DVBI-01 Fundamentals of Digital Marketing & E-Business
On This Page
Introduction to Business Intelligence (BI)
What is Business Intelligence?
-
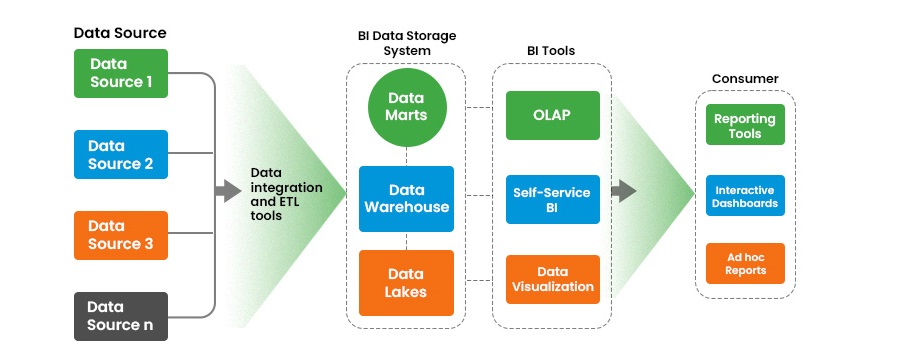
Business Intelligence (BI) refers to a collection of tools, technologies, processes, and strategies used to collect data from different sources, analyze it, and present it in a meaningful way to support better decision-making.
-
Simple Meaning: BI converts raw data into useful information that helps management take correct decisions.
BI Process:
- Data Collection — From databases, files, ERP systems, cloud
- Data Integration — Combine data from multiple sources
- Data Cleaning — Remove errors, duplicates
- Data Analysis — Apply queries, calculations
- Reporting & Visualization — Dashboards, charts Decision Making
Example:
- A university collects: Student attendance, Exam results, Fee payment data
- Using BI, management can: Identify weak students, Improve pass percentage, Plan academic improvements
Importance of BI:
- Improves accuracy of decisions
- Saves time
- Helps identify trends
- Supports long-term planning
Introduction to Power BI
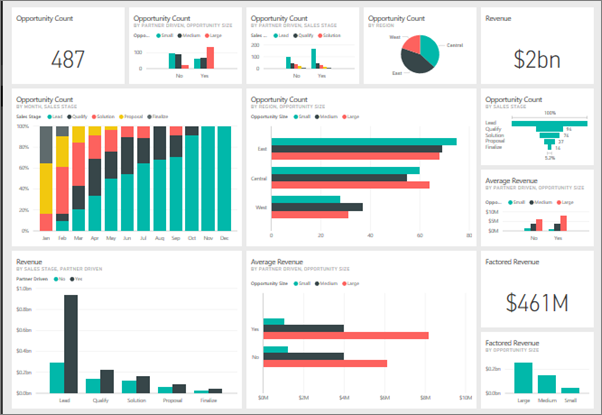
- Power BI is a self-service business intelligence and data visualization tool developed by Microsoft.
What Power BI Does:
- Connects data from multiple sources
- Analyzes large datasets
- Creates interactive reports and dashboards
- Shares reports securely online
Key Features:
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Real-time data refresh
- Integration with Excel, SQL Server, Azure
- Mobile access
Example:
A company uses Power BI to:
- Monitor daily sales
- Compare region-wise revenue
- Identify best-selling products
Traditional Business Intelligence (Traditional BI)
What is Traditional BI?
- Traditional Business Intelligence (Traditional BI) refers to earlier BI systems where data analysis and reporting were centrally controlled by the IT department using complex tools and fixed processes.
Exam-ready definition:
- Traditional BI is a centralized approach to business intelligence where data extraction, analysis, and report generation are handled mainly by IT professionals using predefined reports.
