| In BGP routing operation is performed between two AS | In OSPF routing operation is performed inside an AS |
| In BGP, TCP protocol is used | In OSPF, IP protocol is used |
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Introduction
- Network Address Translation (NAT) allows multiple devices to use the same public IP address and access the Internet.
- There can be a total of 232 (around 4.3 billion) different IPv4 addresses, which is very less considering the number of IPv4 devices connected to the Internet.
- The idea of NAT saves from IP address exhaustion. One public IP address is needed to access the Internet, but we can use multiple IP addresses in our private network and access the Internet from different devices and the same IP address. To achieve this, a private IP address must be translated into a public IP address.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Network Address Translation (NAT) is a process in which one or more local IP addresses are translated into one or more Global IP addresses and vice versa to provide Internet access to the local hosts. It also does the translation of port numbers, i.e., masks the port number of the host with another port number in the packet that will be routed to the destination. It then makes the corresponding entries of IP address and port number in the NAT table. NAT generally operates on a router or firewall.
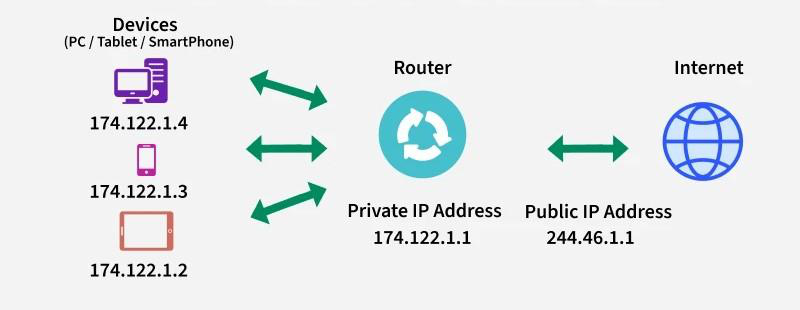
Network Address Translation Examples
Example 1 – Connecting a Private Network to the Internet
- A router configured with Network Address Translation (NAT) links a private network to the internet by converting the private IP addresses of internal devices into a public IP address. This allows devices inside the network to communicate with external systems while keeping their original IP addresses hidden from public view, enhancing privacy and security Example 2 – Linking Multiple Office Locations
- When an organization operates across multiple office locations, NAT can facilitate seamless communication between them. By translating the IP addresses of devices at each site, NAT enables them to interact as though they were on a single unified network. This approach keeps the internal IP structure private and secure while ensuring employees at different locations can collaborate efficiently.
Working of Network Address Translation (NAT)
- When a device in a private network needs to communicate with the internet, it sends a request to the NAT-enabled device (typically a router) using its private IP address and source port number. The NAT device replaces the private IP with its public IP address and assigns a unique public port number before forwarding the request to the internet.
- When the response returns, the NAT device looks up its translation table to find the matching private IP and port. It then replaces the public IP and port in the packet’s destination fields with the original private IP and port, delivering the packet to the correct device inside the network.
- This mechanism enables multiple internal devices to share a single public IP address for internet access, while also hiding internal IP addresses from external networks, adding a layer of security.
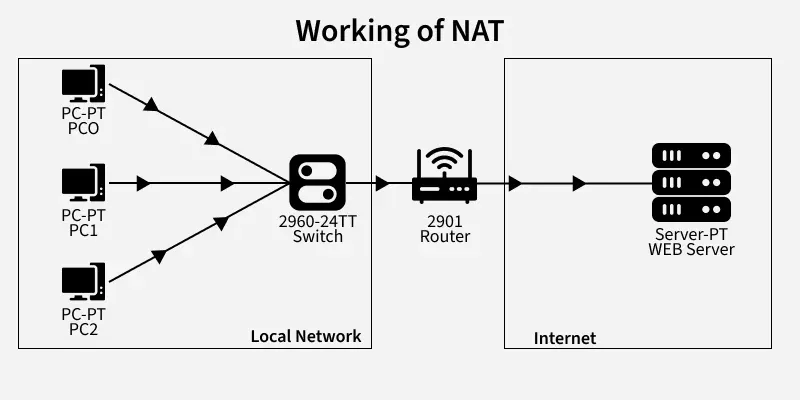
- In this Image, When PC0 sends a request to a web server, the packet reaches the NAT-enabled router. NAT replaces PC0’s private IP with the router’s public IP and assigns a unique public source port for tracking. This translated packet is then sent to the web server over the internet. The NAT table stores this mapping to ensure the reply reaches PC0 correctly.
- The web server’s response arrives at the router’s public IP and assigned port. NAT checks its translation table to identify the matching internal device, replaces the public IP and port with PC0’s private IP and original port, and then forwards the response to PC0.
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 share the same public IP for internet access, and NAT distinguishes their connections by assigning unique port mappings for each device.
Why NAT Masks Port Numbers?
- Suppose, in a network, two hosts A and B are connected. Now, both of them request for the same destination, on the same port number, say 1000, on the host side, at the same time.
- If NAT does only translation of IP addresses, then when their packets will arrive at the NAT, both of their IP addresses would be masked by the public IP address of the network and sent to the destination.
- Destination will send replies to the public IP address of the router. Thus, on receiving a reply, it will be unclear to NAT as to which reply belongs to which host (because source port numbers for both A and B are the same).
- Hence, to avoid such a problem, NAT masks the source port number as well and makes an entry in the NAT table.
NAT Inside and Outside Addresses
- Inside refers to the addresses which must be translated. Outside refers to the addresses which are not in control of an organization. These are the network addresses where the translation will occur.
