DMBS-01 Fundamentals of Digital Marketing & E-Business
On This Page
What is Marketing?
- Marketing is identifying customer needs
- Creating value for customers
- Promoting products and services
- Building long-term customer relationships
- Simple Meaning: Marketing = Selling with customer satisfaction
Example of Traditional Marketing
- Local tea stall near college
- Good quality tea
- Affordable price
- Word-of-mouth promotion
- (This is marketing without internet)
Limitation of Traditional Marketing
- Limited reach
- High cost
- No direct customer feedback
- Difficult to measure results
- Businesses needed a better solution
What is Digital?
- Digital means use of: Internet, Mobile phones, Computers, Online platforms
- Examples: Google, Instagram, YouTube, Email
Definition of Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing refers to the promotion of products, services, or brands using digital technologies such as the internet, mobile devices, search engines, social media, and email.
Digital Marketing – Simple Definition
- Marketing done using internet & digital devices
- Reaching customers online
- Promoting products through digital platforms
- In one line: Digital Marketing Online Marketing
Why Digital Marketing Came into Existence
- Increase in smartphone users
- Internet availability
- Social media growth
- Online shopping trend
- Need for measurable marketing
Real-Life Example
You search “Best shoes under ₹2000” on Google
- You see ads
- You watch YouTube reviews
- You get Instagram ads
- You buy online
This complete process is Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing Platforms
- Search Engines (Google)
- Social Media (Instagram, Facebook)
- Websites
- Mobile Apps
Traditional vs Digital Marketing
| Traditional Marketing | Digital Marketing |
|---|---|
| Newspaper Ads | Google Ads |
| TV Ads | YouTube Ads |
| High Cost | Low Cost |
| No Tracking | Full Tracking |
Features of Digital Marketing
- Global reach
- Target specific audience
- Cost effective
- Measurable results
- Instant communication
Benefits for Businesses
- Small budget required
- Faster promotion