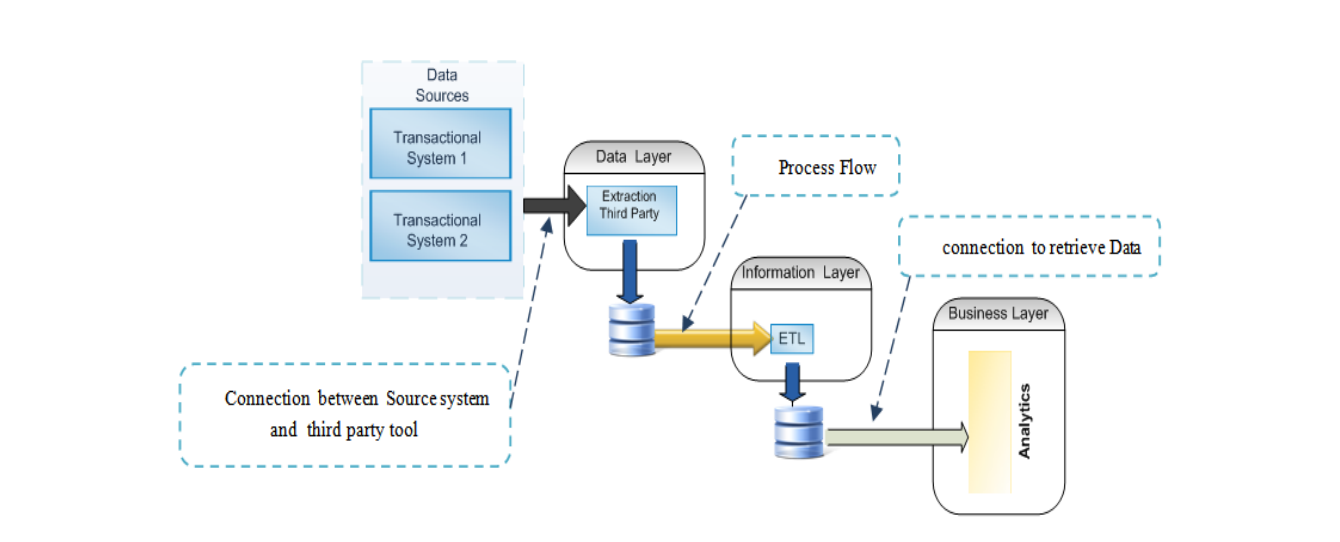
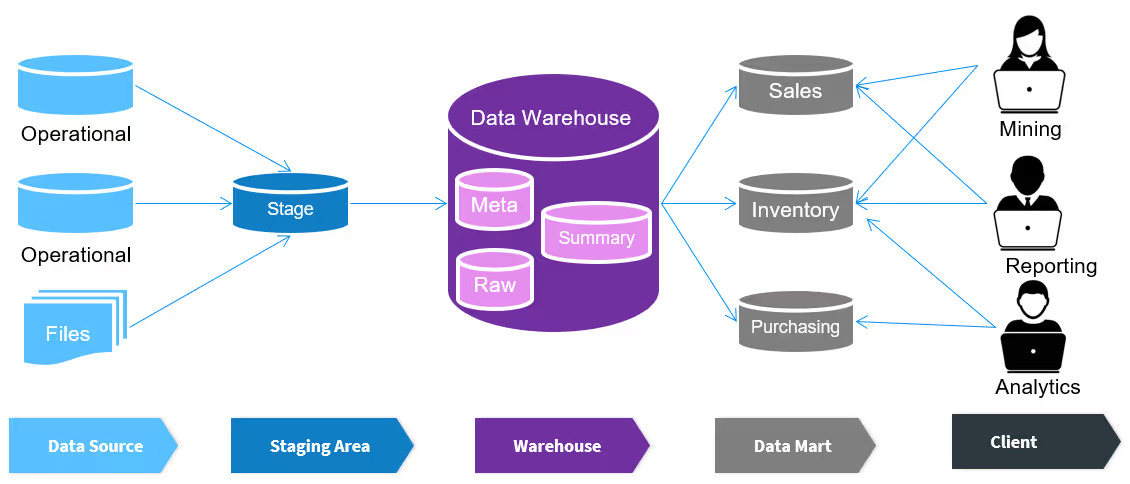
Architecture of Traditional BI
- Data Sources
- Databases
- ERP systems
- Transaction systems
- ETL Process (Extract, Transform, Load)
- Extract data from sources
- Transform (clean, format)
- Load into data warehouse
- Data Warehouse
- Central storage of historical data
- BI Tools / Reports
- Static reports
- Dashboards (limited interactivity)
- Decision Making
- Any change in report = IT team intervention
Role of IT in Traditional BI
- IT designs data models
- IT writes queries
- IT creates reports
- Business users only view reports
- Business users cannot modify reports themselves
Characteristics of Traditional BI
- Centralized system
- Predefined queries
- Static reports
- Batch processing (daily / weekly updates)
- High dependency on IT
- Long development cycle
Limitations of Traditional BI
| Limitation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Time-consuming | Reports take days/weeks |
| Expensive | Requires costly infrastructure |
| Inflexible | Difficult to change reports |
| No real-time data | Data is often outdated |
| IT dependency | Business users have no control |
Example of Traditional BI
Banking System Example:
- Bank collects transaction data daily
- IT team processes data overnight
- Reports generated weekly
- Managers view static PDF/Excel reports
- If manager wants a new report → request to IT → wait days