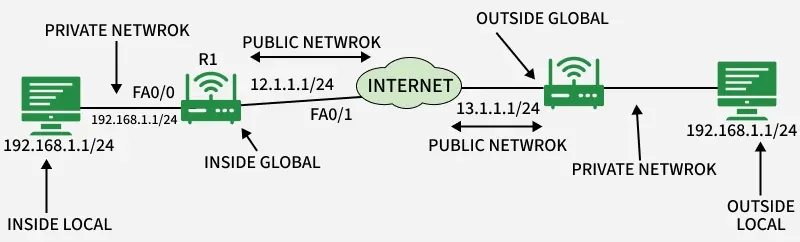
- Inside local address: An IP address that is assigned to a host on the Inside (local) network. The address is probably not an IP address assigned by the service provider i.e., these are private IP addresses. This is the inside host seen from the inside network.
- Inside global address: IP address that represents one or more inside local IP addresses to the outside world. This is the inside host as seen from the outside network.
- Outside local address: This is the actual IP address of the destination host in the local network after translation.
- Outside global address: This is the outside host as seen from the outside network. It is the IP address of the outside destination host before translation.
Types of Network Address Translation (NAT)
There are 3 ways to configure NAT:
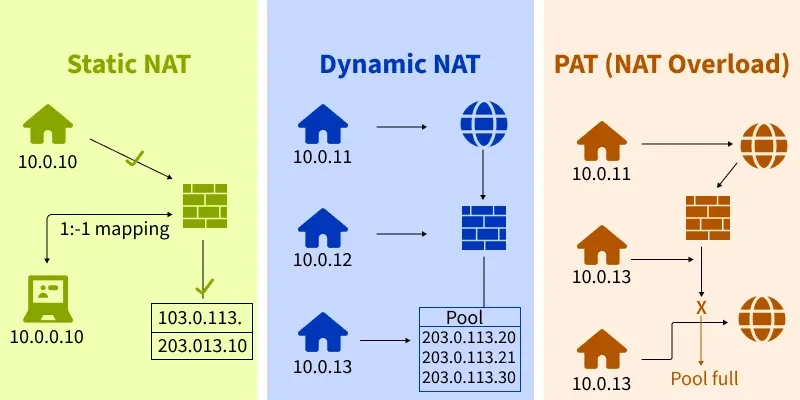
- Static NAT: In this, a single unregistered (Private) IP address is mapped with a legally registered (Public) IP address i.e. one-to-one mapping between local and global addresses. This is generally used for Web hosting. These are not used in organizations as there are many devices that will need Internet access and to provide Internet access, a public IP address is needed. Suppose, if there are 3000 devices that need access to the Internet, the organization has to buy 3000 public addresses that will be very costly.
- Dynamic NAT: In this type of NAT, an unregistered IP address is translated into a registered (Public) IP address from a pool of public IP addresses. If the IP address of the pool is not free, then the packet will be dropped as only a fixed number of private IP addresses can be translated to public addresses.
- Suppose, if there is a pool of 2 public IP addresses then only 2 private IP addresses can be translated at a given time. If 3rd private IP address wants to access the Internet then the packet will be dropped therefore many private IP addresses are mapped to a pool of public IP addresses. NAT is used when the number of users who want to access the Internet is fixed. This is also very costly as the organization has to buy many global IP addresses to make a pool.
- Port Address Translation (PAT): This is also known as NAT overload. In this, many local (private) IP addresses can be translated to a single registered IP address. Port numbers are used to distinguish the traffic i.e., which traffic belongs to which IP address. This is most frequently used as it is cost-effective as thousands of users can be connected to the Internet by using only one real global (public) IP address.
Network Address Translation Techniques
- The Network Address Translation (NAT) mechanism—often called "natting" It is a router feature commonly integrated into corporate firewalls. NAT gateways can map IP addresses in various ways, including:
- Static Mapping: Mapping a specific local IP address to a single global IP address.
- IP Masquerading: Hiding an entire range of private IP addresses behind a single public IP address.
- Translation Table Mapping: Using a translation table to allow a large private network to share a single public IP address.
- Port Address Translation (PAT): Mapping a local IP address and a specific TCP/UDP port to a global IP address or a pool of public IP addresses.
- Round-Robin Mapping: Distributing incoming connections from a single global IP address to a pool of local IP addresses in a round-robin fashion.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a powerful tool that enhances online privacy, protects sensitive data, and enables secure access to the internet. In today's interconnected world, online privacy and data security are more important than ever. One of the best ways to protect yourself and enhance your internet experience is by using a VPN (Virtual Private Network). Whether you're looking to secure your data, bypass geo-restrictions, or simply want to maintain your anonymity online, a VPN is an invaluable tool.
What Is a VPN?
- A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. It essentially acts as a private tunnel for your internet traffic, preventing hackers, ISPs, and even governments from monitoring your activities. When using a VPN, your IP address is masked, and your online actions are routed through a remote server, making it harder to track your online activity.
Benefits of Using a VPN:
- Privacy Protection: A VPN hides your IP address, ensuring that your browsing habits and activities remain private
- Security on Public Networks: Public Wi-Fi networks are often insecure, but a VPN encrypts your connection, making it safer to browse the internet on networks like those in cafes or airports.
- Bypass Geo-restrictions: A VPN allows you to access content that may be blocked in certain regions (such as streaming platforms, social media sites, etc.).
- Prevent Data Throttling: Some ISPs throttle your connection speed when you stream or play games. A VPN can bypass this, allowing for faster internet speeds.
- Accessing Remote Work Resources: A VPN enables secure access to private networks, making it ideal for businesses and remote workers.
Working of VPN
A VPN works by creating an encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server. Here's the process simplified:
- Connection Establishment: When you activate a VPN on your device, it connects to a server operated by the VPN provider.
- Encryption: The VPN encrypts your data (information, files, web traffic) so that it’s unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it, whether it's a hacker on the same Wi-Fi network or an entity trying to monitor your browsing.