- Customer engagement
- Better return on investment (ROI)
Benefits for Customers
- Easy product comparison
- Online reviews
- Personalized ads
- Convenient shopping
Digital Marketing in Daily Life
- WhatsApp offers
- Instagram sponsored posts
- YouTube ads
- Email newsletters
- Students experience digital marketing daily
Importance of Digital Marketing Today
- Essential for modern businesses
- Helps startups grow
- Supports online economy
- Creates employment opportunities
Key Takeaways
- Digital Marketing is online promotion
- Uses internet & digital platforms
- Cost effective & measurable
- Important for both businesses & customers
Evolution & Scope of Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing Careers

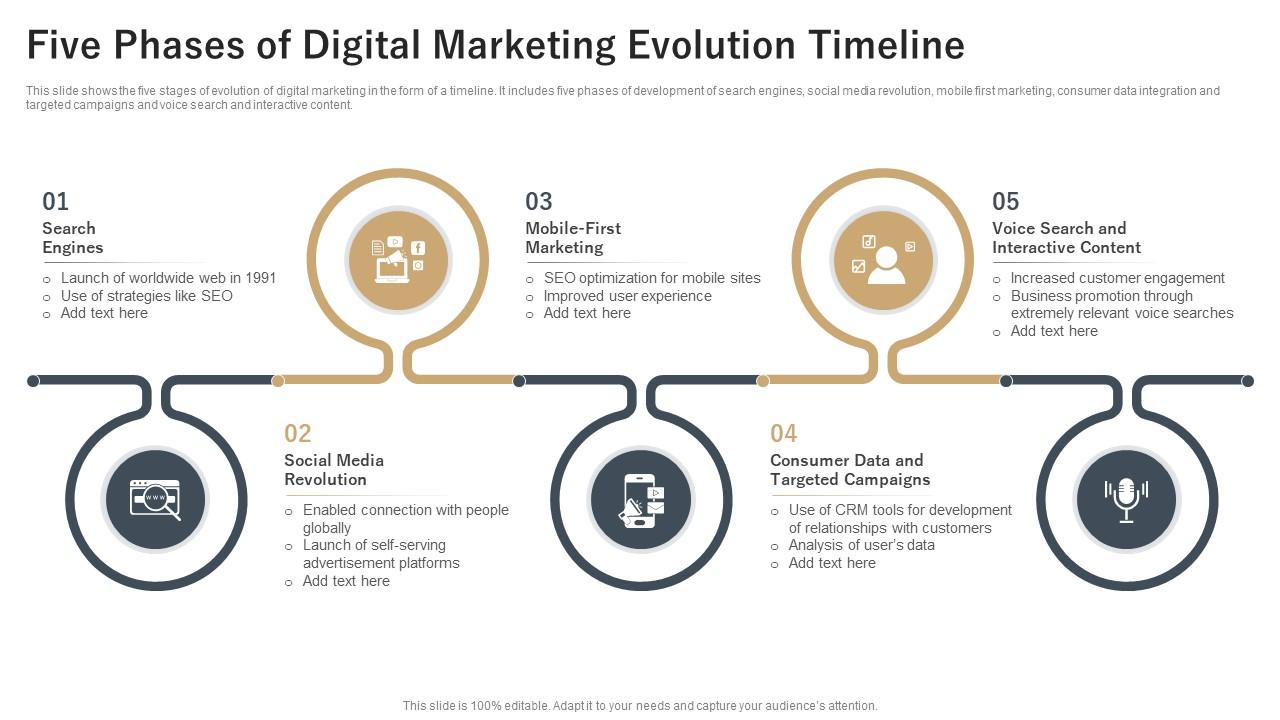
Evolution of Digital Marketing
Meaning of Evolution
- Evolution means gradual and continuous development over time. Digital marketing evolved as technology, internet access, and customer behavior changed.
Traditional Marketing Era
- In the early stage, marketing depended on newspapers, radio, television, banners, and hoardings. Communication was one-way and businesses could not interact with customers or measure results.
Limitations of Traditional Marketing
- Traditional marketing was expensive, limited to local areas, and did not provide exact data about customer response or sales impact.
Internet & Website Era (1990s)
- With the arrival of the internet, businesses created websites and started email marketing. Information sharing became faster, but communication was still mostly one-way.
Search Engine Era (2000s)
- Customers began searching online before purchasing. Businesses focused on appearing in Google search results using SEO and paid ads.
Social Media & Smartphone Era
- Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and YouTube made marketing interactive and affordable. Customers could like, comment, and share content.
AI & Data-Driven Era (Present)
- Digital marketing now uses data analytics and AI to show personalized ads based on customer behavior.
Scope of Digital Marketing
Business Scope