Difference between Traditional BI and Power BI
| Feature | Traditional BI | Power BI |
|---|---|---|
| BI Approach | Old / conventional | Modern self-service BI |
| Control | IT-driven | User-driven |
| Primary Users | IT professionals | Business users, students, analysts |
| Cost | Very expensive | Low cost / affordable |
| Report Type | Static (PDF, Excel) | Interactive dashboards |
| Data Refresh | Batch (daily / weekly) | Real-time or scheduled |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Highly flexible |
| Ease of Use | Complex, technical | Easy, drag-and-drop |
| Performance | Slow | Fast |
| Data Storage | Requires data warehouse & ETL | Cloud-based / direct connection |
| Interactivity | Limited | Rich and interactive |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Development Cycle | Long | Short / quick |
| IT Dependency | Very high | Minimal |
Power BI vs Tableau vs QlikView
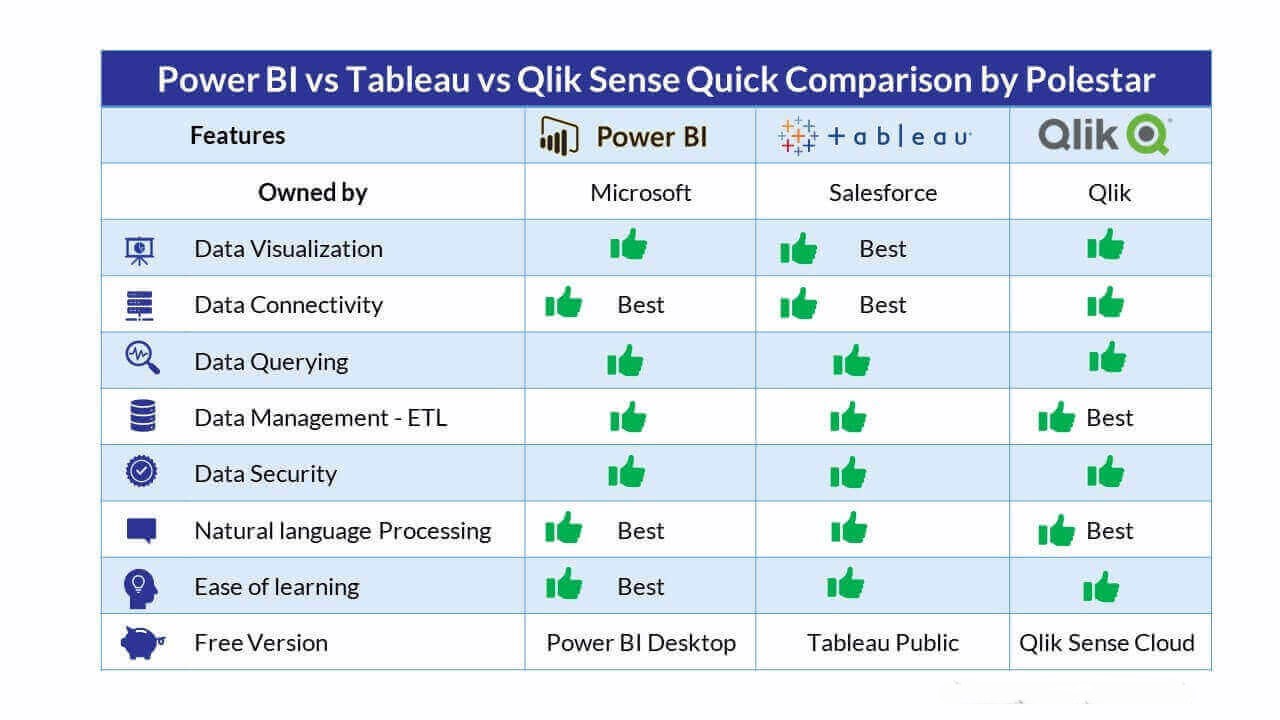
| Feature | Power BI | Tableau | QlikView |
|---|---|---|---|
| Developed By | Microsoft | Tableau Software (Salesforce) | Qlik |
| BI Type | Self-service BI | Advanced visual analytics | Associative BI |
| Ease of Use | Very easy | Moderate | Difficult |
| User Type | Business users, students, analysts | Data analysts, visualization experts | Developers, advanced users |
| Cost | Low / affordable | High | Medium |
| Data Visualization | Good | Excellent (best) | Good |