- Traffic Redirection: Your device’s internet traffic is routed through the VPN server, which can be located in any country. This makes it appear as though you’re browsing from the server’s location, masking your actual IP address.
- Decryption: Once your data reaches the VPN server, it is decrypted and sent to the destination (such as a website, app, or service). Any response from the server is then sent back to you through the encrypted tunnel.
Types of VPN
- VPNs come in various types, each catering to different needs, from individual privacy to enterprise-level solutions. Below are the main types of VPNs:
- Remote Access VPN: A Remote Access VPN allows individual users to connect to a network remotely, such as accessing work files from home. It's ideal for people who need secure access to a private network from anywhere.
- Site-to-Site VPN: A Site-to-Site VPN is used to connect two networks, often used by businesses with multiple office locations. It securely links two private networks over the internet, enabling employees to access resources from both locations.
- Mobile VPN: A Mobile VPN is designed for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. It ensures stable connections even when switching between different networks (such as from Wi-Fi to mobile data) and is used in industries like healthcare and logistics where users need continuous access while moving.
- MPLS VPN (Multiprotocol Label Switching): An MPLS VPN is used mainly by large businesses and enterprise networks. It routes data between different locations through an efficient network that prioritizes data traffic. It's often more complex and provides more scalability compared to traditional VPNs.
- PPTP VPN (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol): PPTP is one of the oldest VPN protocols and is known for being fast but less secure compared to others. It is rarely used in modern systems due to its vulnerabilities, but it’s still available on some legacy systems.
- L2TP/IPsec VPN (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPsec): L2TP combined with IPsec offers more security than PPTP. It uses encryption to secure data, making it a popular option for users who need a reliable, moderately secure connection.
- OpenVPN: OpenVPN is a highly secure, open-source VPN protocol known for its flexibility and strength in encryption. It’s often used for custom VPN setups and is highly configurable, making it a popular choice for advanced users.
- IKEv2/IPsec VPN (Internet Key Exchange version 2): IKEv2 is a fast, stable, and secure VPN protocol that works well on mobile devices. It automatically reconnects when the device switches between networks, providing continuous service without interruptions.
Advantages of Using a VPN
- Privacy Protection: VPNs keep your online activities private and anonymous, preventing third parties from tracking you.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: VPNs enable you to access content that might be restricted in your country or region, such as streaming services (Netflix, BBC iPlayer).
- Enhanced Security: With end-to-end encryption, VPNs protect your data from hackers, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Prevents Data Throttling: VPNs help avoid internet speed throttling imposed by your Internet Service Provider (ISP), particularly when streaming or gaming.
- Safer Online Transactions: VPNs help protect sensitive information like bank details when conducting transactions online.
- Access Work Resources Remotely: Securely access your work or school network, even from remote locations.
Disadvantages of Using a VPN
- Slower Speeds: Using a VPN may slow down your internet speed due to the encryption process and server routing.
- Not All VPNs Are Equal: Some VPN services may log your data or provide subpar protection, so it’s essential to choose a reliable VPN provider.
- Can Be Blocked: Certain websites or countries may block VPN access, limiting your ability to connect to certain services.
- Requires Configuration: Setting up a VPN may require a bit of technical knowledge, especially if you're doing it manually.
- Cost: While there are free VPNs available, premium VPNs offer more reliable services and better security, which can be a recurring expense.
When selecting a VPN, consider the following factors:
- Security Features: Look for strong encryption, no-logs policies, and secure protocols (e.g., OpenVPN, IKEv2).
- Speed: If streaming or gaming is a priority, choose a VPN with high-speed servers.
- Location of Servers: More server locations provide better access to geo-blocked content.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure the VPN is compatible with your devices (Windows, Mac, Android, iOS).
- Customer Support: Choose a VPN with excellent customer support in case you encounter issues.
- A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a powerful tool for protecting your online privacy, securing your internet connection, and accessing content from around the world. It encrypts your data, allowing you to browse the internet securely without fear of hackers, government surveillance, or geo-restrictions.
- Choosing the right VPN depends on your needs—whether you're a casual user who wants to access streaming content, a remote worker needing secure access to company resources, or an enterprise requiring complex, site-to-site connections. By understanding how VPNs work and the different types available, you can make an informed decision and take control of your online privacy and security.
Firewall
Introduction of Firewall
- A firewall is a network security device, either hardware or software-based, which monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic and, based on a defined set of security rules, accepts, rejects, or drops that specific traffic. It acts like a security guard that helps keep your digital world safe from unwanted visitors and potential threats.
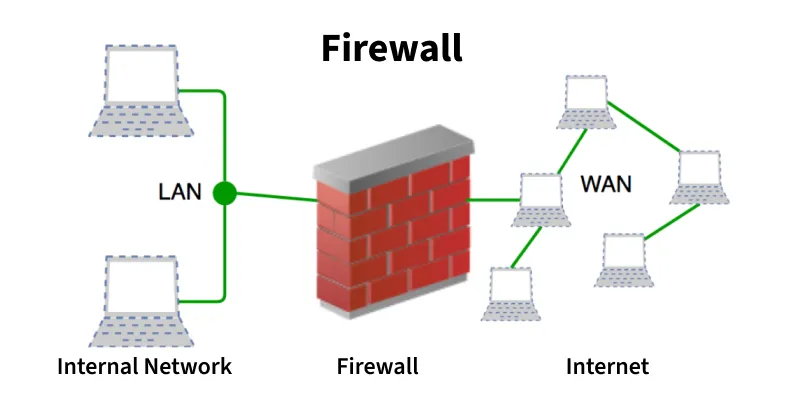
- Accept: Allow the traffic.
- Reject: Block with an error response.
- Drop: Block silently without response.