- Digital marketing helps businesses reach global customers, build brands online, and increase sales at low cost.
Career Scope
- Creates jobs such as SEO executive, social media manager, content marketer, and digital analyst.
Future Scope
- Growing internet users and digitalization ensure long-term demand for digital marketing skills.
Traditional Marketing vs Digital Marketing
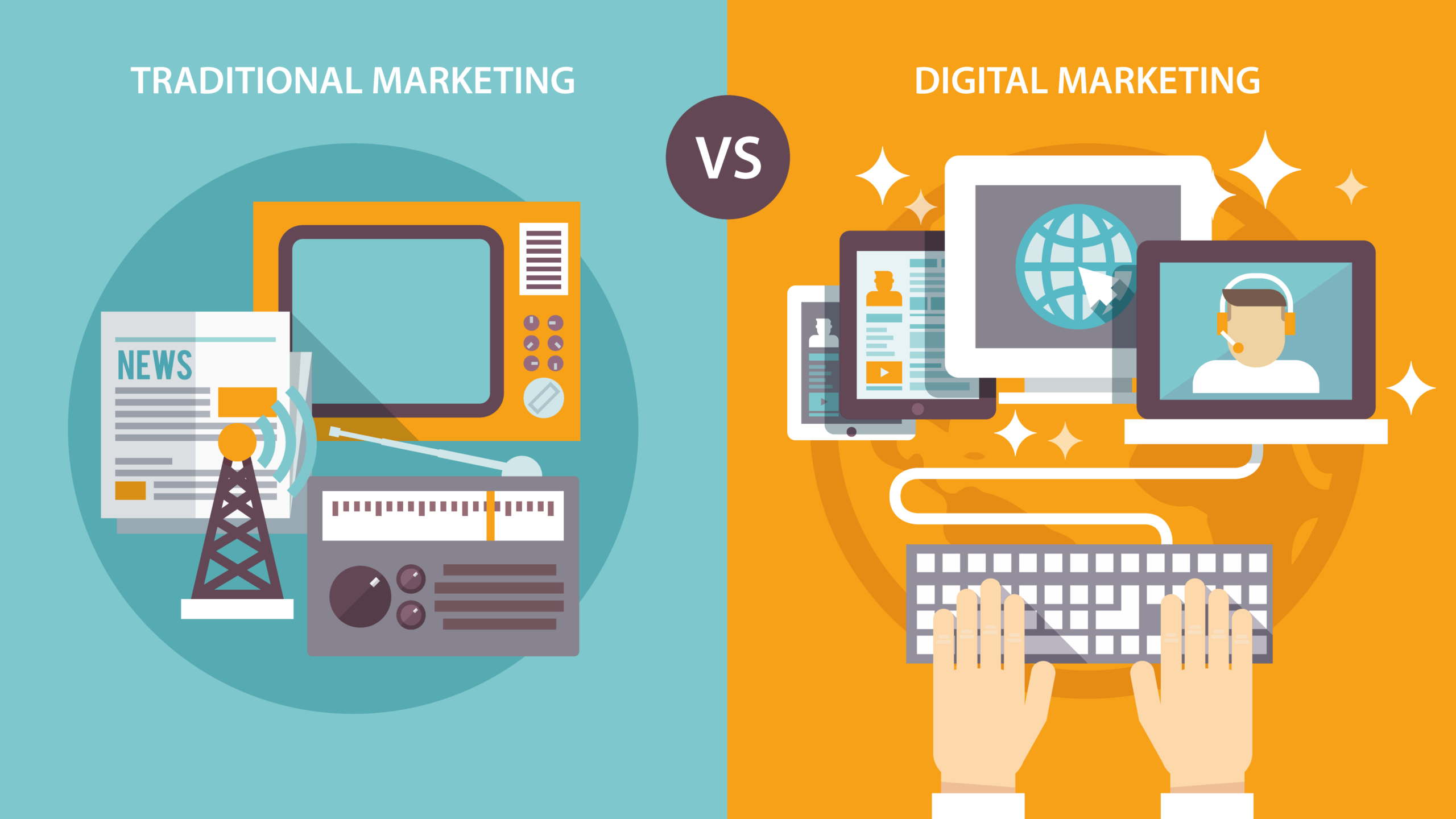
Traditional Marketing
Meaning
- Traditional marketing refers to offline promotion using newspapers, TV, radio, posters, and banners.
Nature of Communication
- Communication is one-way. Customers receive information but cannot respond immediately.
Cost and Reach
- It is expensive and mostly limited to a specific geographical area.
Digital Marketing
Meaning
- Digital marketing refers to promotion using internet-based platforms such as websites, social media, search engines, and email.
Nature of Communication
- Communication is two-way. Customers can like, comment, share, and review products.
Cost and Reach
- It is cost-effective and allows global reach.
Key Differences
- Traditional marketing is difficult to measure, while digital marketing provides exact data.
- Traditional marketing has slow feedback, while digital marketing offers instant feedback.
- Digital marketing is more flexible and result-oriented.
Difference Between E-Commerce and E-Business
Meaning of E-Business
- E-Business means conducting all business activities using internet and digital technologies.
- It includes marketing, sales, payments, customer service, and supply chain management.
E-Commerce vs E-Business
E-Commerce
- Focuses only on buying and selling online.
E-Business
- Covers the complete business process from promotion to after-sales service.
Core Concepts of E-Business
- Online Presence: Businesses need websites or mobile apps to interact with customers.
- Digital Transactions: Orders and services are handled electronically.
- Electronic Payments: Payments are made using UPI, cards, net banking, etc.
- Customer Relationship Management: Online support through chat, email, and helpdesks improves customer satisfaction.