| Interactivity | High | Very high | High |
| Data Model | Simple relational model | Relational model | Associative data model |
| Performance | Fast | Fast | Very fast (in-memory) |
| Learning Curve | Low | Medium | High |
| Integration | Excellent with Microsoft tools | Works across platforms | Strong internal engine |
| Scalability | High | High | Medium |
| Real-time Support | Yes | Yes | Limited |
| Best For | Beginners & Microsoft users | Advanced visual storytelling | Complex data relationships |
| Tool | Description | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Power BI | Easy, Microsoft ecosystem | Low |
| Tableau | Advanced visualization | High |
| QlikView | Associative data model | Medium |
Example
- Power BI —> Excel users
- Tableau —> Data visualization experts
- QlikView —> Complex data relationships
Uses of Power BI
Power BI is widely used in:
- Sales analysis
- Financial reporting
- HR analytics
- Education analytics
- Business forecasting
Example:
HR department uses Power BI to analyze:
- Employee attendance
- Performance trends
- Attrition rate
Basic Components of Power BI
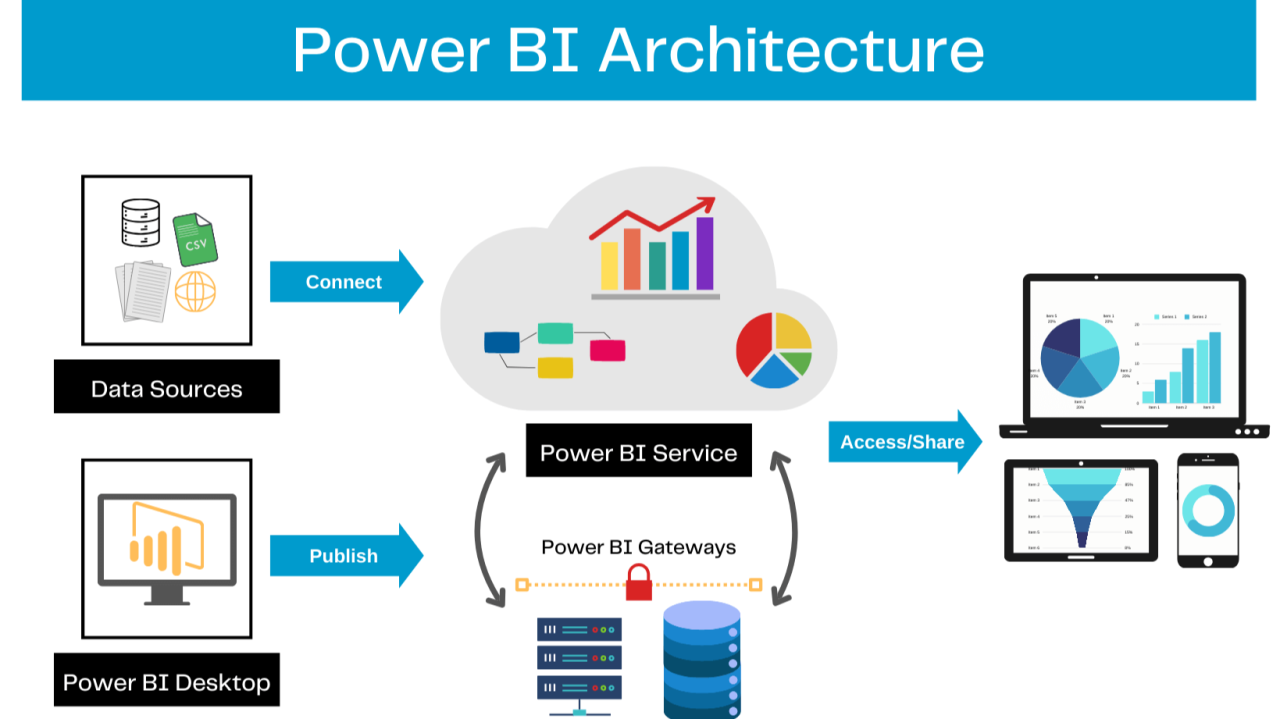
1). Power BI Desktop
- Free Windows application
- Used to create reports and dashboards
2). Power BI Service
- Cloud-based platform
- Used to publish and share reports
3). Power BI Mobile
- Mobile app
- View dashboards anytime, anywhere