Need for a Firewall
- A firewall is essential because networks are constantly exposed to both safe and harmful traffic from the internet or other networks. Without a firewall, your systems would have no protection against unwanted access, malicious activity, or accidental data leaks.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: Imagine your house door is always open. Anyone passing by could walk in and take your things. A firewall is like a locked door with a guard, letting only trusted people in and keeping strangers out.
- Blocking Malicious Traffic: Think of your email inbox. Without a spam filter, you’d get flooded with scam and spam messages. A firewall works like that spam filter it blocks harmful data before it reaches you.
- Protecting Sensitive Information: It’s like keeping your bank PIN in a safe instead of leaving it on the table where anyone can see it. A firewall ensures your personal and business data stays hidden from cyber criminals.
- Preventing Cyber Attacks: If you leave your car unlocked in a parking lot, thieves can steal it. A firewall locks your network so attackers can’t hijack it.
- Controlling Network Usage: Just like parents set parental controls so kids can’t visit unsafe websites, firewalls control where your computers are allowed to connect.
Working of Firewall
Here’s a clear explanation of the working of a firewall, including its types and flow:
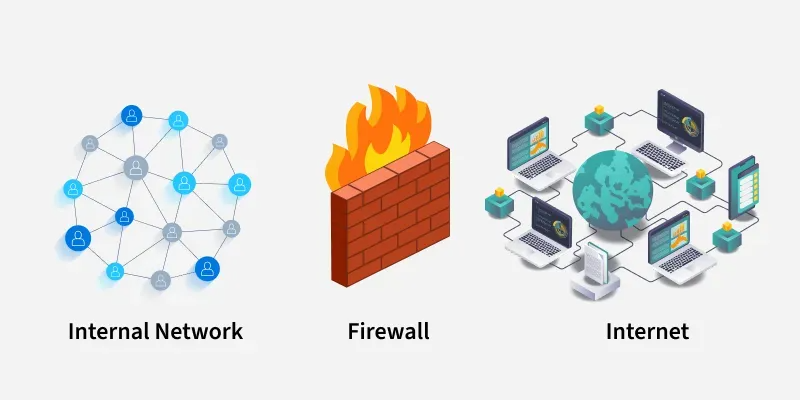
-
A firewall works like a security guard for your network, standing between your internal systems, such as computers, servers, and devices and the outside world, like the internet or other networks. It carefully inspects all data entering or leaving to ensure only safe traffic is allowed through.
-
When data tries to enter or leave your network, it passes through the firewall first.
-
The firewall examines the data packets (small chunks of information) using predefined rules.
-
Rules can be defined on the firewall based on the necessity and security policies of the organization.
-
Firewall allows decision making, such as: Allow → If the packet matches safe rules, or Block → If the packet is suspicious, from a blacklisted source, or contains malicious code.
-
The firewall records blocked or unusual traffic for security teams to review.
-
Alerts can be sent in real time if a major threat is detected.
-
Default policy: It is very difficult to explicitly cover every possible rule on the firewall. For this reason, the firewall must always have a default policy. The default policy only consists of action (accept, reject or drop). Suppose no rule is defined about SSH connection to the server on the firewall. So, it will follow the default policy. If default policy on the firewall is set to accept, then any computer outside of your office can establish an SSH connection to the server. Therefore, setting default policy as drop (or reject) is always a good practice.
Types of Firewalls
Firewalls can be categorized based on their generation.
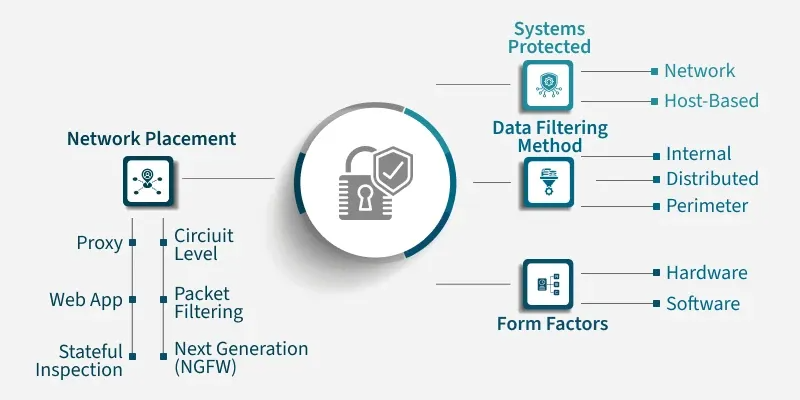
1) Network Placement
- Packet Filtering Firewall: This is the most basic type. It checks packet headers—like IP address, port number, and protocol—and decides whether to allow or block them. Think of it like checking someone's ID at the gate. If the name and ID match the list, they’re allowed in, no questions asked.
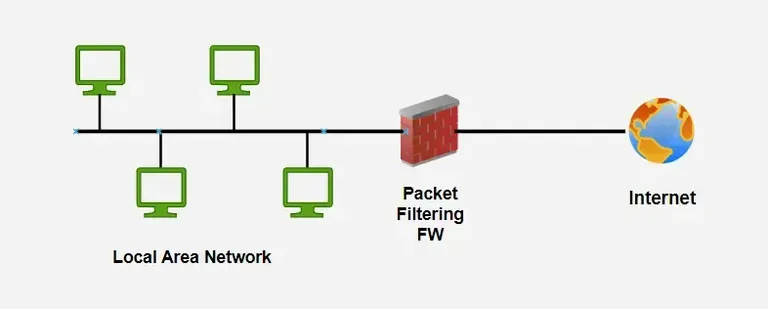
- Stateful Inspection Firewall: Goes a step further. It monitors active connections and makes decisions based on the context of traffic. Imagine a hotel that remembers you checked in earlier, so it doesn’t question you every time you enter.