Business Model
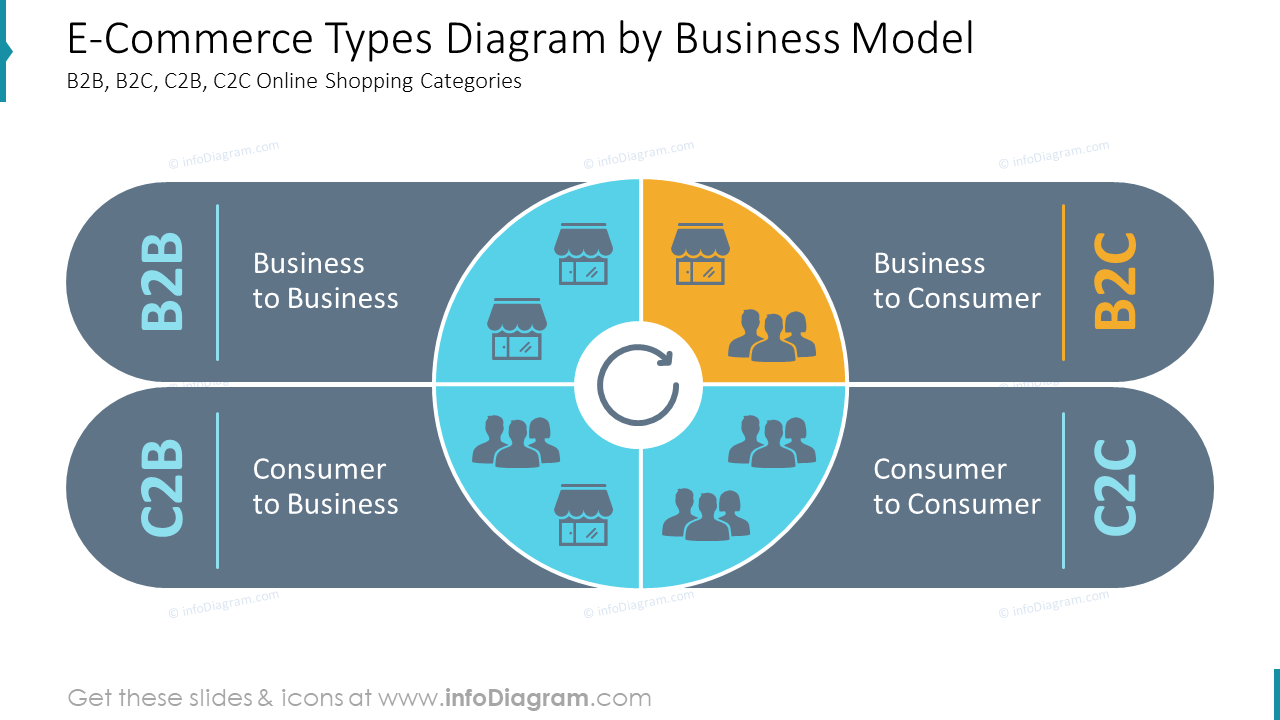
Meaning:
- A business model explains how a company delivers value and earns revenue.
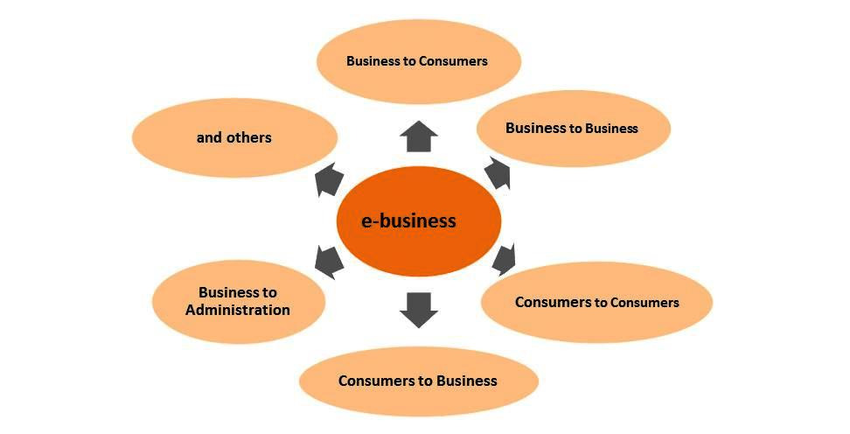
B2B (Business to Business)
- One business sells products or services to another business.
- Transactions are large in volume and relationship-based.