Comparison of Power BI Versions
| Version | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Power BI Desktop | Report creation |
| Power BI Service | Online sharing |
| Power BI Mobile | Mobile viewing |
| Power BI Report Server | On-premise reporting |
Data Sources in Power BI Desktop
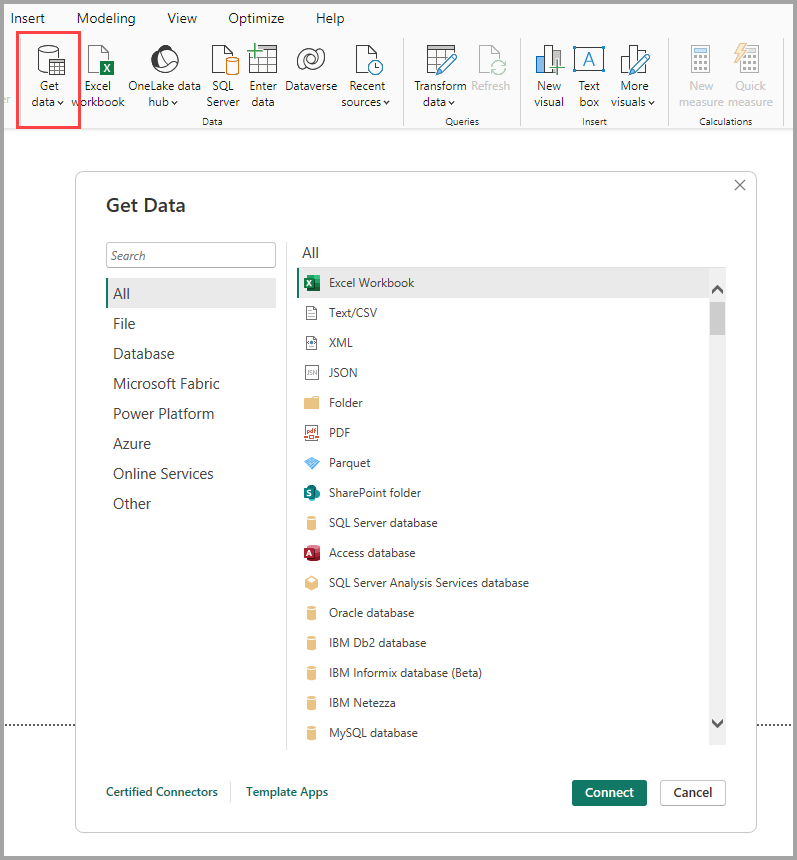
Power BI can connect to:
- Excel, CSV files
- SQL Server
- MySQL, Oracle
- Cloud sources (Azure, Google Analytics)
Example:
- Sales data from Excel and customer data from SQL Server can be analyzed together.
Introduction to Power BI Components
- Power BI is built on four core components that work together to convert raw data into meaningful insights:
- Power Query → Power Pivot → Power View → Power Map
Power Query (Data Preparation & Transformation)
What is Power Query?
- Power Query is used to connect, clean, and transform data before analysis.
Key Functions:
- Connect to data sources (Excel, CSV, SQL Server, Web, Google Sheets, etc.)
- Remove duplicates, null values
- Rename, split, merge columns
- Change data types (text, number, date)
- Combine multiple files or tables
Example:
- A college attendance Excel file has: Different date formats, Empty rows, Extra columns
- Power Query cleans this data without writing code.
Why it matters:
- Saves time
- Ensures accurate analysis
- Repeatable steps (automatic refresh)
Power Pivot (Data Modeling & Calculations)
What is Power Pivot?