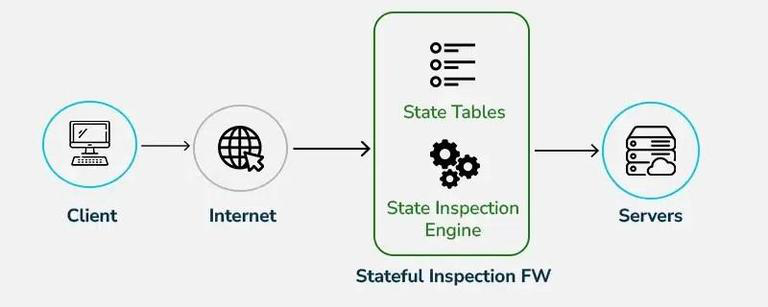
- Proxy Firewall (Application Level): This acts like a middleman between user and destination. It fetches data on your behalf while filtering dangerous content. Like asking your assistant to go to a store for you they check the item first before handing it over.
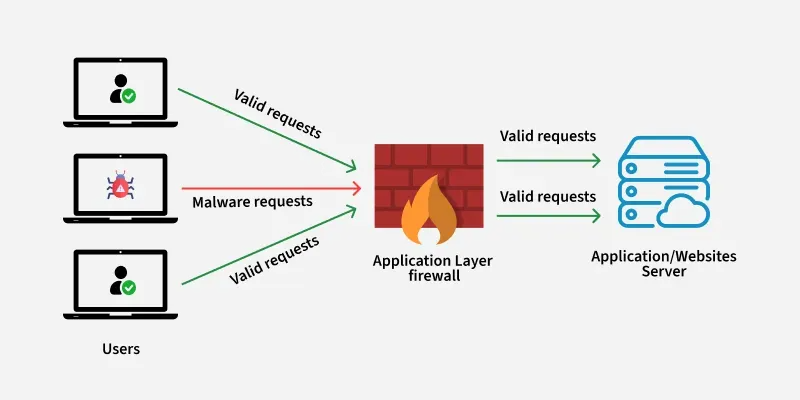
- Circuit-Level Gateway: Validates if a connection is successfully established (like a TCP handshake), but doesn't inspect actual data. Like confirming someone is calling from a known number without listening to the call.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Specifically protects websites and web apps from attacks like SQL injection or cross-site scripting. Imagine a form guard that checks what users type before it reaches your website—blocking any harmful tricks.
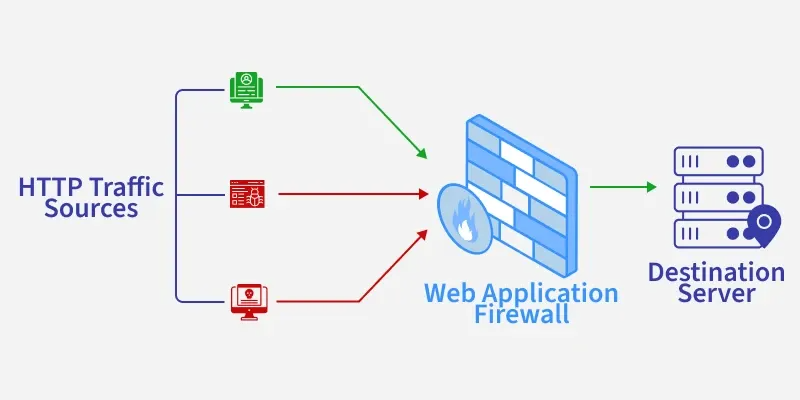
- Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW): Combines traditional firewalls with modern features like app control, intrusion prevention, malware detection, and encrypted traffic inspection. It’s like a security team with surveillance cameras, ID scanners, and behavior monitoring—all working together.
2) Network Firewall
A Network Firewall secures the perimeter, while a host-based firewall protects the endpoint.
- Network Firewall: Protects a whole network—usually placed at the entry/exit point between your internal systems and the internet. Picture it like a guard standing at your building's main entrance.
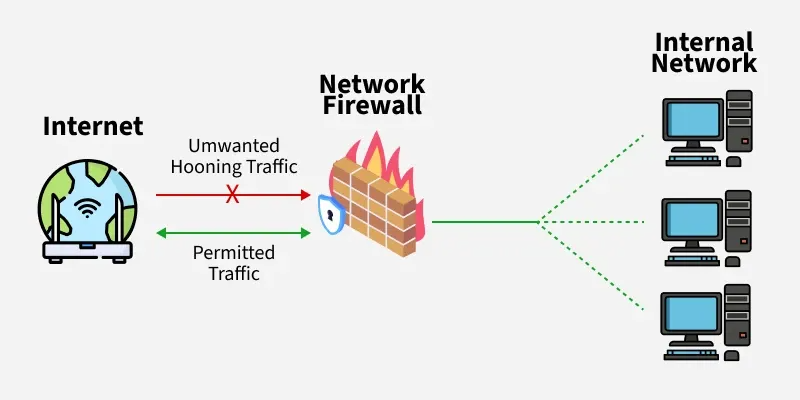
- Host-Based Firewall: Installed on individual devices like laptops, servers, or mobile phones. It protects only that one system. Think of it as having a security app that watches over just your phone, not the whole office.
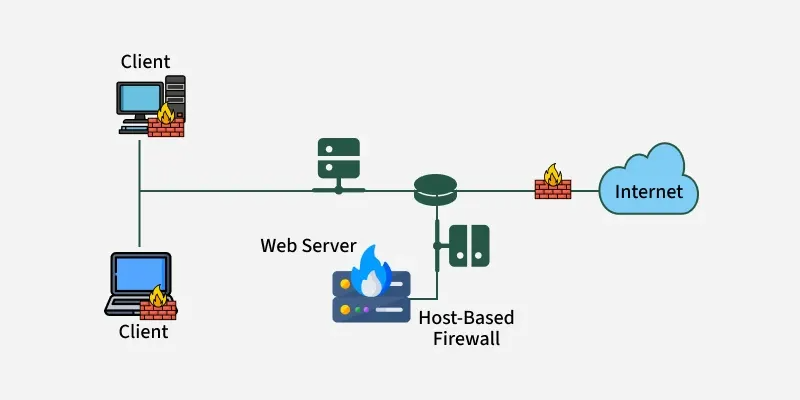
3) Data Filtering Method
All three of these firewall types work to control network access, but they differ in their placement and scope.