- Decisions are logical and based on price, quality, and reliability.
- Example: Software company selling services to banks.
B2C (Business to Consumer)
- Businesses sell directly to individual customers.
- Transactions are smaller and frequent.
- Decisions are influenced by emotions, brand image, and offers.
- Example: Online shopping websites and food delivery apps.
E-Business Models – C2C (Customer to Customer)
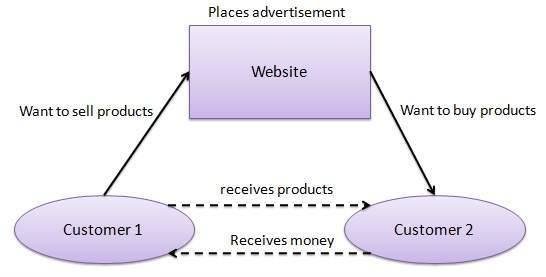
- Consumers sell products or services to other consumers.
- Online platforms act as intermediaries.
- Example: Selling old mobile phone online.
E-Business Models – C2B (Consumer-to-business)
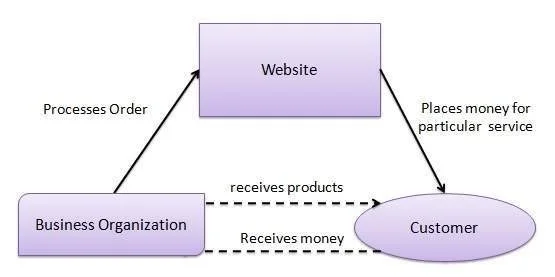
- Individuals provide value to businesses.
- Businesses pay consumers for their services or influence.
- Example: Freelancers, influencers, content creators.
Advantages, Limitations & Challenges of Digital Marketing
Advantages
- Low cost compared to traditional marketing.
- Targeted advertising to specific audiences.
- Measurable results such as clicks, views, and conversions.
- Global reach and faster communication.

Limitations
- Requires internet access.
- Technical knowledge is needed.
- Data privacy and security concerns.
Challenges
- High competition in digital space.
- Ad fatigue among customers.
- Continuous changes in algorithms and platforms.
Digital Customer Behavior
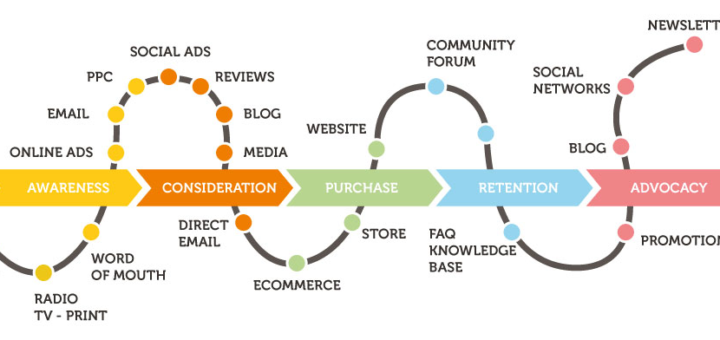
Meaning of Digital Customer Behavior
- Digital customer behavior refers to how customers search, evaluate, purchase, and review products online.
Digital Buying Process
- Awareness: Customer becomes aware of a product.
- Interest: Customer shows interest and seeks information.
- Comparison: Customer compares price, reviews, and features.
- Purchase: Customer buys the product.
- Post-Purchase Behavior: Customer gives reviews and feedback.
Factors Influencing Behavior
- Online reviews and ratings.
- Social media and influencers.
- Price comparison and offers.
- Brand trust and previous experience.
Importance for Businesses
- Helps understand customer needs.
- Enables personalized marketing.
- Improves customer satisfaction and sales.
Simple Businesses Activity
| Group | Business Example |
|---|---|
| Group 1 | Online food delivery |
| Group 2 | Mobile phone shopping |
| Group 3 | Coaching classes |
| Group 4 | Clothing / fashion store |
| Group 5 | Freelancing services |
| Group 6 | Second-hand product selling |
Student Output (What They Submit)
Each group presents:
- Business name
- Digital marketing methods used
- E-business model
- Customer behavior explanation
Presentation can be:
- Oral
- Chart paper
- 1-2 PPT slides