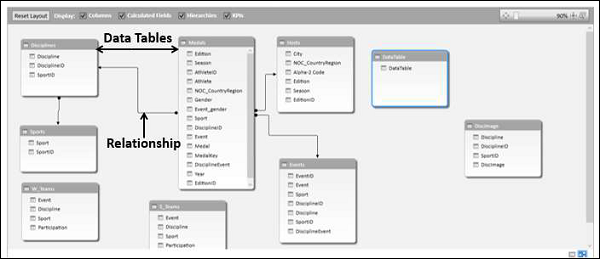
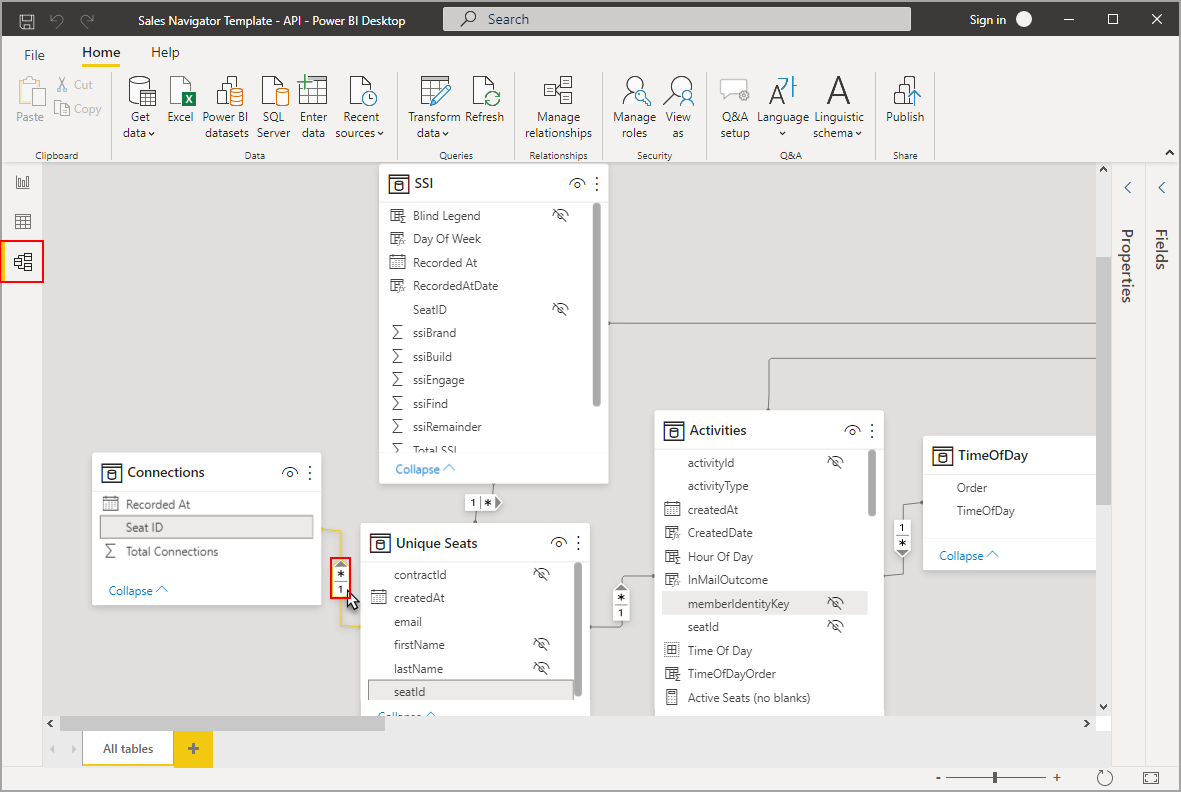
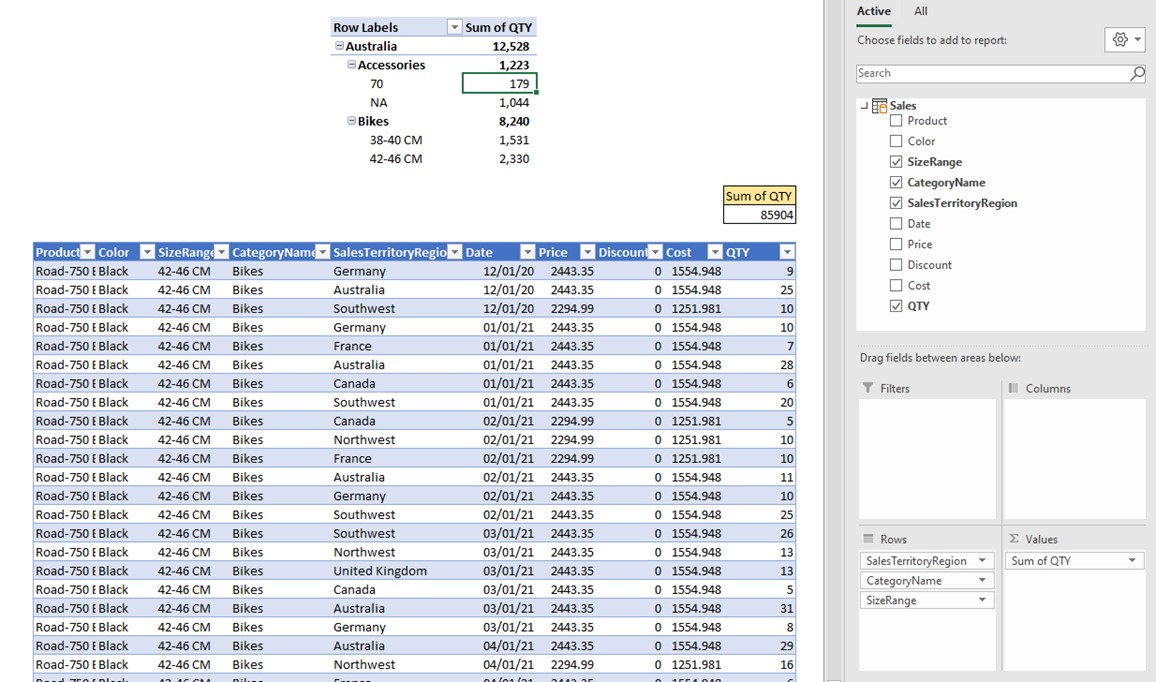
- Power Pivot is the data modeling engine of Power BI.