- Perimeter Firewall: Sits at the edge of your network, filtering traffic coming in and out from the internet. Like a fence with a gate that controls who gets into your property.
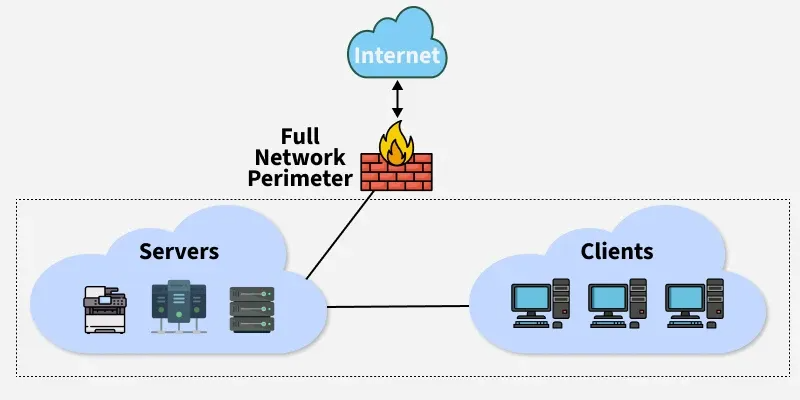
- Internal Firewall: Placed between different segments inside your network, such as departments or sensitive zones. Imagine every department in a company having a door lock with access rules.
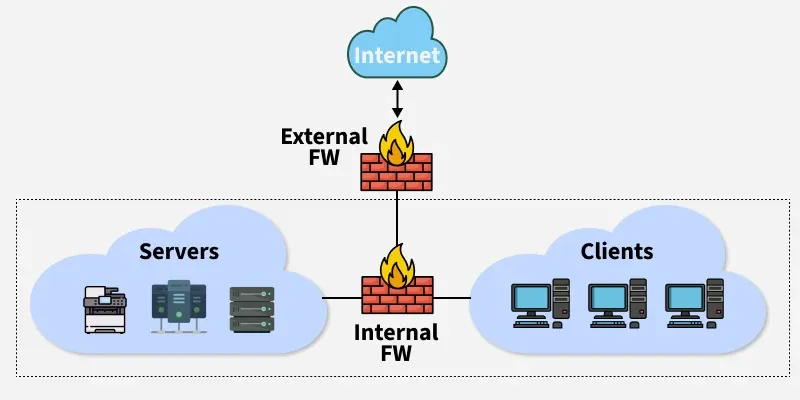
- Distributed Firewall: Instead of one firewall at the edge, security rules are applied at multiple endpoints across the network. Like installing security alarms in every room of your house rather than just at the main door.
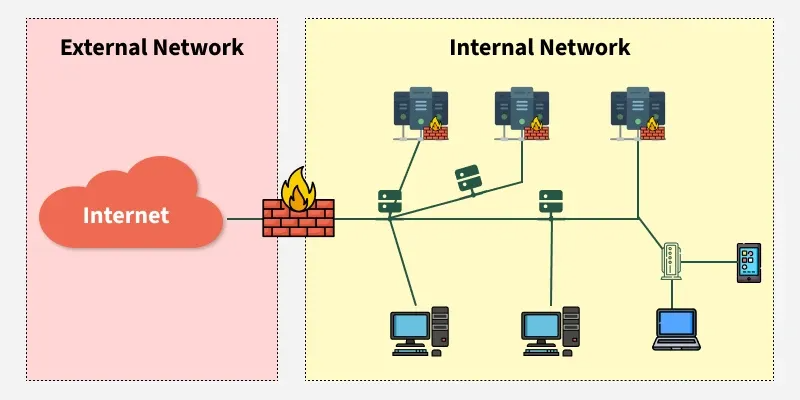
4) Form Factors
A program installed on a computer or server that protects it from network threats.
- Hardware Firewall: A physical box or appliance that connects to your network. Often used in large or office environments. Think of it like a security gate at the main entrance visible, strong, and standalone.
- Software Firewall: Installed as a program on a device or server. Easier to set up and ideal for individuals or virtual setups. Like installing a firewall app on your laptop to control its own internet access.
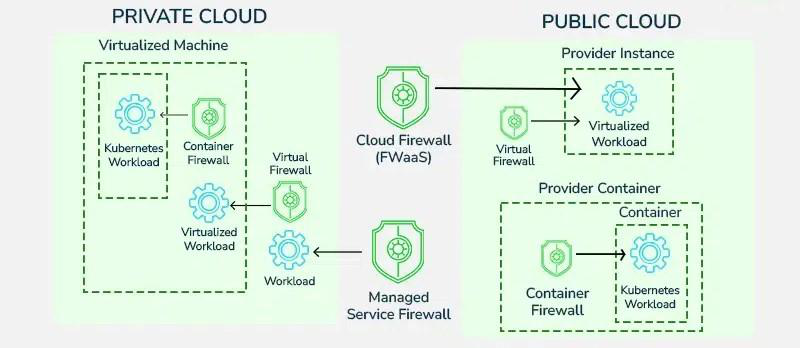
Importance of Firewalls
- A network firewall is your first line of defense in cybersecurity. It monitors, filters, and controls data moving in and out of your network.
- Networks are vulnerable to any traffic trying to access your systems, whether it's harmful or not. That's why it's crucial to check all network traffic.