Key Functions:
- Create relationships between tables
- Build calculated columns & measures
- Use DAX (Data Analysis Expressions)
- Handle large datasets efficiently
Example:
- Tables: Students, Subjects, Marks
- Power Pivot links them and calculates: Total Marks, Average Marks, Pass Percentage
Why it matters:
- Enables advanced calculations
- Supports complex business logic
- Central brain of Power BI
Power View (Reports & Visualizations)
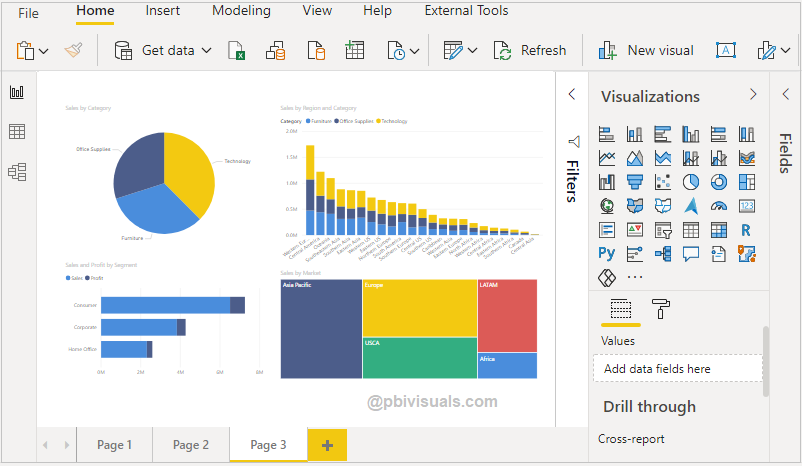
What is Power View?
- Power View is used to create interactive reports and dashboards.
Visuals Supported:
- Bar, Column, Line charts
- Pie & Donut charts
- Tables & Matrix
- Cards & KPIs
- Slicers & Filters
Example: A dashboard showing:
- Department-wise results
- Semester-wise performance
- Gender-based analysis
- Users can click visuals to filter instantly.
Why it matters:
- Easy drag-and-drop
- Interactive & user-friendly
- Decision-makers love visuals
Power Map (3D & Geographic Visualization)
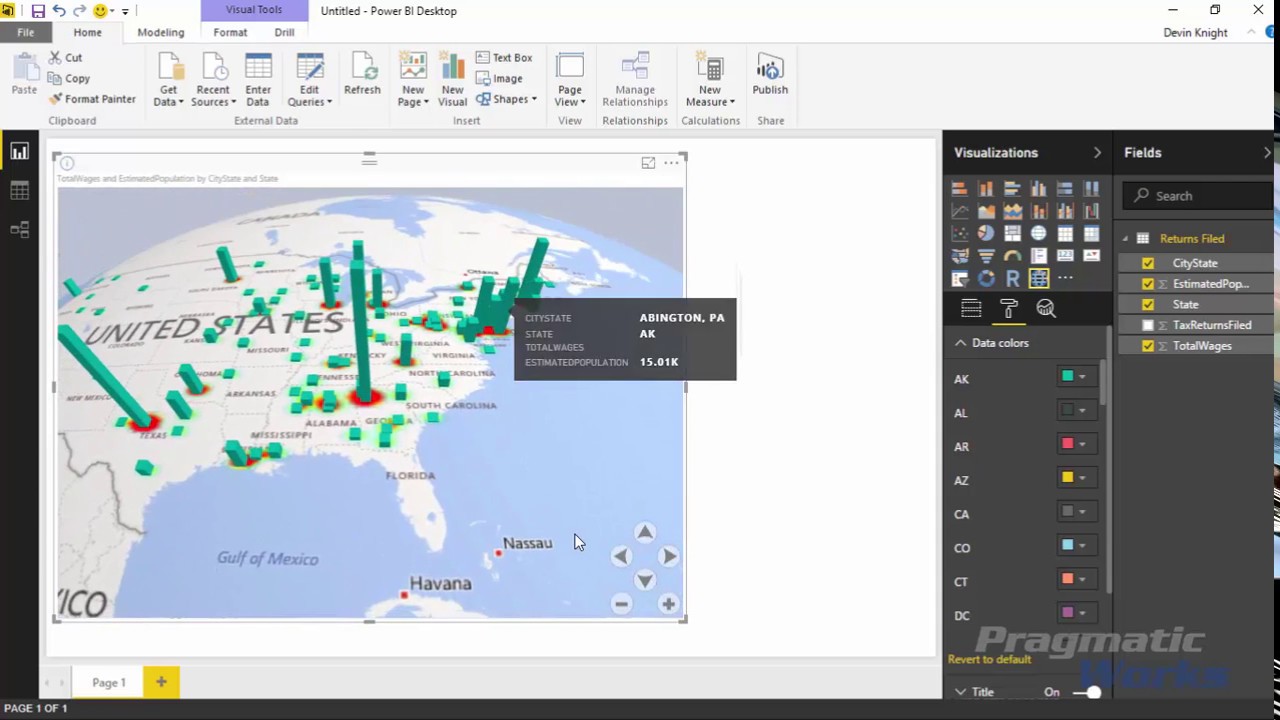
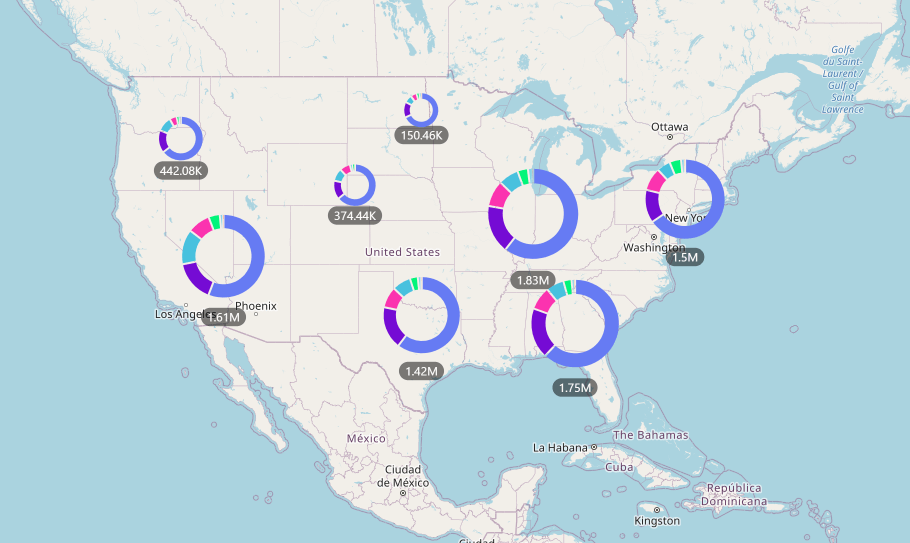
What is Power Map?
- Power Map (now part of Map visuals) is used for geographic and 3D data visualization.
Key Features:
- Plot data on world/India maps
- 3D animations over time
- Heat maps & bubble maps
Example: A university visualizes:
- Student admissions by city
- Campus-wise enrollment growth
- Year-wise expansion on map
Why it matters
- Best for location-based insights
- Makes trends easy to understand visually
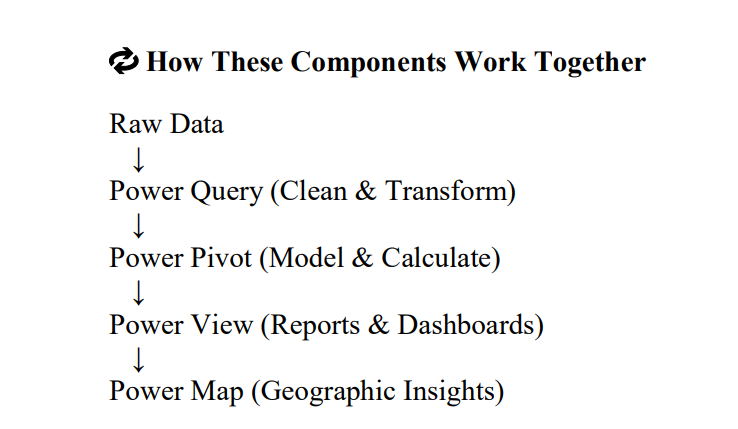
Quick Comparison Table
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Power Query | Data cleaning & transformation |
| Power Pivot | Data modeling & calculations |
| Power View | Interactive reports & dashboards |
| Power Map | Geographic & 3D visualization |