- When you connect personal computers to other IT systems or the internet, it opens up many benefits like collaboration, resource sharing, and creativity. But it also exposes your network and devices to risks like hacking, identity theft, malware, and online fraud.
- Once a malicious person finds your network, they can easily access and threaten it, especially with constant internet connections.
- Using a firewall is essential for proactive protection against these risks. It helps users shield their networks from the worst dangers.
History of Firewalls
- Firewalls evolved from simple packet filtering to advanced, user-friendly security systems used worldwide.
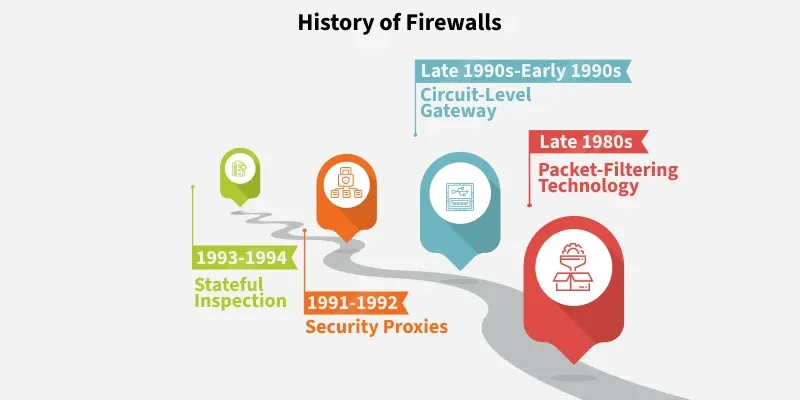
- Late 1980: Jeff Mogul, Brian Reid, and Paul Vixie at Digital Equipment Corp (DEC) developed packet-filtering technology, laying the groundwork for firewalls by checking external connections before they reached internal networks.
- Late 1980s - Early 1990s: AT&T Bell Labs researchers, including Presotto, Sharma, and Nigam, developed the circuit-level gateway, a firewall that vetted ongoing connections without reauthorizing each data packet, paving the way for more efficient security.
- 1991-1992: Marcus Ranum introduced security proxies at DEC, leading to the creation of the Secure External Access Link (SEAL), the first commercially available application-layer firewall, based on earlier DEC work.
- 1993-1994: At Check Point, Gil Shwed pioneered stateful inspection technology, filing a patent in 1993. Nir Zuk developed a graphical interface for Firewall-1, making firewalls accessible and widely adopted by businesses and homes.
What Does Firewall Security Do?
- A firewall serves as a security barrier for a network, narrowing the attack surface to a single point of contact. Instead of every device on a network being exposed to the internet, all traffic must first go through the firewall. This way, the firewall can filter and block non-permitted traffic, whether it's coming in or going out. Additionally, firewalls help create a record of attempted connections, improving security awareness.
Firewalls regulate both inbound and outbound traffic, protecting the network from:
- External threats such as viruses, phishing emails, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and backdoors. Firewalls filter incoming traffic flows, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data and thwarting potential malware infections.
- Insider threats like known bad actors or risky applications. A firewall can enforce rules and policies to restrict certain types of outgoing traffic, which helps identify suspicious activity and mitigate data exfiltration.
What Can Firewalls Protect Against?
Firewalls can protect against a variety of threats by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. Here are the main threats they help defend against:
- Infiltration by Malicious Actors: Firewalls can block suspicious connections, preventing eavesdropping and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Parental Controls: Parents can use firewalls to block their children from accessing explicit web content.
- Workplace Web Browsing Restrictions: Employers can restrict employees from using the company network to access certain services and websites, like social media.
- Nationally Controlled Intranet: Governments can block access to certain web content and services that conflict with national policies or values.
By allowing network owners to set specific rules, firewalls offer customizable protection for various scenarios, enhancing overall network security.
Firewall Security Tips
To maximize your firewall’s protection, enhance its security with these best practices:
- Keep Your Firewall On: Never turn off your firewall just to connect to a device or network. Instead, adjust your firewall rules and add trusted devices to your allow list.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your firewall software or operating system to patch vulnerabilities and stop new security threats.
- Pair with a VPN: A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, adding another layer of protection alongside your firewall. Just be sure to adjust firewall rules if there’s a conflict.
- Deny Unknown Requests: If you get a suspicious access request, block it immediately. Investigate later before making any permanent changes.
- Add Extra Security Tools: Firewalls don’t block all threats, especially malicious programs you install yourself. Use trusted antivirus or anti-malware software for full coverage.
Network Security Threats and Encryption Techniques
Introduction
- In today’s digital era, communication and data exchange occur primarily through computer networks. From online banking and e-commerce to video calls and social media, billions of users depend on networks to carry out daily activities. While this has improved convenience and efficiency, it has also opened doors for malicious activities. Attackers constantly seek ways to steal information, disrupt services, or impersonate legitimate users. To counter such dangers, the field of network security has evolved, combining technical solutions and policies to safeguard information. At the heart of these defenses lies encryption, which ensures that even if information is intercepted, it cannot be read or altered by unauthorized parties. This chapter explores the types of threats faced by computer networks and the encryption techniques that protect sensitive information.
Understanding Network Security
- Network security can be defined as the practice of protecting data and resources in a computer network against unauthorized access, modification, or misuse. Security measures are not limited to software or hardware alone; they also include user awareness, policies, and physical protection of systems.
The primary objectives of network security are described through the CIA triad:
- Confidentiality – Information should be accessible only to authorized users.
- Integrity – Information must not be altered during storage or transmission.
- Availability – The network and its services should remain accessible whenever required.
If any of these principles is violated, the network can suffer serious consequences, including data loss, financial damage, and loss of trust.
Network Security Threats
- Network threats are attempts by attackers to break into a network, disrupt its normal functioning, or steal valuable data. These threats can be broadly classified into passive threats and active threats.
-
Passive Threats: Passive threats involve silently monitoring the network without directly interfering with the flow of information. Though they do not modify data, they still compromise confidentiality.
- Eavesdropping or Sniffing: In this type of attack, the attacker listens to unencrypted communication over the network. For example, if a user logs in to an insecure website, the attacker can capture the username and password. Tools like Wireshark allow hackers to capture network packets. Encryption such as HTTPS can protect against this.
- Traffic Analysis: Even when messages are encrypted, an attacker can study communication patterns. For instance, knowing how often two employees exchange messages might reveal their importance in an organization.
-
Active Threats: Unlike passive threats, active threats involve altering, disrupting, or injecting malicious data into network communication.
- Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): In this attack, the attacker floods a server with a massive number of requests so that it becomes unavailable to genuine users. A DDoS attack is more powerful as it uses thousands of infected machines (called a botnet). For example, GitHub suffered one of the world’s largest DDoS attacks in 2018.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM): Here, the attacker secretly sits between two communicating parties. For example, a fake Wi-Fi hotspot in a coffee shop can allow an attacker to capture bank logins as users browse the internet.
- IP Spoofing: Attackers forge the source address of network packets to impersonate another system, thereby misleading the target machine.
- Session Hijacking: Many web applications use session tokens stored in cookies. If attackers steal these tokens, they can impersonate the legitimate user and access private accounts.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Not all attacks are technical. Many attackers trick users into revealing information. For example, a fake email claiming to be from a bank may request users to “verify” their credentials. This is one of the most successful forms of attack.
-
Malware-Based Threats: Malicious software, commonly known as malware, is another significant threat to networks.
- Viruses are programs that attach themselves to files and spread when the file is executed.
- Worms spread automatically without user intervention, often causing widespread disruption.
- Trojan Horses disguise themselves as useful applications but secretly perform harmful actions, such as opening a backdoor for hackers.
- Ransomware encrypts the user’s files and demands payment to restore access. The WannaCry attack of 2017 is a well-known example that affected thousands of organizations worldwide.
- Spyware and Keyloggers secretly monitor user activity, recording keystrokes to steal passwords and credit card details.
The variety and sophistication of these threats highlight the need for strong defense mechanisms, among which encryption is the most vital.
Fundamentals of Encryption
-
Encryption is the process of converting plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (unreadable data) using a mathematical algorithm and a key. Only users with the correct decryption key can recover the original information. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted, it remains useless to attackers.
-
The goals of encryption include:
- Confidentiality – Preventing unauthorized access to data.
- Integrity – Ensuring the data has not been modified.
- Authentication – Verifying the identity of the sender.
- Non-repudiation – Preventing the sender from denying that they sent a message.
Types of Encryption Techniques
-
Symmetric Key Encryption: In symmetric encryption, the same secret key is used for both encryption and decryption. This makes the process fast and suitable for encrypting large amounts of data. However, the challenge lies in securely sharing the secret key between parties. Examples:
- DES (Data Encryption Standard): Once widely used but now considered insecure due to its small key size (56 bits).
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): The current standard used worldwide, with key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits. It is used in Wi-Fi (WPA2/WPA3), banking systems, and secure file storage.
- Blowfish and Twofish: Alternatives to AES, known for speed and flexibility.
-
Asymmetric Key Encryption: Also known as public-key cryptography, asymmetric encryption uses two different keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This eliminates the problem of key sharing but is slower compared to symmetric encryption. Examples:
- RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman): Based on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers. It is commonly used in digital signatures and SSL/TLS certificates.
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC): Provides strong security with smaller key sizes, making it suitable for mobile devices.
-
Hash Functions: Hashing is a one-way encryption method that converts data into a fixed-size string, known as a hash value. Hash functions are irreversible and mainly used for verifying data integrity and securely storing passwords. Examples:
- MD5 (Message Digest 5): Now considered weak and insecure.
- HA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm): Stronger and widely used in blockchain, digital certificates, and password protection.
-
Digital Signatures: A digital signature is a mathematical scheme for verifying the authenticity and integrity of digital messages. The sender generates a signature using their private key, and the receiver verifies it with the sender’s public key. Digital signatures provide authentication and nonrepudiation
-
Hybrid Encryption: Many real-world systems use a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption, known as hybrid encryption. For example, in HTTPS communication:
- The web server and client use RSA (asymmetric) to exchange a secret session key
- The session key is then used with AES (symmetric) for the actual data transfer.
This approach ensures both security and efficiency.
Applications of Encryption in Real Life
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting data in everyday life:
-
Secure Websites (HTTPS): All sensitive web traffic, such as online shopping and banking, is protected by SSL/TLS encryption.
-
Wi-Fi Networks: WPA2 and WPA3 protocols use AES encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Messaging Apps: Services like WhatsApp and Signal employ end-to-end encryption to ensure that only the intended recipient can read the message.
-
Cloud Storage: Platforms like Google Drive and OneDrive encrypt files to protect against data leaks.
-
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs encrypt the entire communication channel, protecting data from eavesdropping on public networks.
-
Network security threats are growing in number and sophistication, ranging from simple eavesdropping to large-scale ransomware and DDoS attacks. To safeguard against these dangers, encryption remains the most powerful tool. By converting data into unreadable ciphertext, encryption ensures confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. Symmetric encryption offers speed, asymmetric encryption solves key distribution problems, hashing ensures integrity, and hybrid encryption provides a balanced solution. Together, these techniques form the foundation of modern security protocols, enabling safe online banking, secure messaging, and confidential business communication.
-
Ultimately, effective network security requires not just technology but also awareness and responsible behavior from users. A well-encrypted system combined with cautious users can significantly reduce the risks in the digital world.